Production
Fiberboard hardboard is a fairly budget building material, while being thin (due to the “wet” pressing production technology) and durable. In the manufacture of hardboard, wood grinding can occur in several ways:
- thermo-mechanical
- chemical-mechanical
- mechanical.
After grinding, the particles are mixed with special additives, due to which the maximum moisture resistance of the finished material is achieved. After that, the raw material is pressed at high temperature and under high pressure.
There is another method for the manufacture of fiberboard hardboard, when the crushed mass of raw materials is dried in special drying chambers. It is with this method of production that the smoothness of one side of the finished plate is achieved.
Often the front side of the hardboard is varnished. There are also sheets with lamination from a special high-strength film that imitates natural materials such as metal, ceramics, stone, wood, etc.
How to insulate a wall from the inside with your own hands
You can perform internal insulation yourself. To do this, you must follow the technology of work. That is what we will consider next.
Preparatory activities

If you think that the insulation of the inside of the walls begins with the installation of the frame, then you are mistaken.
The first stage of internal insulation includes:
- Drying the surface of the walls.
- Sealing all chips and cracks.
- Surface treatment with antiseptic agents.
- Applying a primer if the insulation is attached to the adhesive.
Performing all of the above actions significantly increases the adhesive properties of the wall.
Mineral wool insulation: frame installation

Mineral wool insulation is performed in the following sequence:
- Cover the walls with waterproofing.
- First, a frame is assembled from a wooden beam. To fasten the bars, use self-tapping screws with a wide thread.
It is best to install wooden frame elements in a vertical position. Thanks to this, moisture that will accumulate under the materials will be able to flow down unhindered. The width between the bars should be slightly less than the mineral wool slabs.
Assembling the pie

When the frame assembly is completed, you will need to:
- Install mineral wool slabs between the bars so that there are no gaps.
- Attach the heat insulator with dowels.
- Stretch the vapor barrier film on top and fix it.
- Stretch the membrane horizontally.
You can additionally seal the joints on the membrane with adhesive tape.
Finishing and ceiling lining

The last stage of mineral wool insulation is sheathing the surface with drywall, clapboard or plywood using self-tapping screws or nails. Fastening of clean material is carried out on the bars of the frame.
Ceiling insulation is performed using the same technology. If it is necessary to insulate an attic or attic from the inside, it is recommended to apply thermal insulation on top of the ceiling. For residential premises, it is better to use a vapor barrier film in 2 layers: 1 layer is under the mineral wool slabs, and 2 is above the insulation.
Use of Styrofoam
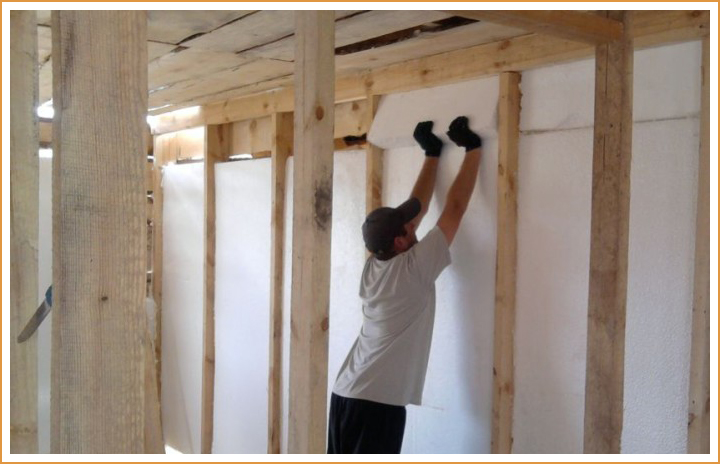
If you want to save time, then you can insulate the walls from the inside with foam. This method of insulation includes the following mandatory steps:
- The surface of the walls must be leveled and primed.
- Further, the walls are treated with an antiseptic.
- When the surface dries, 6 holes are made on the foam board: 4 at the edges, and 2 in the middle. You also need to make a hole in the wall.
