Content
-
slide 1
Student: Plekhanov A.G.
Group: ZOSb-0901
Lecturer: Goncharov V.S. -
slide 2
-
slide 3
Chemical methods of wastewater treatment include neutralization, oxidation and reduction. They are used to remove soluble substances and in closed water supply systems. Chemical treatment is sometimes carried out as a preliminary to biological treatment or after it as a method of post-treatment of wastewater.
G
-
slide 4
Wastewater containing mineral acids or alkalis is neutralized before being discharged into water bodies or before being used in technological processes. Waters with pH = 6.5 ... 8.5 are considered practically neutral.
Neutralization can be carried out in various ways: mixing acidic and alkaline wastewater, adding reagents, filtering acidic waters through neutralizing materials, absorbing acid gases with alkaline waters, or absorbing ammonia with acidic waters. Precipitation may form during the neutralization process. -
slide 5
Biochemical methods are used to purify household and industrial wastewater from many dissolved organic and some inorganic (hydrogen sulfide, sulfides, ammonia, nitrites) substances. The purification process is based on the ability of microorganisms to use these substances for nutrition in the process of life, since organic substances are a source of carbon for microorganisms.
-
slide 6
6.3.2. Oxidation of wastewater pollutants
The following oxidizing agents are used for wastewater treatment; gaseous and liquefied chlorine, chlorine dioxide, calcium chlorate, calcium and sodium hypochlorites, potassium permanganate, potassium dichromate, hydrogen peroxide, atmospheric oxygen, peroxosulfuric acids, ozone, pyrolusite, etc.
During the oxidation process, toxic contaminants contained in wastewater, as a result of chemical reactions, pass into less toxic ones, which are removed from the water. -
Slide 7
Reductive wastewater treatment methods are used to remove mercury, chromium, and arsenic compounds from wastewater.
During the purification process, inorganic mercury compounds are reduced to metallic mercury, which is separated from water by settling, filtering or flotation. To reduce mercury and its compounds, iron sulfide, sodium borohydride, sodium hydrosulfite, hydrazine, iron powder, hydrogen sulfide, and aluminum powder are used.
The most common way to remove arsenic from wastewater is to precipitate it in the form of sparingly soluble compounds with sulfur dioxide. -
Slide 8
To remove compounds of mercury, chromium, cadmium, zinc, lead, copper, nickel, arsenic and other substances from wastewater, the most common reagent treatment methods, the essence of which is to convert water-soluble substances into insoluble substances by adding various reagents, followed by their separation from water in the form of precipitation.
Calcium and sodium hydroxides, sodium carbonate, sodium sulfides, and various wastes are used as reagents for removing heavy metal ions from wastewater. -
Slide 9
Known aerobic and anaerobic methods of biochemical wastewater treatment. The aerobic method is based on the use of aerobic groups of organisms, the life of which requires a constant supply of oxygen and a temperature of 20...40°C. In aerobic treatment, microorganisms are cultivated in activated sludge or biofilm. Anaerobic purification methods proceed without oxygen access; they are used mainly for the neutralization of sediments.
-
Slide 10
Thermal wastewater treatment methods
Thermal methods neutralize wastewater containing
mineral salts of calcium, magnesium, sodium, etc., as well as organic substances
stva.Such wastewater can be neutralized:
- concentration of wastewater with subsequent release of the solution
active substances;
— oxidation of organic substances in the presence of a catalyst;
— liquid-phase oxidation of organic substances;
- fire disposal.
View all slides
Electromechanical processing
The essence of electromechanical processing lies in the fact that a current of high power and low voltage is passed through the contact surface of the tool and the workpiece. The protrusions of microroughnesses of the surface layer are subjected to strong heating and under the force of the tool are deformed and smoothed, and the surface layer is strengthened due to the rapid removal of heat into the bulk of the metal and rapid cooling. In this case, heating to phase transformation temperatures is a necessary condition for hardening processing modes.
The hardening effect is achieved due to the fact that ultra-fast heating and cooling rates are realized and a high degree of grain refinement is achieved.
Electromechanical processing is characterized by the following features:
- thermal and force impact on the surface layer is carried out simultaneously;
- heat release in the zone of contact between the tool and the workpiece is a consequence of the action of two heat sources - external and internal;
- the thermal cycle (heating, holding and cooling) is very short and is measured in fractions of a second.
There are various ways to supply electric current to the point of contact between the tool and the workpiece (Fig. 2).
Figure 2 - Ways of supplying electric current: a - through a fixed contact; b - through rotating elements of equipment; in - through the roller; d - through double rollers
Each of the current supply methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Depending on the purpose and type of equipment for electromechanical processing, turning, milling, drilling and other metal-cutting machines can be used. There are the following modes of electromechanical hardening.
