How much iron does the body need
Iron is a vital element for the normal functioning of the body. Especially a lot of it in the blood. - 4-5 grams. But, once in the body, iron is very slowly excreted, mainly through the intestinal wall 6-10 mg per day.
Based on this, the daily norm of iron for men was determined - 6-10 mg / day. For women (taking into account additional blood loss) - 15-18 mg / day
It seems that we are able to calculate the optimal concentration of iron in water. After all, it is known that a person drinks an average of 2 liters of liquid per day. But the problem is that iron in the body comes not only from water, but also from food. Moreover, it comes from food in much larger quantities. Meat, liver, fish, apples, beans and legumes are especially rich in iron.
Let's try to look at the problem from the other side.
physical aeration
There are 2 types of degassers:
- Non-pressure. Water enters the tank from spray nozzles (by showering) separately or in combination with bubbling. They are considered the simplest.
- Pressure. Their capacity is less than non-pressure. Water falls to the bottom of the tank and is enriched with oxygen, which is supplied by a pump.
There are foam, film, vacuum, ejector (injector) types of degasifiers, in which water is mixed with air by spouting, foaming, boiling under vacuum and other methods. Any of them disrupts the vital activity of sulfur bacteria and leads to 65-70% death of their colonies. Excessive air supply does not increase the efficiency of toxic gas release.
The water is acidified by adjusting the pH to 5 to increase the concentration of hydrogen ions. From this, the hydrogen sulfide molecules cease to decompose into ions, they pass into a molecular form, which is removed well, in contrast to the ionic one.
Disadvantages of aeration cleaning - the equipment is bulky, energy-intensive and expensive.
Otherwise, why bother with all this?
A test, usually supplied by filter manufacturers, can confirm the high iron content in well water.
But for starters, it doesn’t hurt to choose the type of well very carefully, four types of which are clearly shown in the following figure:
- A - river, as a zone of discharge of water layers;
- B - water-resistant layers;
- C - the water level between the layers, the depth is not more than 50 m, here the probability of iron is not high, but there are many other impurities;
- D - artesian water in a fountain from depths from 40 (if you're lucky) to 250 m - it is these wells that are characterized by the presence of iron impurities;
- E - non-pressure water from depths up to 30 m - the probability of iron is low;
- F - the so-called perch water - water at a depth of up to 10 meters, which has almost no chemical impurities, but often with a large sediment;
- G - groundwater recharge zone.
A lot depends on the choice you made - usually ferruginous water in a well is characteristic of artesian-type wells
Thus, there is only one conclusion, if you have a choice of how deep to extract water from, and you want to protect yourself from iron, choose a smaller depth. Perhaps other misfortunes will appear, but you will be spared iron.
