Shutdown schedule in Moscow for 2019 by district
In 2019, it is planned to turn off hot water in the districts. Planned shutdowns will begin on May 13 after all holidays. And will end by September 1, 2019. During the same period, water supply will be turned off in New Moscow. The period of absence of hot water is limited to 10 days. Some areas will be without hot water for only three days. Some houses are not planned to be disconnected from the hot water at all. On the public services portal mos.ru, you can check the terms for turning off hot water at your address.
The official schedule for turning off hot water in 2019 at the address of residence is published on the MIPC website. Andrey Zenin, Deputy Managing Director and Chief Engineer of MIPC, claims that the hot water shutdown period in 2019 will not exceed 10 days.
You can find out the exact information at your address on the official website of JSC "Moscow United Energy Company". Hotline phone +7 (495) 539-59-59 - Free and available 24/7.

In addition, all residents will be additionally notified about the start of shutdowns 10 days before.
Urgent Changes July Bills
The Government of the Russian Federation, by Resolution No. 354 dated May 6, 2011, approved the Rules for the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings (hereinafter - Rules No. 354). These Rules govern relations for the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings, owners and users of residential buildings, including the procedure for calculating fees for water disposal, heating and other utilities using metering devices and in their absence.
According to sub. “c”, paragraph 4 of Regulation No. 354, the public service for sewerage, which is provided to the consumer of such a service, is the removal of domestic wastewater from a residential building (household), from residential and non-residential premises in an apartment building through centralized sewerage networks and in-house engineering systems.
The amount of payment for a utility service for water disposal provided for the billing period in a residential area not equipped with an individual or common (apartment) metering device for domestic waste water is calculated based on the sum of the volumes of cold and hot water provided in such a residential area and determined according to the indications of individual or common (apartment) metering devices for cold and (or) hot water for the billing period, and in the absence of metering devices for cold and (or) hot water - based on the standard for water disposal (clause 42 of Regulation No. 354).
In this regard, according to the Ministry of Construction of Russia, in the absence of an individual hot (cold) water device and the presence of an individual cold (hot) water meter, the payment for a utility service for water disposal provided for the billing period in a residential building of an apartment building that is not equipped with an individual or a common (apartment) metering device for domestic waste water, is determined based on the sum of the readings of the metering device for cold (hot) water and the norm for the consumption of hot (cold) water.
Thus, the provisions of the current housing legislation provide that the volume of wastewater accepted from the owners or users of premises in apartment buildings is accepted by the organization that carries out the wastewater disposal, equal to the volume of water supplied to residential and non-residential premises of consumers in an apartment building from all sources of centralized water supply.
Given the above, according to the Ministry of Construction of Russia, the calculation of payment for water disposal in an apartment building should be made based on the volume of water supplied to residential and non-residential premises of consumers in an apartment building from all sources of centralized water supply.
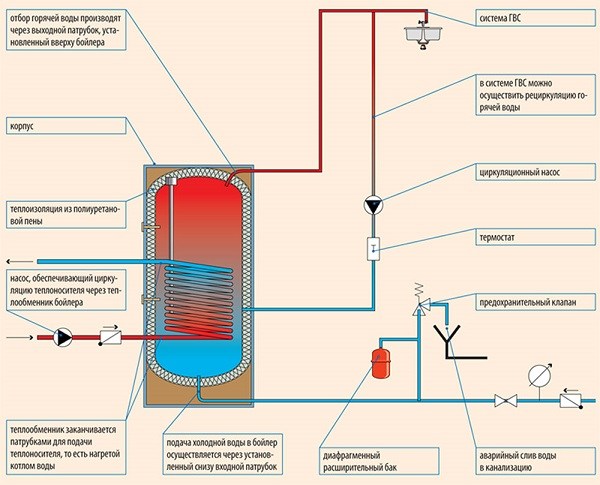
Hot water supply
Hot water supply in an apartment is a whole system of pipelines and various devices that are used to heat cold water and distribute hot water to consumers. In some cases, special pipes are used in bathrooms or toilets to heat such rooms in the apartment. They have the additional function of dryers.
Heating of an apartment building

