The algorithm used to create
- First, pipes of the required volume are prepared and cut into blanks of the required length.
- After that, internal cleaning of pipe products is performed. This reduces the resistance to movement of the heat carrier.
- Plugs are welded on the end parts. Some of them are equipped with holes.
- After that, the pipes, which will be located horizontally, are fastened with vertical pipes, which have a smaller diameter.
- Now it's time to install the faucets. They will be needed in order to release the air accumulated in the pipeline.
- At the final stage, all seams are cleaned and the surfaces are painted with paint.
Calculation of registers from smooth pipes
Steel heating registers are easy to do with your own hands. The cost of such a heating system will depend on who will cook them. If you own the welding technique yourself, the option is the most low-budget, if the welder needs to be paid, there will not be much difference in cost with inexpensive aluminum ones.
At the same time, the registers will occupy larger areas than standard heaters: due to the insignificant surface of contact with air, their efficiency is low. They increase heat transfer by installing a more powerful pump, but there are speed limits due to possible noise in the system. Read about how to choose the power of the pump here.
Diameters, as mentioned - from 32 mm to 100-150 mm. Large pipe sizes lead to an increase in the volume of the system. When starting and accelerating the system, this is a minus - until the coolant heats up, a decent amount of time will pass. When working, a large volume is rather a plus: softer conditions for the boiler. On the other hand, with a large amount of coolant, it is difficult to regulate the temperature.
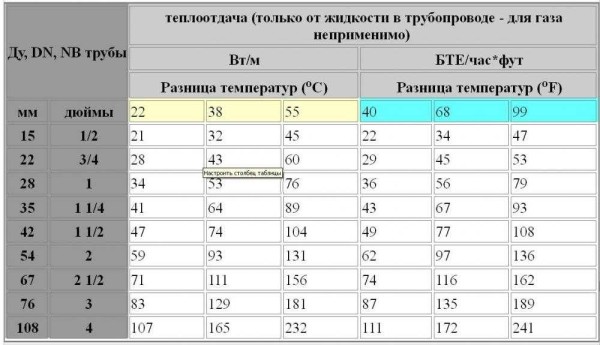
Heat transfer table of steel pipes of different diameters for different operating conditions of the system (click on the picture to enlarge it)
The distance between the two pipes in the register should not be small: this reduces heat transfer. Therefore, they are located at a distance of not less than 1.5 radius. The number of rows and the length of the register depend on the required power, as well as on the diameter of the selected pipes. In the general case (for central Russia, for rooms with medium thermal insulation and a ceiling height of 3m), it can be calculated from the heat transfer of a meter of steel pipe. These values are shown in the table. Using it, you can find the size and number of registers by the area of \u200b\u200bthe room.

Heat transfer of one meter of steel pipes of different diameters - for calculating the heating register by area
To calculate the heat losses of the premises, there are averaged data on the heat output of a linear meter of a steel pipe. You can use them for standard conditions. If the system operates at other temperatures, adjustments up or down are required.
If these tables did not help you, you can calculate the register using the formula.
The formula for calculating registers from steel pipes
Substituting the appropriate values, you will find the heat transfer of one pipe under your conditions. The heat transfer of all subsequent (second and more) will be slightly less. The found value must be multiplied by 0.9. So you will calculate and be able to make a register of smooth pipes with your own hands.
What other types of cast iron pipes are there
One of the vast areas of application of cast iron pipes, in addition to heating systems, is the organization of water pressure pipelines. The characteristics of cast iron pipes allow them to be used in water supply systems (often cold) and sewers. Cast iron pipes can be laid into the ground without problems, they calmly endure low temperatures and soil pressure.But due to their susceptibility to corrosion, it is better to lay them in tunnels than directly in the ground.
Depending on the requirements of the pipeline, different types of products can be selected.
Non-pressure pipes ChK. This type of cast iron pipes has the lowest strength and pressure resistance. Non-pressure pipes are quite thin and fragile. In their production, simple gray cast iron with impurities of lamellar graphite is used. Such cast-iron pipes can be successfully operated only in gravity sewers with a consistently low load. However, cast iron non-pressure pipes have an interesting advantage: they can be used repeatedly. Naturally, this is only possible with good preservation.
If it is necessary to make a connection in a free-flow sewerage system with a plastic pipeline, ChK pipes are best suited. The connection is made using rubber cuffs.
VChShG pressure pipes. In most modern pipelines, it is customary to use a cast-iron pressure pipe. These products are often found on sale under the abbreviation VChShG, which stands for "nodular graphite ductile iron".
There are several types of cast iron pipes, their application and connection method depend on the type and size.
Cast iron pressure pipes have found their application in the construction of gravity sewers, pressure sewers (including in cases where it becomes necessary to raise wastewater to a considerable height), water pipes and heating mains.