Cleaning methods
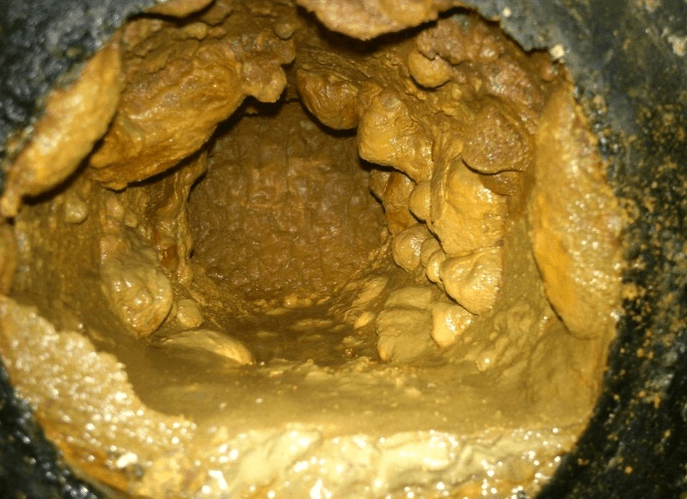
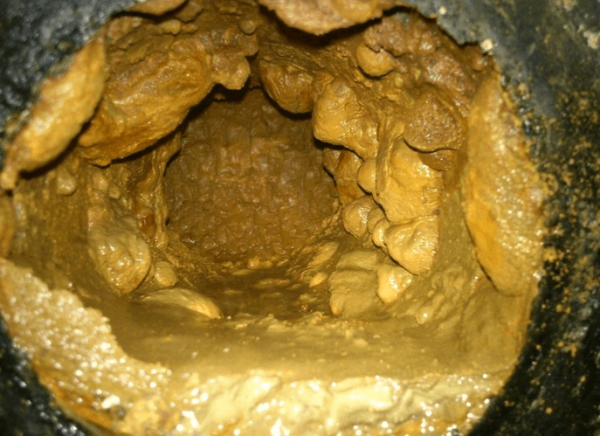
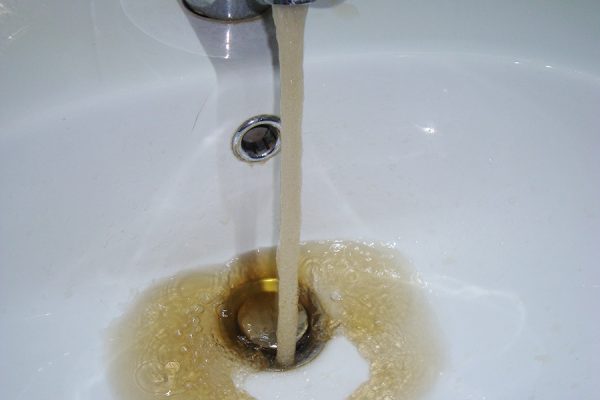
Iron is the most common impurity in well water. As soon as water with iron comes out, the impurity reacts with oxygen, passes into a trivalent form and will not be visible in water for some time.
This is where the danger lies - the water will seem perfectly clean. And only after a while it will acquire a brown color and an unpleasant metallic smell.
The picture looks like this.
The maximum allowable amount of iron in a cubic decimeter of water (in two full glasses) is no more than 1 mg.When excess iron enters the body, they can cause very significant harm, as they neutralize a large number of other elements that are very important for the body.
All cleaning methods can be divided into 4 types:
- filtration,
- aeration - saturation of water with oxygen,
- coagulation - the use of substances that seize iron molecules and precipitate with them, the most famous coagulant is aluminum sulfate - a white salt with a pink or blue tint,
The photo shows aluminum sulfate.
flotation - here also the saturation of water with substances that absorb iron molecules, but everything does not go down, but rises up, which greatly facilitates further purification.
Homemade scheme
The easiest way to iron out water from a well is to create such a system:
- A - pipeline for supplying water from the well to the tank;
- B - stainless steel tank; the tank has a rather large surface area, which ensures maximum contact of water with oxygen, which means the reaction of oxygen with iron, which eventually precipitates in the form of rust; as practice shows, during the year up to 5 cm of sediment accumulates at the bottom (therefore, the tank must be cleaned periodically);
What can manganese water be used for?


Alas, there are practically no options for using such water with benefit. Drinking water with manganese is undesirable. Even one glass can be harmful, not to mention a systematic intake.
In everyday life, the use of such water is also undesirable. After all, the high content of manganese is dangerous for almost all household appliances, because of it:
- the load on the water pipes increases (their permeability is significantly reduced, as well as the service life);
- the temperature in the rooms drops (this is the result of the appearance of manganese deposits in pipes and radiators, which reduces heat transfer);
- electrical appliances (water heaters, kettles, dishwashers and washing machines) on which scale appears are also at risk.
Ultimately, the damage caused to the equipment is reflected in the health of the owners of the house. For example, it can lead to colds due to problems with the heating system.
By the way, it is dangerous not only to drink water with a high content of manganese, but also to simply wash your face with it, rinse your mouth and brush your teeth with such water.
