Description of main components
Careful selection of the main components of the cement mortar will allow you to prepare a high-quality mass that will ensure a solid brick laying. For this you need:
- Water for mixing requires clean, free of impurities, dirt and foreign matter. It is ideal to draw it from the well. The temperature of the liquid depends on the season when it is required to prepare the cement mass: cold water is suitable in summer, in winter it needs additional heating.
- Sand is an integral component of the cement composition. The absence of traces of clay and other impurities is a prerequisite, otherwise the period of weathering of the mortar from the masonry will accelerate.
- The main component that determines the properties of the future composition is cement. In order to correctly prepare the mortar and maintain the correct proportions, the brand of the cement mixture is of key importance. There is a pattern: the higher the brand of the binder component, the smaller the volume is needed to prepare the solution. If you want to prepare a composition of a darker shade, just add graphite or soot to it or purchase a higher brand of cement. At the same time, it is imperative to follow the compliance of the established proportions!
- Detergents will help prepare the cement mass without purchasing expensive plasticizers. Shampoo, washing powder or dishwashing liquid are suitable for this role. The exception is a cleaning agent due to the likelihood of cracks in the brickwork.
Places of its production
They extract sand from a river, from a ravine or from a quarry. There is also artificial (quartz) sand. All these types of sand differ in their characteristics. The sand extracted from the river has few impurities and a fairly uniform structure. This is due to the fact that water naturally polishes each grain of sand, and they acquire an almost perfect smooth, rounded surface and an attractive appearance. However, the too smooth surface of the river sand particles adversely affects the ability of the particles to bind to other components of the solution, and this affects its uniformity. Washing and sifting river sand is not necessary. The cost of river sand is quite high, since it is extracted in a rather costly way from the bottom of the rivers. This sand is mainly used for decorative masonry, for cladding, for the preparation of plaster mixes, cement screeds, in the production of concrete, asphalt concrete and bricks, as a drainage, as a component of grouts and paints. It is usually not used for pouring foundations and ordinary masonry. River sand is fine, medium and coarse-grained. Medium-grained river sand does not shrink, making it ideal for masonry and plaster work. Sand can also be mined from the bottom of the sea, it is similar in characteristics and scope to river sand.
The sand extracted from the quarry needs to be washed and screened, because it has impurities (stone chips, clay, etc.) and is heterogeneous in size of grains of sand. The edges of the grains of sand are sharp, which has a positive effect on the plasticity of the solution due to its good ability to adhere to other components of the mixture. Advantages of quarry sand: it is cheaper than river sand, and the quality of the adhesion of its particles is higher. Clay makes up a small part of the impurities, and organic particles are absent. Raw quarry sand is used for foundations, rough masonry and masonry of load-bearing walls. Alluvial quarry sand can be used for the manufacture of bricks, plasters, cement screeds, in finishing work, in the manufacture of concrete, for pouring foundations.
Ravine sand is also very common and is mined in an open pit. The depth of its occurrence is quite small - from several tens of centimeters to several tens of meters.The grains of sand have a rough and angular surface, which has a positive effect on the ability to grip. There are also impurities, so it needs to be purified. Of the impurities in the ravine sand, most of all are clay and organic compounds. This gives the ravine sand mortar good plasticity, which is why it is this sand that is most often used for brickwork. Its cost is lower than that of the river.
Artificial, or quartz, sand is sand that is not a creation of nature, but obtained as a result of mechanical grinding of rocks that have quartz in their composition. Such sand has a homogeneous structure, has no impurities. Thus, when deciding which sand to use for laying bricks, you first need to decide what type of masonry will be produced, and then decide which type of sand will be easier and cheaper to acquire and deliver.
How to choose
The mortar for masonry plays a major role in giving it the necessary properties and affects the convenience of the work performed, therefore, there is a need to carefully combine all the components included in the composition so as not to get a negative result.
So, why is sand needed in the solution?
Before you know which sand is best suited, you need to determine what role it plays in the production of the solution.
It is the main filler, which is extremely important for the composition
Its functions are as follows:
- correct minor surface irregularities in bricks;
- form the volume of the solution;
- smooth out shrinkage;
- give a certain color.
First you need the sand to be as clean as possible, since clay affects the quality of the solution - it does not let water through, which can lead to lumps. However, other types of pollution are just as harmful.
If at least some foreign particles are present in the sand, the solution may lose its uniformity. At the same time, its plasticity will decrease, which will complicate the alignment of the rows during the laying of bricks. For this reason, sand is best sieved.
When laying, medium sand is well suited, and for rough work it is permissible to use a larger version. And in the case of decorative wall decoration, it is optimal to use the finest sand.
Properties and features
Sand has the following characteristics:
- homogeneous composition;
- acceptable size of sand grains in diameter, mm:
- small - 0.5-1.5;
- medium - 1.5-2.5;
- large - 2.5-3.5;
- high bearing capacity;
- absorption and retention of moisture;
- availability;
- ease of transportation and relative cheapness.

Depending on the origin and methods of extraction, the following types of this natural building material are distinguished:
- River. Has a homogeneous structure, does not contain impurities. However, the expensive method of extraction affects the price. Also, the particles polished with water weakly bind to the components of the solution, as a result of which its plasticity decreases.
- Career. It is located under the ground at a shallow depth, at a cost cheaper than the river one. Elementary particles are characterized by a rough surface and sharp edges, which contributes to a good bond with the constituents of the mixture. The disadvantages include impurities that are heterogeneous in size grains of sand.
- Ravine. Mined by an open method, otherwise similar to quarry sand.