Hard hardening mode, which implies a high surface current density (700...1500 A/mm²), low processing speed (0.5...5 m/min) and low requirements for roughness parameters. Finely dispersed martensite is formed in the surface layer, and there are no significant plastic deformations.
The average strengthening mode is carried out at a surface current density of 800 A / mm² and is characterized by the presence of a ferritic-martensitic structure and significant deformations of the surface layer. Processing speeds are approximately equal to or slightly higher than the speeds in hard mode.
The finishing mode is characterized by the absence of phase transformations, low surface current density and high processing speeds (10..120 m/min). Used for surface hardening. This achieves high performance.
Optimal modes of electromechanical hardening make it possible to achieve not only the required roughness parameters, but also to obtain a complete structure of the surface layer with increased wear resistance.
Compressive residual stresses in the surface layer due to deformation forces have a strengthening effect on various types of breaking loads. Hardening of the surface layers increases their corrosion resistance. This is explained not only by the high degree of hardening, the special structure and dispersion of the surface layer, but also by the combination of favorable physical and mechanical properties of this layer.
In connection with the increase in operational properties, it is advisable to use electromechanical hardening for a wide range of parts operating under various conditions of wear friction.
Magnetic abrasive processing
The essence of magnetic-abrasive machining is the abrasive removal of the allowance by creating a magnetic field directly in the cutting zone from an external source.The following are used as abrasive tools: magnetic abrasive powders, abrasive suspensions, magnetic rheological fluids.
The movement of a metal workpiece in a magnetic field is accompanied by the appearance of induction currents of an alternating direction in it during repeated magnetization reversal.
Abrasive cutting with the imposition of these phenomena has a number of features. As a result of the action of magnetic and electroplastic effects, the strength characteristics of the processed material change, mainly in the near-surface layer. The forces required for cutting and plastic smoothing of the machined surface are reduced; conditions are facilitated for the formation of a surface with small roughness parameters and with an increased bearing area.
The electrical charge of the treated surface intensifies electrochemical phenomena. This explains the high efficiency of the use of chemically and surface-active cutting fluids in the processes of magnetic abrasive processing in comparison with traditional types of abrasive processing.
The mechanical features of magnetic abrasive processing are:
- continuous contact of the powder with the treated surface, which makes it possible to increase the accuracy of geometric dimensions and shape, as well as to reduce cyclic loads on the system “machine - fixture - tool - part”;
- the absence of a rigid fastening of the abrasive grain in the bundle, contributes to the spontaneous leveling of the cutting tool relative to the surface to be treated;
- the ability to control the rigidity of the tool allows you to adjust the removal of metal from the forming surface;
- the absence of friction of the binder on the surface of the product significantly reduces the temperature in the abrasive treatment zone and the roughness Ra from 1.25 ... 0.32 to 0.08 ... 0.01.
Magnetic abrasive powder is used in magnetic abrasive processing processes. The magnetic field is created using special magnetic inductors. On the active surface of magnetic inductors and in the working gap, the powder is held by the forces of the magnetic field and the forces of friction of the powder against the surface of the inductor. The forces required for abrasive cutting are created due to the compression of the powder medium in the working area by magnetic forces and spacer pressures. The friction forces in the contact of the powder with the workpiece create additional pressure in the powder medium and at its boundaries.
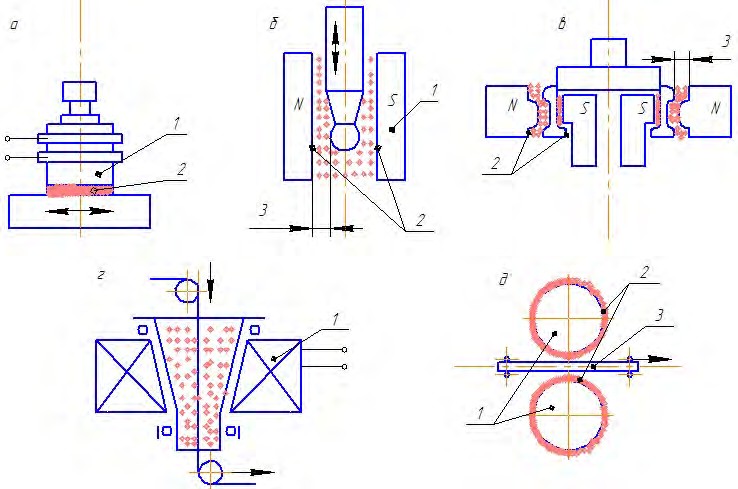
Schemes of magnetic-abrasive processing are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 - Schemes of magnetic-abrasive powder treatment: a - flat surfaces; b - outer cylindrical surfaces of revolution with powder in the working area; c - shaped outer and inner surfaces with powder in the working gaps; g - wire by pulling through a rotating funnel; e - sheet material; 1- magnetic inductor; 2 – active surface; 3 - working gap
Magnetic-abrasive processing is carried out on specialized machines equipped with special technological equipment for MAO. The design of the machines assumes the presence of drives for working and auxiliary movements, a magnetic inductor, a powder hopper with a dispenser, a device for cleaning the working area from waste powder.