In industrial sectors, ductile iron pipes are also involved. With their help, the laying of trunk oil and gas transportation systems is carried out.
Pressure socket pipes ChNR. Cast iron socket pipe is used mainly in large water supply networks. They are produced with different diameters, more often - from 100 mm. The peculiarity of the material makes CHNR pipes somewhat less durable than ductile iron, so their installation requires special skills. In domestic sewer systems, the use of cast iron pressure socket pipes is limited, mainly due to the difficulties of building water pipes. To prolong the service life of ChNR pipes, they are opened with lacquer-bitumen compositions.
Socketless pipes SML. Socketless cast iron pipes are produced by casting an alloy of cast iron and rosette graphite. A relatively new variation of cast iron pipes for water supply and sewerage, a feature of which was a special coating of their epoxy substances. Sewer systems can function for a long time using socketless structures if their installation was carried out correctly. Unlike socket pipes, such pipes are connected with ordinary clamps. A key role in the reliability of the connection is played by the degree of tightness of the clamp being put on.
SML cast iron pipes can withstand both high and low temperatures. The only "contraindication" to their use is pressure sewers.
Cast iron pipes to this day remain a widely used material for the installation of heating networks, main water pipes and sewers. Economizer pipes are an obligatory element of industrial registers; in fact, they are a ready-made radiator. The same quality pipes made of cast iron can serve in water supply and sewerage systems.
Production of heating registers
For the production of heating registers, steel pipes of various diameters (25-200 mm) are used, which are welded together at a distance of 50 mm from each other (reducing the distance between the pipes can lead to a decrease in heat transfer). This distance allows you to achieve maximum heat transfer and minimize mutual radiation.
The register includes supply and return, as well as an air vent with a ball valve installed in the upper part of the device. The supply and return pipes can be made in two versions:
- Threaded connection;
- Weld connection.
When ordering individual registers at the factory, the registers can be supplied both ready-made, assembled, and disassembled, which allows you to save money on logistics.
Ribbed steel registers
Before installing registers from steel pipes with ribs, it is recommended to pay special attention to the volume of the pipe. For a private house, masters advise installations with a volume of 3 or 4 centimeters
When performing calculations, it is necessary to take into account the length of one edge of the register and its heat transfer per square meter. To give an example, a meter pipe with a cross section of 60 mm inside can heat approximately one square meter.
Having counted the required number of registers, rounding is carried out in the direction of increase. But, there are certain conditions under which the obtained indicators increase by 20, and even by 50 percent. This includes:
- The presence in the room of a large number of openings for windows and doors.
- Small wall thickness.
- Low-quality insulation of the room, or its complete absence.
A simple heating register has a lower heat transfer than devices with fins. They not only increase heat dissipation, but also turn the register into a design – a radiator that can play an important role in the aesthetic solution of the interior.
Types of registers
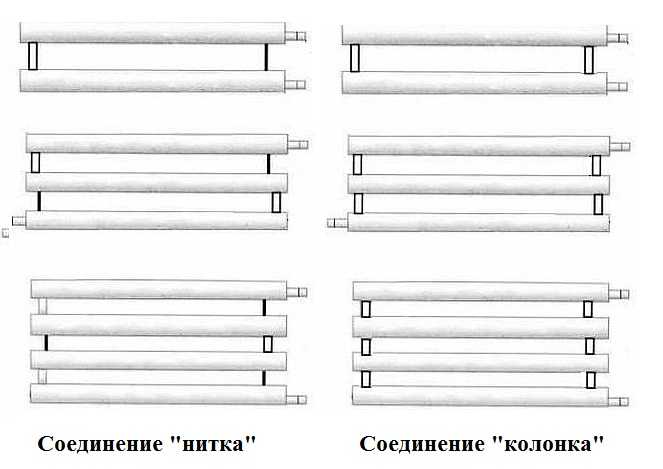
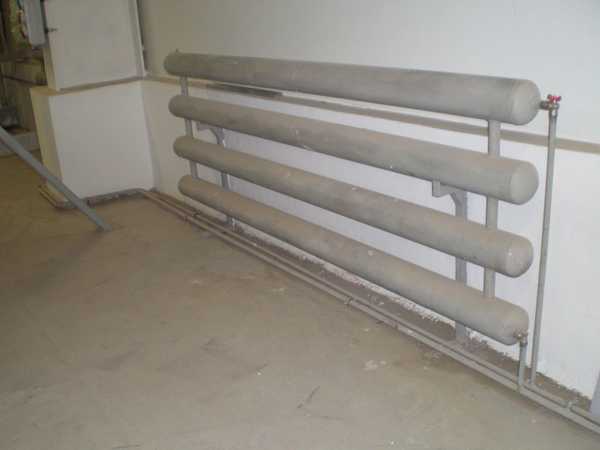
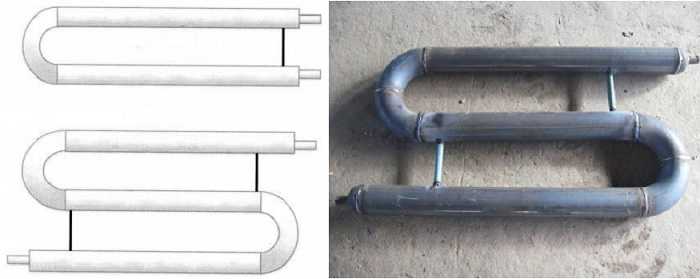
The most common type is registers made of smooth pipes, and most often - steel electric-welded ones. Diameters - from 32 mm to 100 mm, sometimes up to 150 mm. They are made of two types - serpentine and register. Moreover, register ones can have two types of connections: a thread and a column. A thread is when the jumpers, through which the coolant flows from one pipe to another, are installed either on the right or on the left. It turns out that the coolant sequentially runs around all the pipes, that is, the connection is serial. When connecting the "column" type, all horizontal sections are interconnected at both ends. In this case, the movement of the coolant is parallel.