Even washing things, as a rule, brings disappointment - a favorite thing can easily lose its usual color and be spoiled by a brown or gray tint that appears due to manganese compounds present in the water.
It is also worth refusing to water the garden with water with a high content of manganese. Of course, plants may be happy with such feeding, but do not forget that vegetables and fruits from the garden will soon be on the home table and they may also be unsafe.
Perhaps one of the few options for using water with manganese is watering houseplants, which will disinfect the earth and protect flowers from insects. However, constantly watering flowers with such water is also not worth it. The effect will give one-time events.
As for taking baths that supposedly have a therapeutic effect, it is important not to confuse baths with manganese from baths with therapeutic potassium permanganate - potassium permanganate, which really has an antibacterial, healing effect and is effective for fungal and bacterial diseases, as well as for urological problems.
How to purify water from manganese

Purification of water from manganese is carried out by methods used for rusty tap water - high iron content. Manganese is a metal, so it needs to be oxidized and filtered.
Before you clean up, you need to establish the extent of the problem. To do this, a water analysis is done and the level of element concentration is determined.
Manganese aeration is among the main effective methods of water purification. It is suitable for cases where the permanganate oxidation index exceeds 9.5 mg02 / l and includes two stages:
- the release of free carbon dioxide from water, which occurs under vacuum and allows you to increase the pH to 8 units;
- filtration using a granular filler, which can be quartz sand.
This method is considered one of the most accessible. You can even make an installation for this procedure with your own hands.
However, it is important that ferrous iron be present in the water, which can turn into hydroxide during oxidation, and then absorb and oxidize divalent manganese
For everything to be successful, the ratio of manganese to ferrous iron must be in proportion - seven to one. When aerating, it is necessary to have an aeration column, additional filters and a special valve that allows excess gases to be removed.


Another option to deal with a high content of manganese is to settling water with mechanical purification. With it, cartridge systems are used. Such cleaning is considered rough, it is able to filter out only large particles of the element. Therefore, its use is suitable in combination with other types of cleaning.
Ways to solve the problem include:
- the use of potassium permanganate (it causes manganese to precipitate, and as a result, turn into a catalyst for subsequent water purification);
- oxidation with catalysts (it is possible when using a dosing pump and installations that allow the metal to be oxidized to a state in which it can no longer be dissolved);
- reagents in combination with reverse osmosis (in this case, ozone, chlorine or sodium hypochlorite can act as reagents that prevent the concentration of the element in water).
Reverse osmosis is one of the most effective methods. It removes almost all existing impurities, directing them to the drain, and clean water to taps and pipes. However, such a cleaning system has a number of disadvantages - from high cost to too much water consumption, in which up to two-thirds of the incoming liquid is sent to the sewer. In addition, water during the operation of the system turns out to be even too pure and similar in properties and taste to distilled water.
When choosing filters, it is important to consider two points:
- the current composition of water and the amount of manganese in it;
- the desired composition of the water, which should be after filtration.
If the manganese content is very high, you should pay attention to the iron-removal filter. It performs high-quality aeration and filtration

Effective and ion exchange cleaning. With it, the problem with the composition of water is solved with the help of resins that soften it and retain manganese along with iron. Ion exchange is carried out as part of complex treatment, which has a positive effect on water in all directions at once. This method requires regular replacement of the reagent. Although there is an option to restore its properties. This is ordinary edible salt, thanks to the addition of which the filter can work from three to four years.
There is also an option with reagentless water purification, which is carried out using a catalyst. This is done by backflushing.
To achieve a result, it is important to correlate the chemical composition of water, the depth of the well and the amount of maximum water consumed.
Manganese in water from an artesian well significantly impairs its taste, it is dangerous for the health of residents of the house and for equipment in the apartment.The element is very insidious: it is not easy to find it, and by the time it is discovered, it already manages to make trouble. Water purification and proactive control of its quality should be one of the primary tasks of the homeowner.