Magnetic abrasive powder treatment is used in finishing technological operations for polishing surfaces, cleaning them from oxide and chemical films, removing small burrs, rounding edges, finishing and hardening cutting and stamping tools.
Views:
277
Cutting method
Metal cutting is one of the methods that allows you to process elements mechanically on different types of devices. The most difficult thing is to work with colored varieties of material that are difficult to deform. Previously, plasma processing was used to cut them. But with the advent of the laser, this method has lost its relevance.
Currently, a fiber laser is used, which allows processing the material in other ways, for example, drilling or engraving. There are several types of metal cutting:
- turning;
- drilling;
- planing;
- milling;
- grinding.
Principles of turning and drilling. When turning a part, its size practically does not change. Turning involves processing on a lathe or other types of devices, including drilling and grinding.
Drilling is used to create a hole that changes the appearance of a part. This mechanical method can be performed on any device. The main condition is the presence of a drill and a vice in which the workpiece is installed.
Planing details. Planing is carried out on a special planer equipped with a cutter. The complexity of this type of machining lies in the need for accurate calculations of idle and working strokes that allow the cutter to enter and exit the workpiece.
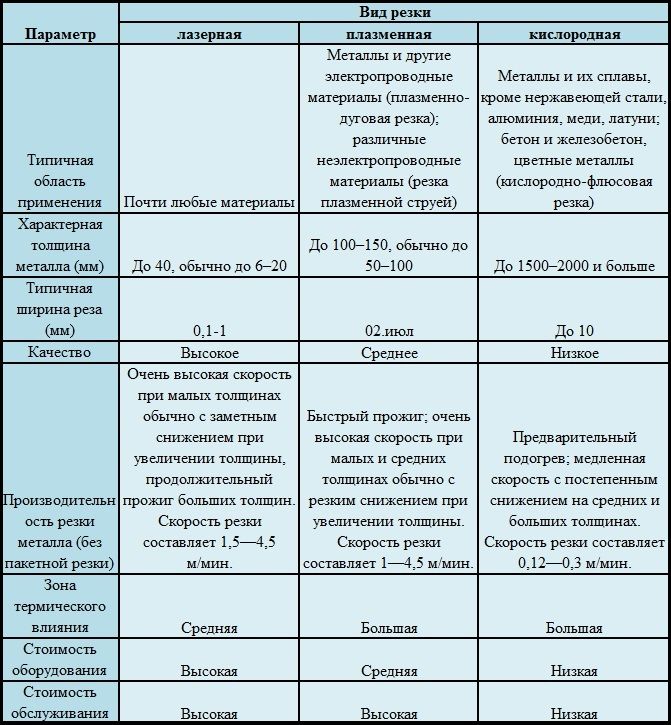
Methods of milling and grinding. Milling is a complex mechanical method that is carried out on a horizontal milling machine. The workpiece is fixed on the work surface, and then processed using a cutter that acts on the workpiece at an angle.
Metal grinding is the final stage, which allows you to give the surface of the part the necessary smoothness and remove the excess layer. Grinding does not require special devices. The final look of the part can be given independently using a grinding wheel. In production conditions, grinding machines are used for these purposes. Cylindrical parts are machined by rotational movements with straight and circular feed. In the case of a flat workpiece, metal grinding is carried out only in the forward direction.
Related video: Precision metal processing
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ZyqCmfg8aBQ
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
General characteristics of antimicrobial agents
Significant
the number of human diseases caused
bacteria, viruses, fungi, spirochetes, and
also some helminths. Substances
that neutralize pathogens
environment or in the body
human are called antimicrobial
means.
Pharmacological
the effect of substances in this group is
bacteriostatic (the ability
stop growing and reproducing
microorganisms) or bactericidal
(property to neutralize microorganisms).
Antimicrobial
funds are divided into two groups:
I.
Antiseptic and disinfectant
facilities.
drugs,
do not exhibit selective antimicrobial activity
actions and have significant toxicity
for a person.
Antiseptic
means can lead to death
or stop growing and developing
microorganisms on the surface of the body
human (skin or mucous membranes).
Disinfection
means neutralize pathogens
microorganisms in the environment, their
used for room treatment
linen, dishes, medical instruments,
equipment, patient care items.
Classification
antiseptic and disinfectant
funds
I.
Antiseptic and disinfectant
means of inorganic nature
1.
Halogens (halides)
1.1.