All hot water supply systems can be divided according to several criteria:
- local hot water systems;
- centralized systems;
- open heating networks;
- closed heating networks.
According to the radius of action, hot water supply systems are divided into local and central.
Local hot water systems
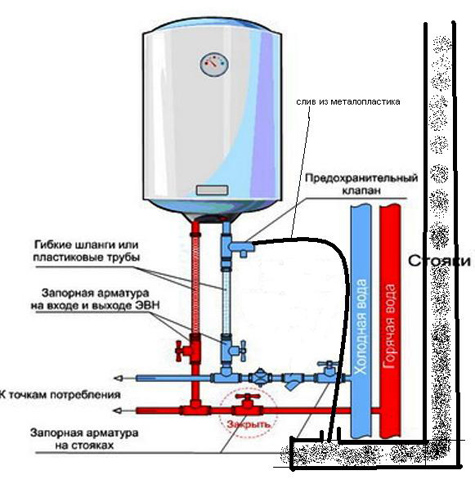
Local hot water supply systems are equipped for a group of small objects or one building. Water in this case is heated directly by the consumer. Water heating is carried out using gas or electric flow-type boilers.
Such systems require regular maintenance and are used only if it is not possible to use a centralized hot water supply.
The advantage of local hot water supply systems:
- offline work;
- ease of repair;
- small heat losses.
Central hot water systems
The appearance of central systems for supplying hot water to an apartment is due to the elimination of district and local boiler houses, as well as heat supply systems. As for convenience, central hot water systems will be much more practical.
All this depends on the fact that there is no need to install appropriate equipment for heating cold water and additional wiring. Also, the system of such hot water supply has its drawbacks. Pipes need to be constantly maintained and repaired, but local utilities can rarely fulfill customer requests. There are also large drops in water pressure in the system and insufficient temperature, which cannot be said about local water supply systems.
To heat water and supply it to the consumer, centralized systems can use open or closed heating networks. Open heating networks provide for the mixing of network water with that already heated in special equipment. After that, the water is supplied to consumers. Closed heating networks provide for heating water through the surface. The heat carrier (superheated water or steam) and the heated water do not come into contact in any way.
Open heating networks are considered more rational, but the quality of the supplied water can significantly deteriorate in terms of the temperature regime. Such systems are currently very rare to find.
Hot water supply in the apartment can be carried out in several ways:
- Heating water in the boiler room with subsequent supply to the consumer.
- Water heating is carried out in special points located in neighborhoods or districts.
- Water heating is carried out using special equipment, which is installed in the basement of a multi-storey building.
- Water is heated in the consumer's apartment.
Hot water supply can be circulating. In this case, water is constantly moving through the pipes and provides not only the supply of hot water, but also heating. The water is constantly heated. There is also a dead-end hot water supply. In this case, the water is not used immediately and may simply cool down over time. It is for this reason that special containers are installed in the apartment to heat and maintain the temperature of the water.
With regard to savings, it would be rational to use individual systems for providing hot water to the apartment. The user must pay a monthly fee for the centralized supply of hot water.
Currently, hot water supply is an integral part of the life of most people on the planet.Without it, they can not do in any apartment and residential building. The arrangement of hot water supply is a difficult process, moreover, there are several types of system connection. In this article we will consider all hot water supply systems, calculation and types of water heaters.
Regardless of the type of hot water supply, a set of equipment is connected that is designed to heat water and distribute it to various water intake points. In this equipment, water is heated to the required temperature, after which, using a pump, it is supplied to the house and through the pipeline. Distinguish between open and closed hot water systems.