- Using a roller, the surface of the sheet is smeared with glue.
- The foam is applied to the wall and held for several seconds.
Gluing foam sheets should be done in a checkerboard pattern.
The final stage
When all foam sheets are glued, it is necessary to seal the seams:
- Narrow seams are sealed with mounting foam.
- Slots from 4 cm are sealed with pieces of foam.
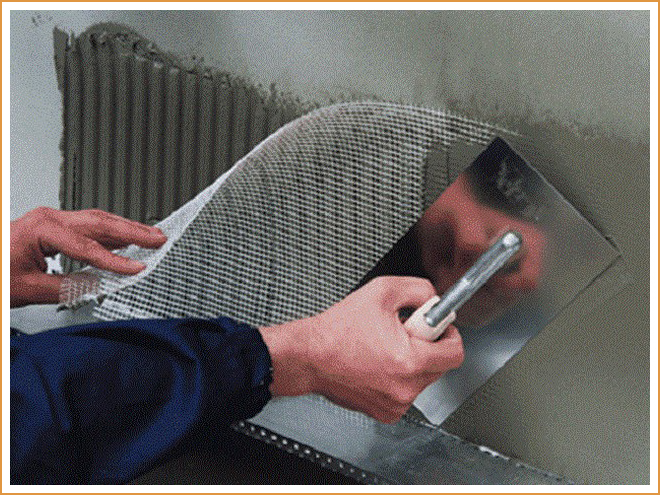
The next step is to attach the reinforcing mesh
The technology of its installation is as follows:
- Styrofoam plates are lubricated with glue.
- The mesh is soaked in glue, and then applied to the foam sheets.
- When the glue dries, do not forget to sand the surface.
- Further walls can be plastered or wallpapered on them.
We hope that after reading this article, you are convinced that the procedure for insulating walls from the inside is not complicated. Even a non-professional builder can cope with this task.
Styrofoam finishing
If almost everyone can handle wallpapering, then plastering can be done by a person who has the necessary knowledge.
For plastering foam sheets, it is recommended to use a special mixture that has refractory properties. Additionally, you can use the mixture to improve the "breathing" of the insulation.
The plastering process occurs in the following sequence:
- After the adhesive has completely dried, the surface must be sanded. By the way, instead of glue for mounting the reinforcing mesh, you can use a primer.
- Then the mixture is applied with a thickness of 0.4-0.5 cm.
- When the layer dries in about a day, grout the walls.
- After that, the surface is re-primed and covered with a finishing layer 0.2-0.3 cm thick.
Plastering the surface is allowed only in dry and warm weather.
Production technology
The feedstock for the production of fiberboard is waste from the woodworking industry: wood chips, sawdust, fire (lignified parts of the stems of spinning plants). The raw material is washed, foreign inclusions are removed from it, then it is dried. The dried material is crushed in special machines (defibrators and refiners) into the smallest particles - fibers. The degree of grinding can be from coarse to fine. Further, the process is different for different production methods.
Feedstock for fiberboard production
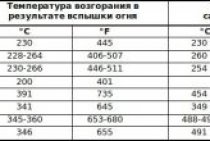
Pressing is carried out under high pressure - 3-5 MPa and high temperature - above 300°C. Due to this, the material is bonded and compacted. Before pressing, additional components are added to the initial material that change the properties of the material - binders (synthetic resins), water repellents, flame retardants, etc.
Forming methods
There are two ways to produce fiberboard - wet and dry pressing. The "wet" method is more environmentally friendly. In wet pressing, fewer binders are used (sometimes without synthetic additives at all), but the material is more expensive, since the process is more energy-intensive. It takes up to 15 minutes to dry one sheet, which limits the productivity of the presses, and therefore increases the price of the material. With this method, the necessary additives, water, are introduced into the crushed material. The slurry enters the dispenser, which spreads it in an even layer on the tape. For faster removal of water, the tape has a mesh structure. After passing through the press, the back side of such fiberboard has an imprint of this fine mesh.