Preparations containing chlorine - chlorine
lime, chloramine B, chlorhexidine
digluconate, chlorantoin, sodium hypochlorite
1.2.
Preparations containing iodine - iodine solution
alcohol, iodonate, iodoform
(triiodomethane), Lugol's solution, iodine-dicerin,
iodinol, povidone-iodine (betadine)
2.
Oxidizing agents - hydrogen peroxide solution
(hydrogen peroxide) diluted and
concentrated, potassium permanganate,
benzoyl pe-hydroxide (hydroxy 5, 10)
3.
Acids and bases - boric acid,
benzoic acid, ammonia solution,
sodium tetraborate (borax)
4.
Heavy metal salts - mercury dichloride
(sublimate), silver nitrate, collargol,
protargol, zinc sulfate, dermatol,
xeroform
II.
Antiseptic and disinfectant
means of organic origin
1.
Phenols - pure phenol (carbolic acid),
birch tar, resorcinol, Tricresol,
polycresulene (vagothyl)
2.
Tar and resins - ichthyol (ichthammol), vinizol
3.
Dyes - brilliant green,
methylene blue, etacridine lactate
(rivanol)
4.
Nitrofuran derivatives - furatsilin
(Nitrofural), furoplast, furagin
(furazidin)
5.
Aldehydes and alcohols - ethyl alcohol,
formaldehyde (formalin), Lysoform
6.
Detergents - green soap, Zerigel,
etonium, decamethoxin (septefril),
miramistin.
II.
Chemotherapeutic drugs.
drugs,
which provide selective
antimicrobial activity, exhibit
wide range of therapeutic
their actions are used to treat and
prevention of infectious diseases.
General description of the technological process
Machining blanks can be done in two ways:
- pressure (without chip removal);
- cutting (with chip removal).
In the first case, the material is given the desired shape and volume by the force of the tool, for example, forging. In the second case, surface layers (allowance) are removed from it, for example, milling, planing, grinding.
Machining of metals is one of the stages of obtaining a finished product from a workpiece and requires preliminary preparation of a technological map indicating the required dimensions and accuracy classes. Based on the technological map, a drawing of the finished material is drawn up, which also indicates the dimensions and accuracy classes.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=WmTQqaIKFNc
Vibratory mechanical cutting
Vibration superimposed machining is becoming more and more widely used. There are two directions of vibration imposition. The first direction is associated with the damping of unfavorable vibrations during machining, which cause a decrease in surface quality, machining accuracy and tool life. This direction is of particular importance when cutting hard-to-cut materials.
The second direction is connected with the achievement of a positive effect in the process of imposing vibrations. The use of vibratory cutting provides effective chip breaking, as well as a significant improvement in the machinability of a variety of materials.
The general physical features of cutting with vibration are:
- short-term periodic increase in cutting speed;
- variable cyclic load on the deformable material;
- reduction of friction forces on the contact surfaces of the tool with chips and workpiece;
- increased efficiency in the use of cutting fluid.
In the direction of action, vibrations can be axial, radial or tangential.
Cutting with axial vibrations is used for chip breaking. The main features of vibratory cutting with axial oscillations are a large change in feeds (cut thickness) in one cycle of tool oscillations, as well as a significant change in the working cutting angles. In all cases, when turning, the wear depth of the front surface of the cutters decreases.
The most effective use of axial vibration cutting is when drilling, during which the conditions for crushing and removing chips are significantly improved.In conventional drilling, in the process of moving along the helical groove, the chips jam and periodically form plugs, which makes it necessary to stop and withdraw the drill from the hole. This circumstance complicates the automation of drilling.
Together with the possibility of automation, vibratory drilling can increase productivity by 2.5 times and increase tool life by three times.
Cutting with radial vibration negatively affects the results of processing - the roughness parameters increase, since the movement of the cutting edge during vibration is directly fixed on the machined surface. The working conditions of the cutting edge are also unsatisfactory, since a large load during oscillatory motion is perceived by the cutting edge, as a result, there is increased wear and chipping of the edges.
Cutting with tangential oscillations, i.e., with oscillations in the direction of the circumferential cutting speed, is used to significantly increase productivity and tool life. The method showed positive results in turning, milling, reaming, threading, grinding, abrasive tool sharpening.
Used equipment
Machining is used at specialized enterprises provided with a sufficient number of production facilities and the necessary equipment.
To remove the surface layers, the product is processed on a lathe and milling machines. The most popular among them are:
- CNC turning centers;
- vertical milling machines.
New models of working attachments allow maintaining high geometry accuracy and surface roughness.
Equipment that allows you to process the material mechanically is presented in a wide variety. Each company independently decides on the need to purchase a particular device. For example, in some industries, rotary machines are installed that can process products up to 9 meters in diameter.