Types of water heaters
All water heaters are classified as follows:
- flow devices. Such heaters heat water in a constant mode, leaving no reserve. Since water has a high heat capacity, it requires an increased energy consumption to constantly heat it. In addition to this factor, the flow heater must be immediately put into working condition: when turned on, supply hot water, when turned off, stop heating. Traditional flow heaters include a gas column.
- storage devices. They are characterized by slow heating of a certain volume of water, which often consumes 1 kW / h. Hot liquid is used as needed. Storage heaters work instantly after opening the tap, but the power is much less. Among the disadvantages of such devices, large sizes are also noted, the larger the volume, the larger the device.
Features of open hot water supply
When installing an open hot water supply, it is necessary to take into account the principle of operation. Open DHW is of two types, depending on the type of circulation and transportation of the coolant to the radiators. There are open systems with natural circulation and with the use of pumping equipment for this purpose.
Natural circulation is carried out in this way: an open system eliminates the presence of excess pressure, therefore at the highest point it corresponds to atmospheric pressure, and at the lowest point it is slightly higher due to the hydrostatic action of the liquid column. Due to the low pressure, natural circulation of the coolant occurs.
The principle of natural circulation is quite simple, due to the different temperature of the coolant and, accordingly, different density and mass, cooled water with a low temperature and a larger mass displaces hot water with a smaller mass. This simply explains the existence of a gravity-flowing system, which is also called gravitational. The main advantage of such a system is absolute energy independence, if parallel heating boilers do not use electricity.
If natural circulation is not possible, pumping equipment is used, which increases the flow rate of the coolant through the pipeline and reduces the heating time of the room. The circulation pump produces the movement of the coolant at a speed of 0.3 - 0.7 m / s.
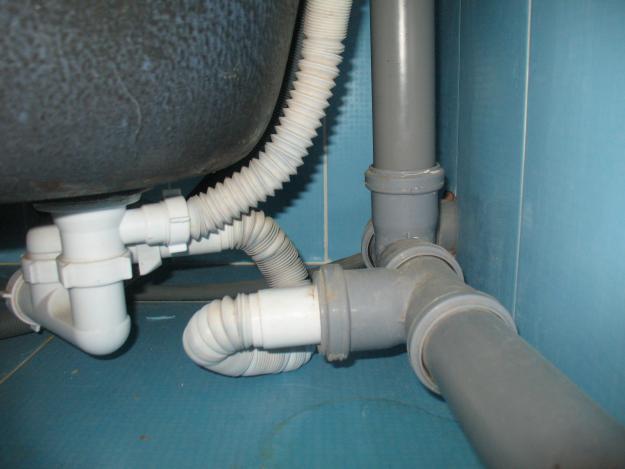
Dismantling the sewer in the apartment
Replacing an old sewer pipe with a new one has many nuances that must be taken into account in this process. Initially, it is necessary to determine the most vulnerable places in the pipe to deformation. It is also required to disconnect all existing connections from the pipe and remove all debris. All this is necessary to ensure a more convenient work.
Then, near the riser, the tap is turned off, which supplies water to the apartment. If the replacement is long, then it is best to completely disconnect the entire riser from the water supply. At the very last moment, it is necessary to carefully dismantle the cast-iron sewer pipes. All this can be done with adjustable wrenches or other tools.
It is necessary to mount a new pipe in a complete set with a variety of adapters and couplings, since then it will not be possible to do it qualitatively.All connections must be coated with sealant to protect the riser from leakage.
Advice. All fittings or cuffs must be clean. Silicone grease should be designed specifically for connecting sewer pipes.
Traditional DHW distribution
The device of the hot water supply system in stalinkas and early Khrushchevs is no different from the distribution of cold water. The only bottling ends with dead-end risers, from which the apartment wiring departs. In the elevator unit, the filling branches into two tie-ins - into the supply and return threads.