Methods for purifying water from iron
Methods for removing iron from water largely depend on the form of iron in your water.
Most often, civilians deal with ferrous iron. The water is colorless and transparent, but has a metallic taste.
In this case, two methods will help you.
Cartridge Fe 10 SL
Many filters have an ion exchange cartridge. which uses ion exchange resins. But in this case, we are specifically interested in the resin, which replaces iron with sodium.
Such "iron removal cartridges" are produced by all manufacturers of household filters. Depending on the design and the resins used, "iron removal cartridges" can work effectively up to an iron concentration in water of 5 mg/l
For example, “Fe 10″SL cartridge” or Fe 20″BB from Geyser.
There are cartridges that work on other principles, for example, the “BA cartridge” for Geyser filters. This is a specialized cartridge for efficient removal of excess dissolved iron (up to 5 mg/l) by alkaline precipitation. The natural material calcite is used as a filtering medium.
2. Reverse osmosis.
reverse osmosis filter
Reverse osmosis filters are effective in removing any impurities, including ferrous iron. They purify water much better than ion exchange resins. Since ferrous ions are much larger than the pores of reverse osmosis membranes, the membranes retain them well.
At the same time, the membrane does not clog, since all the impurities that the filter has retained are drained into the sewer. Reverse osmosis systems well purify water with iron content up to 10-20 mg/l.
Problems with ion-exchange cartridges and reverse osmosis filters begin to arise when, in addition to ferrous iron, ferric iron is also present in the water. If there is not much of it, this is half the trouble. Filters do the job.
But when the concentration of ferric iron is high, the pores of the ion exchange filter and the reverse osmosis membrane begin to clog. Filters lose their effectiveness.
On the other hand, it is even easier to purify water from insoluble ferric iron (in the common people - rust). A significant part of it is retained by mechanical cleaning filters.
Thus, the biggest problem is the purification of water containing high concentrations of both ferrous and ferric iron.
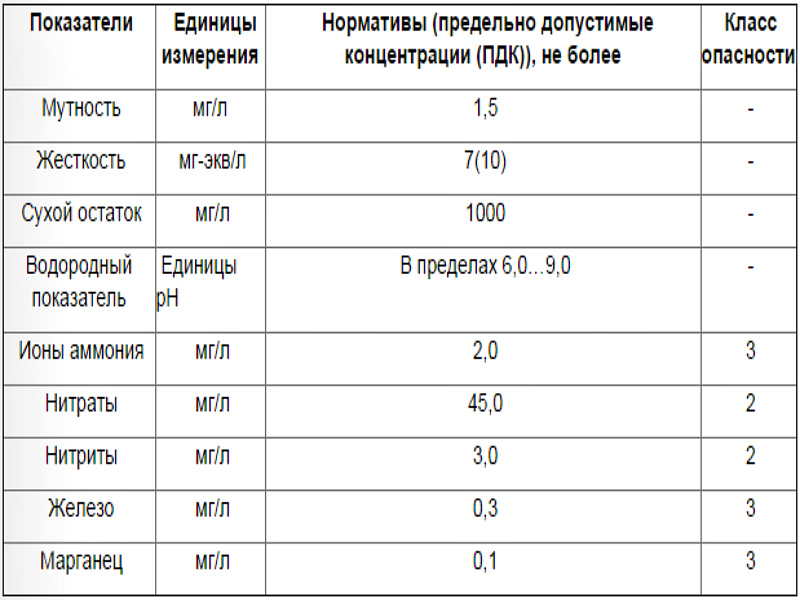
Content rate
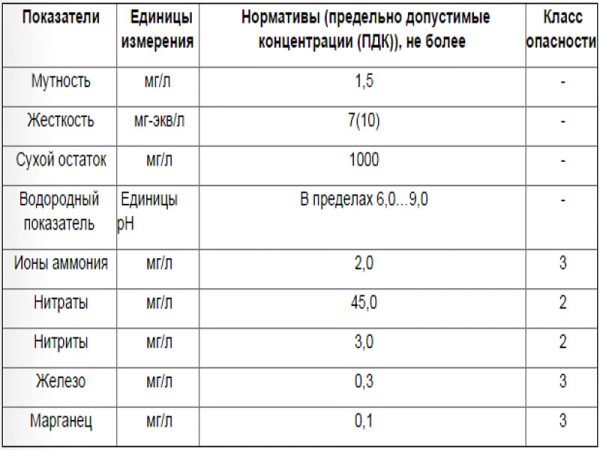
The presence of manganese in water is normal
It is important that its quantity does not go beyond certain limits. According to the standards in force in Russia, the presence of an element in drinking water should not exceed 0.1 milligrams per liter.