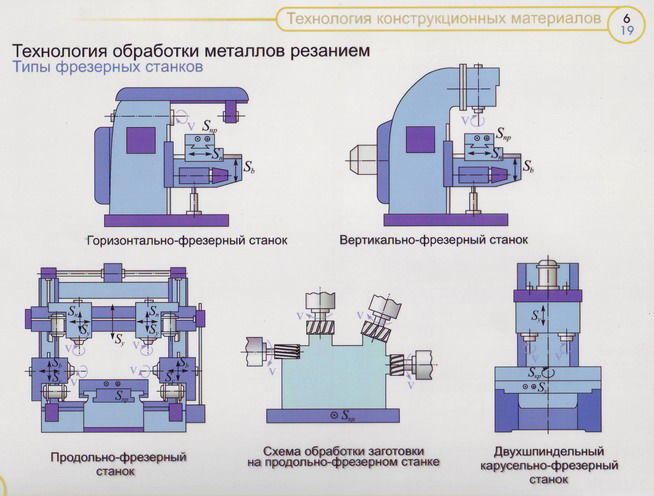
- milling;
- gear hobbing;
- radial drilling;
- horizontal drilling;
- vertical drilling.
Pressure Treatment Equipment
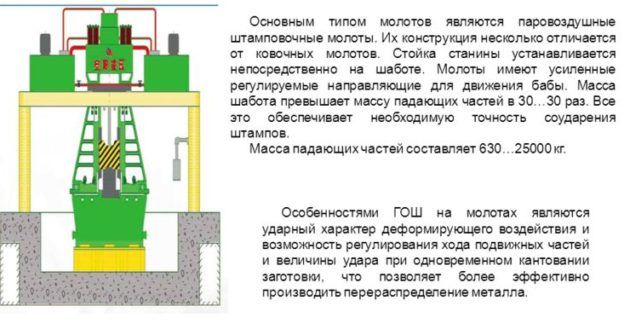
Forging can be done by hand using a hammer and anvil. The mechanical method consists in using a press lowered onto a heated metal surface.
Both devices are mechanical. But the hammer strikes, due to which the processed surface takes on the desired shape, and the press exerts pressure.
The hammer can be of the following types:
- steam;
- steam-air;
- falling;
- spring.
There are also several types of press device:
- hydraulic;
- steam-hydraulic;
- screw;
- friction;
- eccentric;
- crank;
- spring.
Before proceeding with pressure treatment, the surface of the metal is heated. However, in recent years, instead of hot exposure, cold exposure, called stamping, is more often used. Stamping is suitable for working with any type of metal. It allows you to give the product the desired shape without affecting the physical characteristics of the material.
The most popular types of stamping include:
- bending;
- stretching;
- compression;
- molding;
- buckling;
- disassembly.
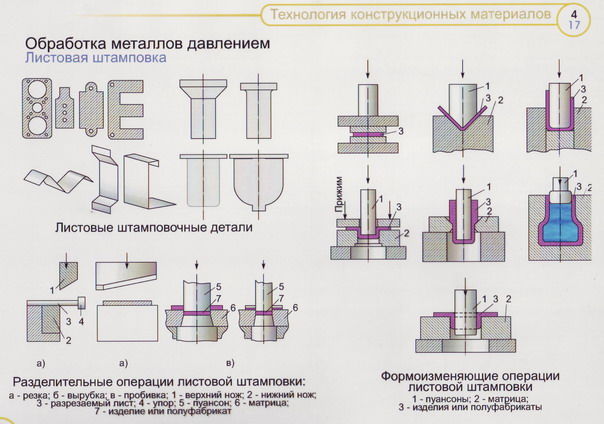
Bending is used to change the axial shape of a metal element and is performed using a vice mounted on bending dies and presses. Stretching is performed on a spinning machine and is used to create complex products. By compression, the cross section of the part with the cavity is reduced. Shaping is used to create elements of spatial forms. To perform these works, special molding dies are used.
Presentation on the topic Biological methods of wastewater treatment. The principle of biological wastewater treatment is that, under certain conditions, microbes are able to break down organic matter. transcript
1
Biological wastewater treatment methods
2
The principle of biological wastewater treatment is that, under certain conditions, microbes are able to break down organic matter into simple substances, such as water, carbon dioxide, etc.
3
Biological methods of wastewater treatment can be divided into two types, according to the types of microorganisms involved in the processing of wastewater pollutants: 1. aerobic biological methods of industrial and domestic wastewater treatment (microorganisms need oxygen for their vital activity) without oxygen).