When wet pressed, some grades of fiberboard can be made without the addition of a foreign binder. Under pressure and at high temperature, lignin (a substance that characterizes the stiff walls of plant cells) is released from wood fibers. It is a natural binder. Lignin is found in significant amounts in coniferous wood. But not for all grades of fiberboard, a natural binder is enough. In this case, 4 to 7% synthetic binder is added.

Forming type is easy to distinguish by the back side of the plate
In dry pressing, synthetic resins are usually added to the mass, which bind the fibers.It is this method that makes it possible to obtain fiberboard of great thickness - up to 12-15 mm, some factories can produce pits up to 40 mm thick. The compaction and pressing of the dry mass takes much less time - 3-5 minutes, depending on the class and thickness. The productivity of the press increases significantly. In addition, a smaller amount of additives is put into the dry mass - they are not washed out with water. All this leads to a reduction in the cost of the material. But cheap binders contain formaldehyde, and its content must be controlled, since in large quantities it is harmful to health.
For the production of furniture and interior decoration, material with formaldehyde emission class E0.5 or E1 must be used. This is usually wet pressed fiberboard. You can distinguish fiberboard made by the wet method by the print of the grid on the back of the sheet (see photo above).
Termination Processes
During high-temperature pressing, the particles stick together. The time spent under the press is not always enough, therefore, already formed sheets are transferred to a special chamber, where the material “ripens” at high temperature. The fiberboards are kept here for several hours. During this time, the fibers are sintered, glued together, the material becomes homogeneous and durable.

Wood fiber boards have different thicknesses
The slabs leave the chamber with almost zero humidity and begin to actively absorb moisture from the air. As a result of this process, the edges of the sheets swell. To avoid this disadvantage, the material is transferred to another chamber, where it is brought to normal humidity. And only after that, sheet fiberboard can go on sale or to other machines - for painting, laminating.
What is good is that the technology for the production of fibreboard is plastic. The press can have any shape, which allows you to make not only sheet material, but also figured products. For example, skirting boards or furniture facades.
Causes of moisture
Dew Point Shift Results
In the winter season, with the onset of frost, the walls of our houses freeze through. In a correctly calculated wall thickness, the transition point from minus to plus temperature, it is called the dew point, is located inside the wall and condensation does not occur. That is why they used to build houses with stone walls no less than 80 cm thick. Today, with the use of the latest construction technologies and innovative materials, it has become possible to build houses with thinner walls, but such buildings require the installation of additional heat-insulating structures.
The question arises: from the outside or the inside to carry out insulation?
The issue of exterior finishes disappears when the house is made of timber and does not require exterior finishing. If the house is made of stone, then it will be more competent to make insulation from the facade, but this does not exclude the carrying out of internal work.
There is the only exception - the internal insulation of the walls of an apartment in a multi-storey residential building, where the use of any type of heat-insulating material will not give tangible results.
Materials for thermal insulation
Materials for thermal insulation
As a result, several main conclusions can be drawn:
When installing thermal insulation on the inside of the walls of the house, the dew point inevitably moves to the inner surface of the wall. This will happen even with correct calculations of the thickness of the heat insulator. As a result, the service life of the entire thermal insulation structure is reduced.
The thermal insulation structure must necessarily include a vapor barrier membrane. As a result, it is necessary to solve the issue of normalizing the humidity in the room (increase in the cost of heating and ventilation systems).
Insulation inside the room reduces the volume of rooms.
Since the entire structure is installed inside the house, the issue of human safety becomes the most important
It is important to understand which of the heaters best meets this requirement. Materials from natural raw materials are the best choice
Soft slabs or mineral wool rolls, which have high heat-shielding and sound-proofing properties, are well suited. All materials with good vapor permeability and ability to absorb moisture will lose their functional properties over time.
The use of expanded polystyrene or polystyrene, as materials that practically do not absorb moisture, is more beneficial. In this case, it is necessary to consider the hermetic fit of the plates to each other. The main disadvantage of this option is a completely synthetic material, and they will have to breathe.