Types of smooth pipe registers
In the case of use in systems with natural circulation, it is required to observe a slight slope towards the movement of the coolant of the order of 0.5 cm per meter of pipe. Such a small slope is explained by a large diameter (low hydraulic resistance).
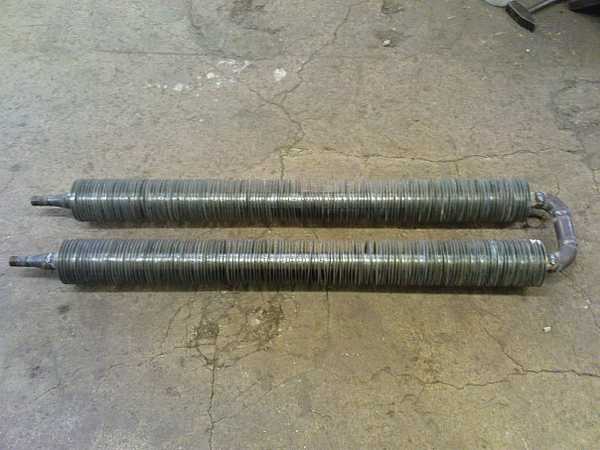
This is a serpentine heating register
These products are made not only of their round, but also of square pipes. They are practically no different, only it is more difficult to work with them, and the hydraulic resistance is slightly greater. But the advantages of this design include more compact dimensions with the same volume of coolant.
Square tube registers
There are also registers made of pipes with fins. In this case, the area of \u200b\u200bcontact of the metal with air increases, and heat transfer increases. Actually, until now, in some budget new buildings, builders install just such heating devices: the well-known “pipe with fins”. With not the best appearance, they heat the room well.
A register with plates will have a much higher heat dissipation
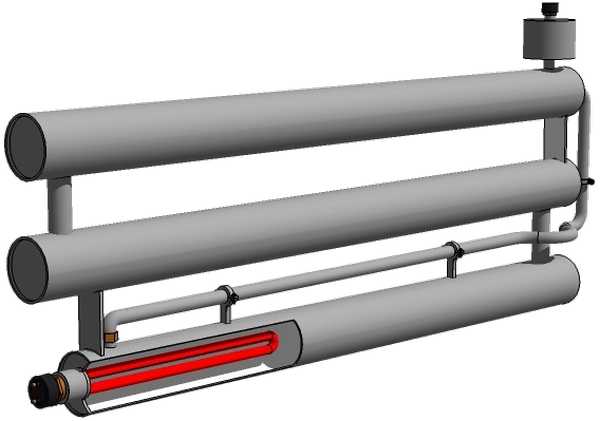
If you insert a heating element into any register, you can get a combined heater. It can be separate, not connected to the system, or used as an additional heat source. If the radiator is insulated with heating only from the heating element, it is necessary to install an expansion tank at the top point (10% of the total coolant volume). When heated from a domestic boiler, an expansion tank is usually built into the structure. If it is not there (often happens in solid fuel boilers), then in this case it is also necessary to install an expansion tank. If the material for the registers is steel, then the tank needs a closed type.
Electric heating can be useful in the most severe cold, when the boiler power is not enough. Also, this option can help out in the off-season, when it makes no sense to load a long-burning solid fuel boiler and overclock the system “to the fullest”.You just need to warm up the room a little. This is not possible with solid fuel boilers. And such a fallback option will help warm up in the offseason.