A similar standard applies to water intended for household needs.
With a not very large (but, alas, already dangerous for humans) excess of this norm of manganese in water, it turns out to be difficult to detect it on your own
Special signs that the owner of the house can pay attention to appear only with the exorbitant content of the element, including:
- a yellowish tint that appeared at the water from the tap;
- an unpleasant astringent taste of water before and after boiling, which is felt even in tea or coffee (and not just in pure water);
- unusual smell;
- black sediment, which is easy to see in settled water;
- dark spots of unknown origin appearing on plumbing;
- an unexpected cold snap in the apartment, apparently associated with blockage of pipes.
The content of manganese in the water from the well must be constantly monitored.It is advisable to regularly take samples that will protect yourself from trouble.
It should be borne in mind that the amount of manganese in water depends on many factors, including even the time of year. In the cold months, the figure turns out to be slightly higher, and this is due to the seasonal stagnation of water. Whereas in spring and summer the figure decreases sharply.
Hazardous effects of hydrogen sulfide
The limit of the established norm is 0.03 mg / l.
Its danger to the human body is as follows:
- when inhaling air containing even a small amount of gas, the transfer of oxygen through the body becomes difficult, headaches, dizziness, symptoms of poisoning, discomfort in the epigastric region, visual impairment appear;
- elevated concentrations can lead to coma, convulsions and pulmonary edema;
- when drinking water with hydrogen sulfide, metabolism is disturbed;
- the sense of smell and taste are dulled, it becomes difficult to catch the surrounding aromas.
- causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
Hydrogen sulfide in combination with hemoglobin provokes processes in tissues similar to suffocation. They proceed slowly and are most dangerous for children.
Water that smells of hydrogen sulfide cannot be used for sanitary purposes, for drinking animals. A solution of hydrogen sulfide has the properties of an acid and, when combined with iron in water, forms a precipitate of iron sulfide, which accumulates on the walls of communication networks, household appliances and contributes to corrosion. As a result of the development of sulfur bacteria, pipelines become overgrown.
Kulibins' advice
Since divalent iron dissolved in water, in contact with atmospheric oxygen, turns into trivalent iron with precipitation, many craftsmen have created home-made cleaner designs.
They usually include large open water tanks in which the water is stored for some time. Sometimes air is blown through the water to intensify the oxidation process. For example, using an aquarium compressor.
Ferrous iron combines with atmospheric oxygen and precipitates. Now water can be taken for drinking needs. When the sediment becomes too thick, the tank is cleaned out.
The same process can be repeated in a regular bucket. Type in a bucket of water and leave it for a day. Then carefully drain the water without stirring up the sediment. After such a procedure, the amount of iron in the water will decrease several times.