Today there is a lot of talk about polyurethane foam, which hardens when applied to the surface, and, of course, gives a strong adhesion to the inner surface of the wall. Condensation does not form, but for the work it is necessary to construct technological formwork. This process is quite long, while the wall does not breathe.
There are many wall heaters, there are plenty to choose from, but the decision must be made correctly. People will live, work and breathe in this house.
What is fiberboard, scope
Fiberboard is an abbreviation for the name "Wood Fibreboard". It is a sheet building or finishing material. It has a relatively low price, it can be of different density - soft, hard and superhard. Sheet thickness - from 2-3 mm to 12-15 mm, some types can be up to 40 mm.

Fibreboards can be of different thicknesses and densities
Sheet fiberboards are distinguished by high density and strength, and have a relatively low price. Thin sheets bend perfectly, which allows them to be used for sheathing curved surfaces. Fiberboard is used in construction, as a sheathing in frame housing construction, for leveling floors and walls. Partitions in railway passenger cars are also made from this material.
Low density fiberboard is used as a soundproofing material. The chaotic arrangement of wood fibers contributes to the fact that the sounds "get stuck" in the material. This is the most inexpensive and easy-to-install type of soundproofing materials. There are more effective ones, but cheaper ones still need to be looked for.
Some types of fiberboards can be used as finishing materials - for finishing walls in rooms with normal humidity. For these purposes, fiberboard is used, one of the sides of the sheet of which is painted, covered with a decorative film, laminated.
These are decorative options.
Another area of application of fiberboard is the production of furniture. Usually this material is used as an auxiliary material - they make the back wall of cabinet furniture, hem the bottom in armchairs and chairs, bottoms in drawers, etc. In general, the scope is extensive. The disadvantage, in fact, is one - without hydrophobic additives, the material behaves poorly at high humidity. It swells, increasing in size. At the same time, the sheet material "goes in waves." When dried, it remains deformed. So in unheated or damp rooms, only certain brands of fiberboard can be used.
Versatility
Due to its universal properties, fiberboard hardboard is used in a wide variety of areas during construction:
- As a heater for roofs and walls in frame-and-frame construction and wooden houses;
- As a floor base for carpet, linoleum, parquet and laminate;
- As a sound and noise insulating material in specialized rooms;
- As the final post-repair finishing of premises;
- As a furniture material, for the manufacture of some parts;
- As a decorative and artistic element in hand-made.
Key words: Production, Versatility, How to distinguish ordinary fiberboard from hardboard hardboard, Hardboard, Properties, Advantages, strength, store, delivery, lumber
This is interesting: Expanded clay for dry floor screed with your own hands: we disassemble thoroughly
Literature
- GOST 4598-86 Wood fiber boards. Specifications
- GOST 8904-2014 Painted hardboard fibreboards. Specifications
- GOST 27935-88 Wood-fibre and chipboards. Terms and Definitions
- GOST 32274-2013 Monostructural wood boards. Specifications
- GOST 32297-2013 Decorative panels for walls based on dry-process fibreboard. Specifications
- GOST 32304-2013 Laminate floor coverings based on dry-process fibreboard. Specifications
- GOST 32687-2014 Dry-process wood-fiber boards lined with films based on thermosetting polymers. Specifications
A few words about the history of chipboard and fiberboard production

 The annual output of chipboard in the world is about 55 million cubic meters, in Russia - about 5 million cubic meters.
The annual output of chipboard in the world is about 55 million cubic meters, in Russia - about 5 million cubic meters.
There is intense competition in the particle board market. The technology of their production is in continuous development. Manufacturers offer both uncoated boards and those with a laminated surface. Many companies provide sawing and edging services for parts.
Fiberboard was first produced back in the 1920s in the USA. However, the first technological patent was registered in Sweden in 1931. Defibrator's fiberboard sheeting equipment is widely used in many countries around the world. Domestic production of this material started in Moscow in 1936. Now the production of fiberboard is one of the most actively developing and successful sectors of the national economy.