4
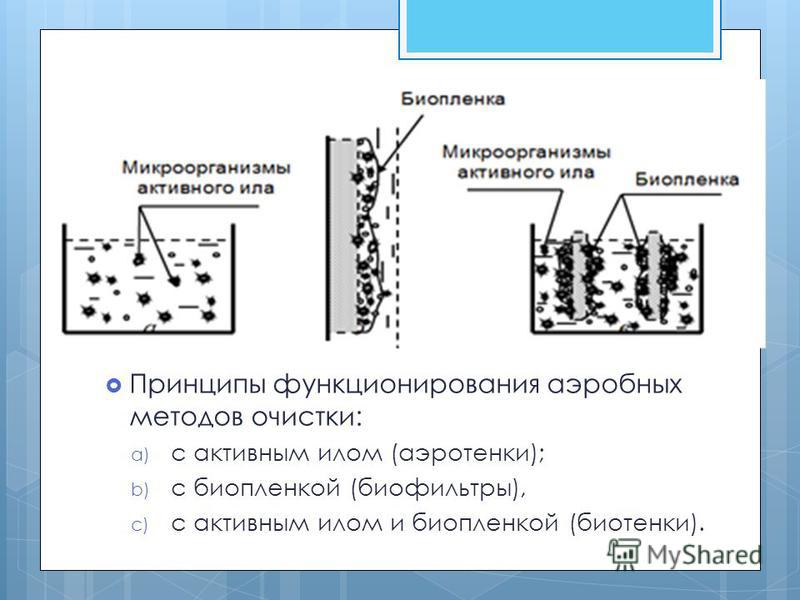
Wastewater treatment methods involving aerobic bacteria are divided according to the type of tank in which wastewater is oxidized. The container can be a biopond, a biological filter, or a filtration field.
5
Principles of operation of aerobic treatment methods: a) with activated sludge (aerotanks); b) with biofilm (biofilters), c) with activated sludge and biofilm (bioten).
6
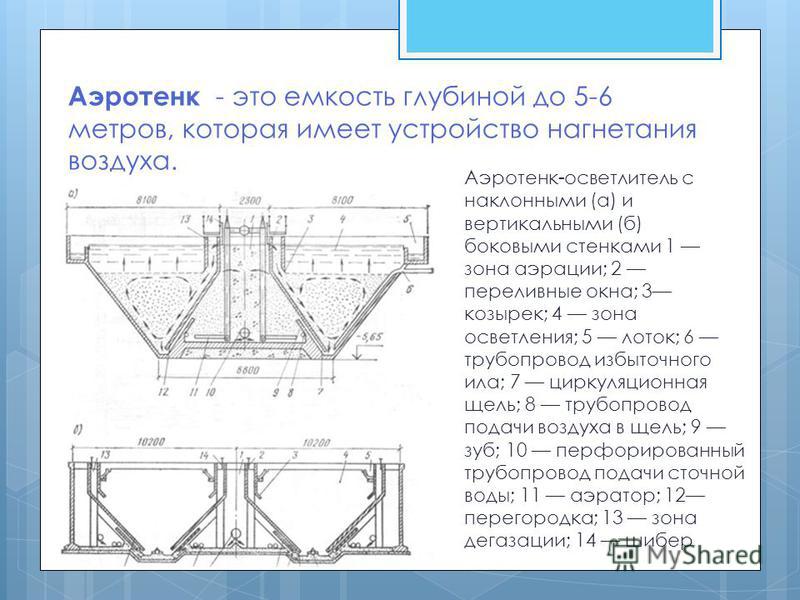
An aerotank is a container up to 5-6 meters deep, which has an air injection device. Aerotank-clarifier with inclined (a) and vertical (b) side walls 1 aeration zone; 2 overflow windows; 3 visor; 4 clarification zone; 5 tray; 6 excess sludge pipeline; 7 circulation gap; 8 pipeline for supplying air to the gap; 9 tooth; 10 perforated wastewater supply pipeline; 11 aerator; 12 partition; 13 degassing zone; 14 gate
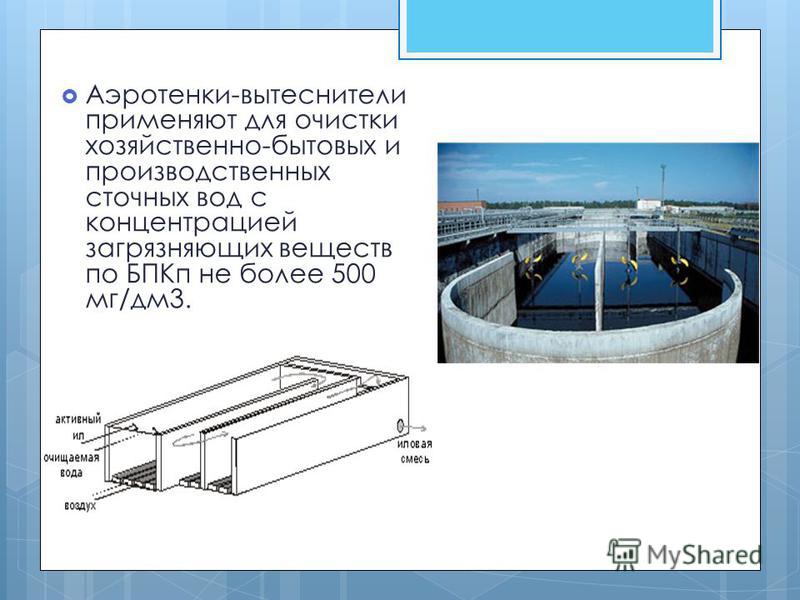
7
Aerotanks-displacers are used to treat household and industrial wastewater with a concentration of pollutants in terms of BODp not more than 500 mg / dm 3.