What is the danger of the presence of iron in water
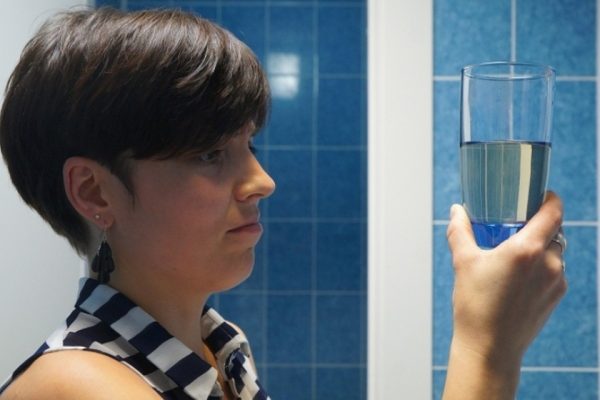
Drinking rusty water is unpleasant - the metallic smell and taste in the mouth cause rejection, but this is not so bad. We would like to know what danger the water from the well with iron brings to the house, whether it is dangerous for health, whether its composition will affect the operation of water-consuming household appliances.
Impact on health and well-being
It all depends on concentration. A small amount of iron is quite acceptable and may not show external signs. But if, after settling, it becomes cloudy or a precipitate forms in it, measures must be taken.
For reference. Permissible and safe is the daily intake of iron in the body in the amount of 0.8 mg per kilogram of body weight. If your weight is 60 kg, you can quite easily “consume” 48 mg of a pure substance. Even if its concentration is 10 mg / l, which is a lot, you will have to drink almost 5 liters of water for this.
Dermatological problems may be due to the use of rusty water
Such water, oddly enough, can cause the greatest harm to the body not when ingested, but when carrying out hygiene procedures - bathing, washing. It can cause allergic reactions on the skin. This alone should make you think about deferrization of water from a well. But there are other reasons as well.
Impact on sanitary and household appliances
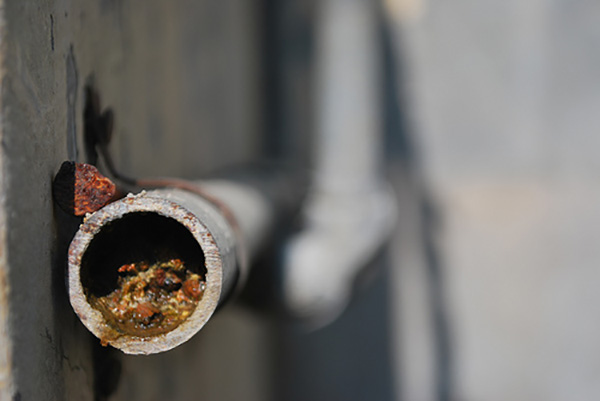
Interacting with atmospheric oxygen, the iron dissolved in water is oxidized and forms an insoluble iron oxide compound - rust. It gradually settles on everything it comes into contact with: on the inner surface of pipes and faucets, in the bathroom and sink, on the working parts of water-consuming equipment - washing machines, dishwashers.
Rust in the dishwasher
If plumbing can still be maintained in relative order with the regular use of cleaning products, then everything else will quickly fall into disrepair. And the price of high-quality equipment or a complete replacement of the plumbing system is not so small as to neglect the ability to protect it from damage. We can also mention the fact that when washing in rusty water, it is quite difficult to keep linen and clothes in perfect condition. But compared to all of the above, these are already trifles. Conclusion: a high content of iron in water from a well is a problem that needs to be eliminated. The question is how to do it?
Why is this water dangerous for humans?


Of course, in small quantities, manganese can be necessary and even very useful for a person - for the work of the pituitary gland, blood-forming functions, and also for the sex glands. Magnesium enters the human body with animal and plant foods. An adult needs from 2.5 to 5 mg of an element per day. Children under one year of age - 1 mg. Children from one year to 15 years - 3 mg.
However, exceeding the norm is extremely dangerous. 40 mg per day is the daily dose that is already considered toxic. Moreover, manganese poisoning is especially dangerous, which lasts for weeks and months, day after day. Over time this results in:
- to the deterioration of the human skeleton;
- decrease in muscle tone;
- the development of muscle atrophy;
- the occurrence of allergies;
- the appearance of problems with the kidneys, liver, small intestine;
- increased stress on the brain.