The essence and problems of internal insulation
When insulating a house from the inside, you need to take into account some features.
Most experts really believe that it is worth insulating a house inside only in extreme cases, advising insulation from the outside. What is meant in this case by the word "within"? This refers to the direct coating of the walls of rooms with any materials. And if floors, ceilings and some other areas can be easily insulated, it is with the insulation of walls that a lot of problems arise.
The main difficulty is the transition of the wall surface to the cold zone. Usually, if there is no thermal insulation, the warm air from the room passes through the walls, heating them. If insulation is laid from the inside, air masses will collide with them, not being able to go outside. All walls in this case remain cold, and there is a risk of cracks.
For this reason alone, it is worth considering whether it is necessary to insulate a private house from the inside instead of thermal insulation from the outside. It is logical: why waste money and your strength, if as a result you can get only cracked walls and a cold room? But this is only part of the difficulty. In addition to damage to the insulated surfaces, there is condensate and other troubles that will appear after a minimum time if at least a small mistake is made during the insulation work.
How to insulate your home
Independent wall insulation
If it is decided to abandon facade insulation, then how to insulate the house from the inside to avoid condensation? After all, it is he who leads to the appearance of fungal formations, the destruction of thermal insulation materials.Each owner needs the entire thermal insulation internal structure to work efficiently and functionally. There are several widely used home insulation technologies.
Insulation of a log or timber house has its own characteristics. The thermal conductivity of wood in comparison with stone is, of course, lower, and wood retains heat well, however, when walls are insulated from the inside, moisture can form between the inner surface of the wall and the surface of the insulation. To avoid this, an air gap is made to blow wood and insulation. Technically, the problem is solved using a frame crate made of wood with a frame width equal to the width of the insulation boards. The crate is mounted at a distance of several centimeters from the wall to provide a ventilation effect.
From the side of the wall, a windproof membrane is pulled onto the frame, which performs a dual function: it protects the air gap from overlapping with the fibers of the heat insulator and limits excess air movement inside the insulation. In this case, it is more expedient to insulate the walls from the inside with natural environmentally friendly materials. There is a wide selection of mineral wool insulation, in Russia the most famous manufacturers are: URSA, ISOVER, ROCKWOOL, KNAUF and others. From the side of the room, the insulation is hermetically covered with a material that provides protection against the penetration of steam into the inner layers of the heat insulator.
The technology for insulating concrete or stone walls is similar to the previous design, but in this case it is necessary to provide for a larger number of technological openings for air to enter. Much more condensate will appear than in the first case, and the air gap must be wide enough for intensive ventilation. In fact, it is necessary to build an additional internal wall.
When carrying out thermal insulation work indoors, it must be understood that natural physical processes will affect the entire structure. This work requires a competent professional solution.
Myth 10. All frame houses are cheap.
The cost of building a frame house ranges from $150 to $1200/m². Such a wide range is due to various technologies and the possibility for the customer to choose the degree of readiness of the building: from purchasing a set of houses for self-construction to turnkey construction. Within the same technology, cost fluctuations are possible depending on the materials used. For example, a house with a frame made of glued laminated timber will cost more than a house made of solid wood. The material of insulation and cladding, etc. matters. Houses with insulation from expanded polystyrene are cheaper than from basalt wool, cladding from OSB is cheaper than from DSP.
With additional insulation, the value of the house will increase. Some technologies use imported energy-efficient windows and doors, especially reliable membranes, which also increases the cost of construction. But in general, in terms of material consumption and labor intensity, frame walls are among the most economical. This is due to the smaller volume of the foundation and walls, as well as the lower price of insulation compared to massive materials.