By adding a heating element to the register and putting an expansion tank, we get a combined heating system
Technical data for heating registers
- Working pressure: 10 atmospheres
- Working medium (heat carrier): water, steam.
- Connection type: threaded or welded.
- Heat dissipation: 500-600W/meter
There are 3 main types of registers:
- sectional U-shaped;
- serpentine S-shaped;
- "Mixed" (coil U-shaped).
The main elements of the heating registers are steel pipes (or pipes made of stainless steel grade 304) with a diameter of 25 to 200 mm. Registers with a diameter of 25 to 100 mm are used for heating factory premises for administrative or household purposes, devices with a diameter of 100 to 200 mm are used in production workshops or large sports complexes (pools, volleyball, basketball halls).
As for private households, the use of registers is one of the most inefficient ways of heating a private house.
2-pipe register.
The number of sections of the device can be unlimited and depends only on the area of the room and the required heat transfer.
Advice! Using too many pipes (more than 4) will still not be able to significantly increase the power of the entire device, because. the rising warm air heated by the lower pipes will be less able to receive thermal energy from the upper pipes.
Features of Cast Iron Finned Economizer Tube
The heating pipe for industrial economizers can be rectangular and with round fins. The dimensions of the products are standard: the inner diameter is 70 mm, and the outer diameter is 175 mm. Due to the differences between the outer and inner diameters, the effect of a low temperature of the pipe surface is achieved with a sufficiently hot coolant.
The economizer tubes are available in the same lengths: 2 m and 3 m. Cast iron finned tubes are available for sale with two perforated plugs and two blind plugs. Plugs with holes are left-handed and right-handed, and left-handed are marked with the designation "L".
There are certain operating conditions under which a cast-iron pipe with a ribbed surface will function as efficiently as possible:
- the highest temperature allowed for cast iron economizer pipes is 95 degrees. In emergency cases, a short-term rise in temperature to 150 degrees is allowed;
- constant working pressure - 0.6-1 MPa (10 atmospheres). However, cast iron finned tubes are compatible with steam boilers whose pressure is maximum 2.4 MPa;
- the outer surface of the economizer is coated with a special primer;
- when installing finned tubes, the obligatory distance from the floor to the economizer median axis, which is at least 200 mm, is taken into account. From the surface of the side wall, the distance to the axis of the pipe is taken into account from 130 mm;
- if the economizers are arranged in two rows, the distance between the axes of the radiators is maintained at 250 mm. Rows of economizers are interconnected by a special arc.
All economizer pipes are equipped with plugs - blind and with holes
The main disadvantages of economizer pipes are rather heavy weight, which makes transportation difficult, and low resistance to mechanical damage.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages include a simple design and simple calculation, the availability of materials. All this together allows you to make registers for heating with your own hands.
The next positive thing is that most of the heat is transferred with the help of radiant energy, and it is perceived by a person as more pleasant.
Heating registers are usually located in utility, industrial, auxiliary rooms
The next plus is the smooth surface, which ensures easy cleaning.
Excellent quality - compatible with any system - both with natural and forced circulation.
There are also disadvantages: low heat dissipation, susceptibility to corrosion, not the most attractive appearance, the need for regular painting (read how to choose a paint here).
What are
Heating registers are made of different materials, they have different shapes. Each has pros and cons.
What are they made of
If we talk about materials, then the most common is steel, or rather, steel electric-welded pipes. Steel does not have the best heat transfer, but this is offset by a low price, ease of processing, availability and a large selection of sizes.
It is very rare to find stainless pipes - decent power requires a large number of pipes, and how much stainless steel products cost, you have an idea. If they did, it must have been a long time ago. They also use “galvanizing”, but it is more difficult to work with it - it will not work to cook.
Registers made of copper pipes have a high heat transfer and no less high price
- requires a neutral and clean heat transfer fluid, free of solid particles
- the presence of other metals and alloys in the system is undesirable, except for compatible ones - bronze, brass, nickel, chromium, therefore all fittings and fittings will need to be sought from these materials;
- carefully performed grounding is mandatory - without it, in the presence of water, electrochemical corrosion processes begin;
- the softness of the material requires protection - screens, casings, etc. are needed.
There are registers made of cast iron. But they are too bulky. In addition, they have a very large mass, under them you need to make no less massive racks. Plus, cast iron is brittle - one blow, and it can crack. It turns out that this type of registers also needs protective covers, and they reduce heat transfer and increase the cost. Moreover, installing them is a difficult and hard job. The advantages include high reliability and chemical neutrality: this alloy does not care what coolant to work with.
Cast iron registers made of finned tubes
In general, copper and cast iron are not easy. So it turns out that the best choice is steel registers.