The list of consequences of systemic exposure to manganese also includes the threat of developing such terrible diseases as cancer and Parkinson's disease.
Water with manganese can provoke poisoning, in which the patient will complain:
- for dizziness and headache;
- cramps and sharp back pain;
- frequent mood swings;
- apathy and general decline in strength;
- reluctance to eat.
For young children, drinking water with a high content of manganese is fraught with problems with intellectual development. The element is no less dangerous for the psyche of adults.
At first, all disorders associated with the nervous system are exclusively functional in nature. A person begins to feel overwork and sleepy more often. In addition, he has:
- weakness in the legs and arms (they periodically go numb);
- signs of vegetative dystonia;
- increased sweating and decreased muscle tone.
Changes also affect the habitual way of life for a person:
- activity, previously characteristic of the patient, suddenly decreases sharply;
- the area of human interests is limited and becomes extremely narrow;
- there are memory lapses that never happened before;
- the ability for associative thinking is reduced.
The person himself usually does not notice the frightening symptoms, but more often writes them off, for example, for vitamin deficiency or for tiredness from hard work that has piled on. Because of this, it is not possible to recognize the source of the disease in time - an increased concentration of manganese in the body - and problems in the body begin to grow.


At the next, second stage, a person's performance decreases even more. He is constantly sleepy. The speed of movement slows down, facial expressions weaken, involuntary muscle contraction begins to be observed.
In addition to external, there may be internal manifestations. The work of the endocrine glands is disturbed in the victim, which leads to numbness of the limbs.
Often it is at this stage that it is possible to establish the cause of the disease. The intake of manganese into the body stops, but it takes a long time to recover after the test. And, most likely, the patient has not so many chances for a complete recovery.
Moreover, the third stage of poisoning can begin in the body. This is manganese parkinsonism, in which the patient has:
- even greater problems with motor activity;
- a change in the characteristic gait, the appearance of paresis of the feet - features of walking, in which the foot begins to drag along the ground;
- communication difficulties, speech retardation.
Even the patient's handwriting changes.
The person's face becomes like a mask. Dramatic changes occur in the psyche. They can be completely different: they manifest themselves both in the form of constant apathy, and, on the contrary, turn into complacent euphoria. Hence the mood swings that occur in the patient - from laughter for no reason to crying.
In addition to these manifestations, drinking water with manganese can lead to other health problems:
- the appearance of an allergy to manganese, as well as to other substances;
- the development of urolithiasis;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- liver problems;
- violations of the vegetovascular system;
- lung diseases.
Forms of iron in water
Iron can be found in water in several forms. But for us the following will be important:
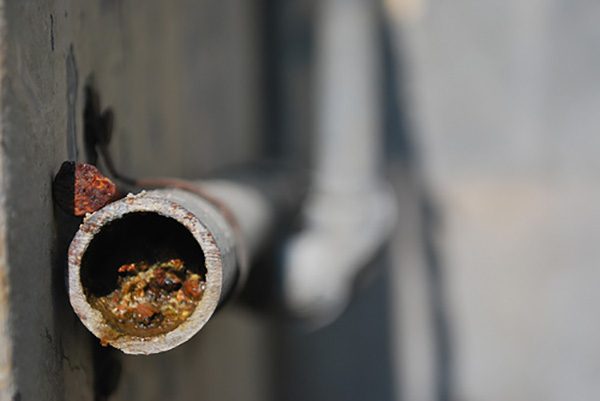
1. Ferrous iron - it is soluble in water. Therefore, water with a high content of ferrous iron is transparent and colorless. But if you pour it into an open container and let it stand for a while, a brown precipitate will fall to the bottom.
2. Trivalent iron - insoluble in water. At its increased concentration, the water has a yellowish color. And when settling, a brown precipitate falls out.