8
Aerotanks-mixers (aerotanks of complete mixing) are characterized by a uniform supply of source water and activated sludge along the length of the structure and a uniform removal of the sludge mixture.
9
Biological filter A biological filter is a container filled with coarse material. Colonies of microorganisms live on the particles of this material.
10
In a conventional biofilter, nitrification and denitrification processes can be carried out along with the biodegradation of wastewater organic substances. nitrifiers transform ammonium nitrogen into nitrogen of nitrites and nitrates denitrifiers transform nitrate nitrogen into molecular nitrogen or other volatile forms of nitrogen High loads on organic substances fall on the biocenosis of the upper part of the biofilter, therefore, a biofilm is formed in this part, consisting of heterotrophs that intensively oxidize waste organic substances water.
11
According to the type of loading material, all biofilters are divided into two categories: with volumetric loading In biological filters with volumetric loading, crushed stone of strong rocks, pebbles, slag, and expanded clay are used. with planar In filters with planar loading - plastics capable of withstanding temperatures of 6 - 30 0C without loss of strength.
12
According to the generally accepted classification, biofilters with volumetric loading are distinguished: drip high-load towers with flat loading with hard filling hard block soft loading
13
Drip biofilters Drip biofilters are usually designed rectangular in plan, waste water is supplied from above to the loading surface, using various types of switchgears.
14
Highly loaded biofilters differ from drip biofilters in a higher oxidizing power equal to 0.75–2.25 kgBOD/(m 3 day), due to better air exchange and non-silt loading, which is achieved by using loading material with a particle size of mm, increasing the working height of loading up to 2–4 m and hydraulic load up to 10–30 m3/(m2 day).
15
Flat loading filters To increase the throughput of biofilters, a flat loading is used, the porosity of which is %. The working surface for biofilm formation is from 60 to 250 m 2 /m 3 loading.
16
Anaerobic reactors However, the vital activity of anaerobic microorganisms is associated with the release of methane into the air, which requires the organization of a special system for monitoring its concentration. are metal tanks containing a minimum amount of complex non-standard equipment.
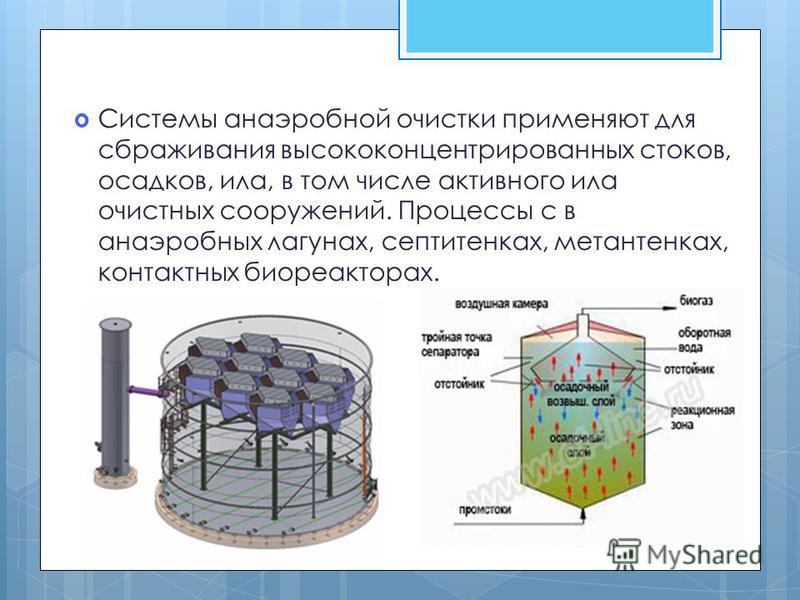
17
Anaerobic treatment systems are used for the fermentation of highly concentrated effluents, precipitation, sludge, including activated sludge from treatment facilities. Processes in anaerobic lagoons, septic tanks, digesters, contact bioreactors.
18
Thank you for your attention!