The cost of 1 m² of a standard frame wall with a thickness of 20 cm is 1.3 times cheaper than a wall made of timber, 1.7 times cheaper than a wall made of foam concrete blocks and 2.2 times cheaper than a wall made of bricks (with the same energy-saving capacity and different wall thicknesses required for its achievements). But too low a price should alert you: perhaps the wood of the frame will not be dry enough, the sheathing will be of the minimum thickness, etc. You should always make sure of the quality of the structures and materials for assembling the house. A reliable indicator of quality is a certificate of technology compliance with European standards (construction, energy-saving, environmental), as well as a guarantee provided by the company (for the highest quality frame houses it is 30 years). One of the advantages of frame construction is the transparency of investments and the accuracy of estimates.The cost of a house set is determined individually after the development of the project and does not change further.
Density, weight, sheet thickness
The technology for the production of wood-fiber boards allows you to make them of different densities. Depending on the density, they have different technical characteristics and scope. There are such types of fiberboard:
-
low density. They are also called soft, they can be designated with the help of the attached letter “M” - DVP-M. Pretty loose material with a density of 200-350 kg/m³. Sheet thickness can be 8, 12, 16, 25 mm. If desired, you can find up to 40 mm. They are usually used for soundproofing or as finishing / cladding in places that are not subject to stress.
- Medium density - up to 850 kg / m³, sheet thickness can be 8, 12, 16, 25 mm. According to the classification, they also pass as soft.
- Semi-solid - from 860 to 900 kg / m³, sheet thickness 6, 8, 12 mm.
- Solid (DVP T) - 950 kg / m³, sheet thickness 2.5, 3.2, 4.5 and 6 mm.
- Superhard (DVP-ST) - 960-1000 kg / m³, can be 2.5, 3.2, 4.5 and 6 mm thick.
Hard and superhard grades are used where resistance to mechanical stress is important. In household construction and decoration of houses / apartments, fiberboard-T is placed on the floor, walls can be sheathed with them.
Types of solid boards
For all that, general-purpose solid fibreboards come in several types - with different front and back sides. According to GOST, solid fiberboards have the following marking:
- T - solid slabs with an unfinished front surface. Often referred to as "technical" fiberboard. It is used for works in which appearance is not important.
-
T-P - solid slabs with a tinted front layer. This is the so-called hardboard. It is used in the furniture industry for back walls in cabinets, tables, etc.
- T-S - solid boards with a front layer of finely dispersed wood pulp. One side of the sheet has the same color, but is smooth, like varnished. It can be used for sheathing frame buildings from the inside. Requires minimal finishing work. Wallpaper can be glued to such a surface of a rhinestone, but it will be very inconvenient to remove them. But the putty does not fit well on the smoothed surface - it rolls off.
- T-SP - solid boards with a tinted front layer of finely ground wood pulp. It can be used as a finishing finishing material.
Solid fiberboard grades can be in two classes - A and B. They are distinguished by quality. As you can see, even in the same class there are different materials. With the same (or almost the same) technical characteristics, they have different applications.
Subspecies of superhard fiber boards
Superhard fiberboards are rarely used in domestic construction and repair - the price is too high, and high density and rigidity may not be in demand. Sometimes excessive rigidity can be uncomfortable.
According to the standard, there are two types of such material:
- ST - "construction" brand, not very attractive in appearance;
-
ST-S - with a smooth face layer - finely ground wood pulp is compacted to a very smooth state.
There are practically no laminated or decorative types - material that is too heavy and hard for finishing is also not needed.
Names depending on the density
Also, fiberboards have different names depending on the density. Usually this is a calque (transliteration) of English / international names. Although, under the same name, in other countries, a different material is often meant.
-
LDF - from English low density fiberboard - LDF. Translated - low-density fiberboard. In fact, this is the name of the material of medium density, simply having characteristics at the lower boundary of the zone. It has nothing to do with softwood boards.
- MDF - from English medium density fiberboard - MDF. In translation - medium-density fibreboard. If we talk about standards, then this material corresponds to the GOST definitions of medium density fiberboard.
-
HDF - hight density fiberboard - HDF. According to the characteristics, the DVP-T brand (solid) can be put in line.
As you can see, there is no clear distinction. Another confusion is added by the incorrect use of names. In general, each time it is necessary to clarify what exactly the speaker means by this or that term.