3. Organic iron compounds - compounds of iron with organic molecules. Most often, water containing such compounds has a yellow color, but does not form a precipitate upon settling.
It is worth mentioning another form of iron - the so-called "bacterial iron". Water containing bacterial iron often has a specific iridescent film on the surface and forms a jelly-like deposit in the plumbing system.
If you observe signs of the presence of one of the listed forms of iron in your water, the question immediately arises, how much is the constant consumption of such water dangerous for health?
Chemical disinfection

Methods of chemical disinfection.
Chemical methods provide the most complete degassing.
They are based:
- on the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide compounds;
- on the binding of sulfur molecules to other molecules and their transformation into elements that are less toxic to humans.
Chemical decontamination requires precise dosages of reagents, constant process control and is therefore considered complex. But in some cases, special equipment is not required, it is enough to use filters.
Chlorine cleansing
For degassing 1 mg of molecular hydrogen sulfide, 2.1 ml of chlorine is added. The most commonly used reagent is sodium hypochlorite. The solution is supplied by a special dosing system. As a result of the reaction, colloidal (suspended) sulfur is formed.
To remove it, sediment filters are installed, which work on the principle of coagulation (enlargement of sediment particles). Water treated with chlorine must have a minimum hardness, so it requires additional demineralization.
Cleansing with ozone and hydrogen peroxide

Ozone water purification.
Ozone completely purifies water from bad-smelling gas, from harmful bacteria, metal ions, deodorizes and gives it a fresh taste.Bubbles of air saturated with ozone pass through the liquid, oxidize it and burst on the surface.
For purification from 1 mg of hydrogen sulfide, 1.5-3 mg of ozone is consumed. The production of 2 g of ozone requires 0.1-1.4 kW of electricity. Unused ozone is decomposed at the outlet by an activated carbon filter.
The action of ozone is faster, stronger and safer than chlorine, but the method has the following disadvantages:
- water becomes corrosive, especially when the temperature rises or the pressure in the system decreases;
- The equipment must be placed in a separate ventilated room.
Ozonation costs more than chlorination, although the cost of ozone treatment systems is gradually decreasing due to the use of semiconductors.
Benefits of using hydrogen peroxide:
- the possibility of using at different concentrations, temperatures and acidity;
- good solubility;
- little corrosiveness.
The water is treated with a 30% hydrogen peroxide solution. To neutralize 1 mg of hydrogen sulfide, 3.09 cm³ of solution is needed. Oxidation with peroxide occurs rapidly, resulting in the formation of large yellow associates. The water is filtered through activated carbon, and the smell completely disappears, the amount of dissolved oxygen increases, and with the help of a suspension of iron hydroxide, iron sulfide is formed, which is isolated by settling.
Cleansing with potassium permanganate
Water purification with potassium permanganate.
For the oxidation of 1 mg of sulfide compounds, 6.2 mg of potassium permanganate is needed. This forms a mixture of finely dispersed manganese dioxide, which must also be removed.
If the water is oversaturated with manganese salts, it will take a long time to remove them, therefore, installations with filters with fine manganese-glauconite sand are used. A 1-4% solution of potassium permanganate is added to them in a constant volume and spent manganese accumulates.
During oxidation, it turns into an insoluble hydroxide, which acts as a coagulant and adsorbent. Suspended particles are retained by a double-acting filter.
Sorption disinfection
Of the natural ones, activated charcoal is most often used, because. it has a high ability to absorb and retain H2S molecules, pronounced catalytic properties, and is easy to maintain.
The pores of the sorbent absorb hydrogen sulfide, and the iron in the water precipitates in the form of rust.
The quality of cleaning is affected by:
- material porosity;
- concentration of sulfur compounds;
- the structure of oxides that appear on the surface of coal during the reaction.
Sorption disinfection is used when water is supplied from a well, but at a high level of hydrogen sulfide it is combined with the installation of a pressure degasser.