Chemical sterilization agents
Destruction
microorganisms through chemical
substances is called disinfection
(from lat.
infection
- infection and French. negative
prefixes des).
Chemicals are used for
destruction of pathogenic microorganisms
in objects of the external environment - at the working
place, indoors, on work clothes,
hands, technological equipment and
inventory.
TO
substances used for the purpose
disinfection, a number of
requirements:
- they
must be readily soluble in water;
- v
short time to show bactericidal
action;
- not
have a toxic effect on
human and animals;
- not
cause damage to disinfected
items.
Disinfectants
substances are divided into several
groups:
1.
Chlorine-containing compounds (chlorine
lime, sodium hypochlorite, chloramine,
pantocid, chlordesinsulfochloranthin and
etc.).
2.
Compounds based on iodine and bromine
(iodopyrine, dibromantine).
3.
Oxidizing agents (hydrogen peroxide, permanganate
potassium, etc.).
4.
Phenols and their derivatives (phenol, lysol,
creolin, hexachlorophene).
5.
Heavy metal salts (sodium merthiolate,
corrosive sublimate).
Antimicrobial
acids and their
salts (boric, salicylic), alkalis, alcohols
(70% ethanol solution) aldehydes
(formaldehyde).
Issued
also bactericidal soaps: phenolic,
tar, "Hygiene", containing 3-5%
hexachlorophene.
Equipment for mechanical wastewater treatment
In order for the cleaning process to take place as thoroughly as possible, various facilities are used:
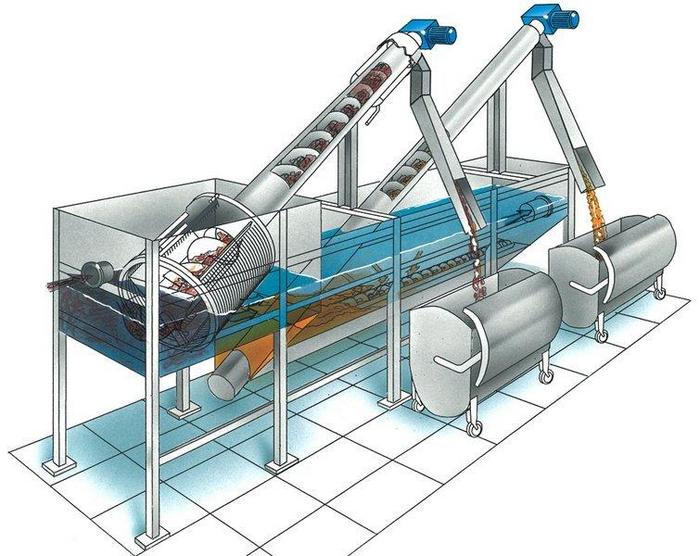
Lattices hold elements from large to medium. The gratings are mounted in the direction of the liquid flow, and the elements can be installed inclined or vertically, but it is necessary to equip the sinuses of the gratings with rake teeth that remove debris and send waste to the belt. After that, the garbage is sent to the crusher, if the method does not immediately involve the installation of crusher grates to trap and grind the garbage.
Sand traps are used to hold particles with a low specific gravity. Due to the fact that the specific gravity of even small particles is greater than the specific gravity of water, the inclusions settle to the bottom. Therefore, the functionality of sand traps directly depends on the speed of water flow. As a rule, the equipment is designed to hold elements no more than 0.25 mm, while the flow velocity is specially regulated: 0.15-0.3 m/s with horizontal flow
It is important to understand that the movement of water must be rectilinear or circular, but horizontal, only in this case the elements of the sand traps will work at full strength. The method of cleaning equipment can be either using a pump that sucks out the collected sand or by means of scrapers, augers, hydraulic elevators at centralized treatment plants
Sand traps are capable of cleaning streams by 75% of mineral impurities - this is an almost ideal indicator.
Settling tanks are also used as equipment for separating mechanical impurities from wastewater. There are many types of sedimentation tanks:
primary, mounted in front of biotreatment stations;
secondary, which are installed after bioprocessing stations.
According to their design features, sedimentation tanks can be horizontal, radial and vertical.
- Sludge beds are also included in the process of mechanical wastewater treatment. They are used to collect sediment that remains in sedimentation tanks and other structures. The process of drying and distribution of discharges takes place exactly on the sludge sites, while the humidity decreases to 75%, which reduces the volume of discharges by 3-8 times. As a structure, a site is a site delineated by earthen ramparts. After drying, the sludge residues are collected and removed, and the liquid stream, purified in this way, partially enters the soil, partially evaporates. The rest of the interstitial water is pumped to treatment plants, where biological treatment is already used due to the content of a large number of fine particles that are unable to be precipitated by mechanical traps.
It is worth remembering that the process of mechanical removal of impurities does not always completely release harmful substances and biological treatment of streams is required.