Switching DHW from supply to return is carried out manually in accordance with the heating temperature schedule:
- When the temperature of service water at the outlet of the CHP is up to 80-90 degrees, DHW is supplied from the supply;
- When 90°C is exceeded, the water supply switches to reverse water supply.

Why is it bad
The advantages of such a scheme are the low cost of implementation and extremely simple maintenance. There are also downsides.
We have already mentioned two of them:
- Without water intake, the water in the risers and piping cools down. To wash or take a shower, it has to be drained into the sewer for a long time (up to several minutes). For apartment residents, this means not only a loss of time, but also significant costs: in fact, you drain cold water, but if you have a water meter, you pay for it as if it were hot;

- Towel dryers that open the domestic hot water supply lines are heated only from the water intake in your apartment. You can forget about high-quality bathroom heating.
Let's throw a handful of little things into the common treasury of the shortcomings of the solution:
Cold and dampness in the bathroom contribute to the appearance of the fungus;

- Towels hung in a cold dryer quickly become musty;
- Cyclic heating and cooling of DHW risers are accompanied by cycles of their elongation and reduction in size. As a result, the sealing of the risers in the ceiling with cement mortar is gradually destroyed.
All in white and on a white horse
How does a hot water system with recirculation differ from the one described above? It's easy to guess. In it, hot water continuously circulates through spills and (in the case of a multi-storey building) hot water risers.
As a result:
- Provides instantaneous supply of hot water to the draw-off point in any part of the circuit;
- Towel dryers are transferred from the intra-apartment supply to the riser (or, in the case of a private house, bottling) of hot water. Thanks to continuous circulation, they remain hot around the clock, provide heating for bathrooms and toilets, and at the same time, fast drying of towels;

The temperature regime of the DHW system remains stable, without cyclic cooling and heating.
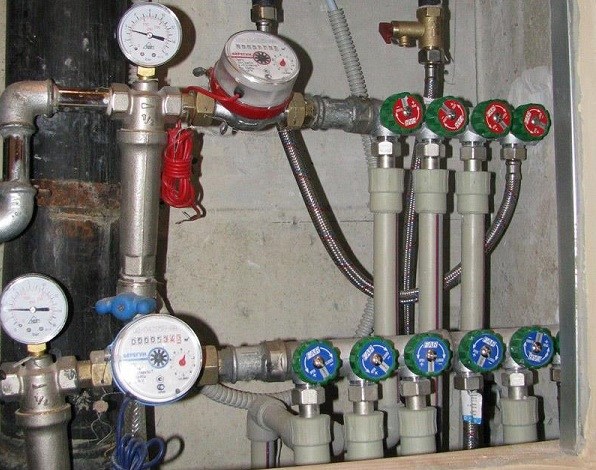
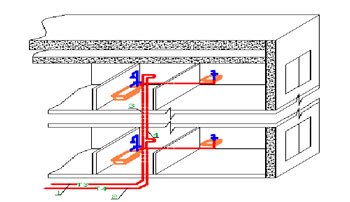
Features of water supply schemes
The effectiveness of the MKD water supply scheme depends on the correct piping. When the water reaches the microdistrict, a branching into smaller sections follows, each building has its own route. Further, in the water supply network, there is a division by floors, and already on the floor, the pipeline branches into apartments. Smaller diameter pipes are used after each separation to maintain the correct pressure in the water supply.
There is a return line, along which movement occurs in the opposite direction with the formation of a common contour. This ensures constant circulation, the circulation movement is carried out from top to bottom and back to the basement.
The creation of conditions for ensuring a constant temperature is taken into account even at the stage of developing an apartment building project. Pumps are used to properly circulate the water supply. The norms of the temperature regime are observed, the water temperature ranges from 65 to 75 degrees Celsius. This standard is used for several reasons:
- high water temperature leads to the death of pathogenic bacteria;
- too hot water can cause burns;
- temperature limits are chosen taking into account the continuous operation of the network.
In rare cases, the dead-end hot water supply scheme for MKD continues to be used, where the coolant cools down in the apartment until it is used up. Such a system leads to excessive waste of water, becomes financially unprofitable for end users and the service organization, which, due to restrictions in this case, is unable to provide services of a suitable level.
Closed DHW system
The closed system is based on the following principle: cold drinking water is taken from the central water supply and heated in an additional heat exchanger. After heating, it is supplied to the water intake points.
A closed system implies a separate operation of the coolant and hot water, it is also distinguished by the presence of a return and supply pipeline, which are used for the annular circulation of water.
Such a system will provide normal pressure even when using the shower and sink at the same time. Among the advantages of the system, the simplicity of regulating the temperature of the hot liquid is also noted.
DHW can be circulating and dead-end. The dead-end system consists only of pipes supplying water, the method of connection of which is the same as in the first case.
The advantage of a closed hot water supply is cost savings due to stable temperatures. It is possible to install a heated towel rail. In a closed hot water supply, water heaters are needed, the types of which we will consider later.
Advantages and disadvantages of an open system
Open DHW is still relevant, primarily due to energy independence and other advantages:
- Ease of filling open DHW and venting. There is no need to control the high pressure and to bleed additional air, as the bleed is carried out automatically when filling through an open expansion tank.
- Easy to recharge. Since you do not need to monitor the maximum pressure. It is also possible to add water to the tank even with a bucket.
- The system, regardless of leaks, functions properly, since the working pressure is not large and the presence of such malfunctions does not affect it.
Among the shortcomings, the need to control the water level in the tank and its constant replenishment is noted.