To improve the quality of crude raw materials, it is removed from unnecessary particles by washing with water. Thus, an alluvial option appears. Sifting through a sieve is another way to get rid of impurities. The use of special calibrated fixtures helps to achieve homogeneity of the substance.
Career
The name clearly indicates the origin of the sand. Clay and stones are found in it, so quarry material is used to a limited extent: for site planning, pouring under concrete screeds or foundations.
To improve the properties, quarry sand is washed with water right at the place of extraction, freeing it from dust particles and clay. This is how alluvial (washed) sand is obtained. It is suitable for plaster and masonry mortars. In addition, sieving can be used to remove clay.
An important practical conclusion: if you are offered to buy quarry (ravine) sand, do not forget to clarify whether it has been cleaned (washed, screened) or not.
Areas of application for washed (sifted) quarry sand:
- cement screed, masonry and plaster mortars;
- Finishing work;
- brick production;
- foundation device;
- concrete preparation.
river sand
This building material is mined by a dredger from the bottom of the river. River sand contains no clay particles and very few stones. This allows you to use it without restrictions for concrete work.
It is very valuable that river sand of medium size (1.8-2.2 mm) practically does not shrink. Therefore, it is optimally suited for masonry and plastering.
Quarry sand is more difficult to use in this capacity. In the solution, it sits on the bottom and has to be periodically mixed.
Areas of application for river sand:
- concrete production;
- brick production;
- masonry work and cement screed;
- preparation of asphalt concrete;
- drainage device;
- filler for paints and grouts.
Sea sand is similar in properties to river sand. It is also highly valued in the construction industry for its high purity and uniform particle size distribution.
Quartz sand
This material is obtained as a result of mechanical crushing of quartz-containing rocks. It is homogeneous in structure, chemically inert and pure.
The main field of application of this type of sand is the building materials industry. It goes into dry building mixtures, sand-lime bricks, blocks and concrete, and is used to prepare grinding compounds. Landscaping, expensive interior and facade plasters also cannot do without quartz sand.
It is impossible to unambiguously answer the question of which sand is better, since each material is designed for certain types of work.
Nevertheless, the main conclusions are already clear:
- for brick and large-block masonry, it is better to take river sand. If you mix it with a small amount of unwashed quarry sand, the solution will become more plastic (due to clay particles);
- coarse or medium river sand is better suited for concrete (you can add a little fine washed quarry sand to it);
- for plaster, washed quarry sand with a small addition of river sand or without it is better.
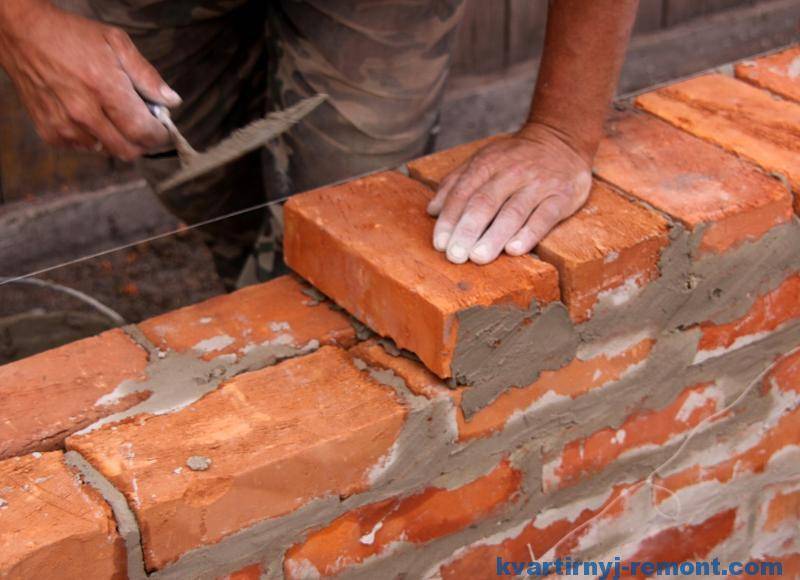
Preparation of mortar for laying bricks
The dry matter and water are mixed and mixed well.
lime mortars

Dry ingredients are thoroughly mixed, and then only water is added. After adding water, everything is mixed well, the masonry mixture at the exit should not contain lumps and impurities.
The components for the solution are taken in proportions: 1 part lime, 2-5 parts sand.
cement mortars
In cement mortar, the main components are cement and sand. The proportions of the ingredients depend on the brand of cement. For example: 1 part of cement and 3-6 parts of sand.
Mix dry ingredients with water until a single mass is formed. First, knead the dry ingredients, and only then add water. But this method is not very good, since even when using different grades of concrete, the solution comes out inactive and rigid.
Cement-lime mortar
The solution consists of lime and cement. The principle of preparing the solution:
- Lime mass (slaked lime), diluted with water to a thick state, then filtered;
- Dry cement and sand are combined;
- Dry components are diluted with lime mortar and mixed.
Simple mortar
A conventional mortar is made from a binder and sand. Sometimes clay is taken as an astringent, but this solution is used for highly specialized work.
Cement - sand mixture is prepared 1: 3. We mix all the dry ingredients, then gradually pour water. After adding water, the mixture is stirred.
Complex mortar
The consistency of the solution should not be liquid, like water.
A complex mixture of a solution is considered to be a mixture in which several components and a binder are involved. For example: cement-lime-clay or cement-lime.
When adding clay, the solution does not fall apart, it fits neatly and easily.
For brick laying of facade walls, plasticizers are added to the mortar. Such a solution is very economical, it is applied to the surface in an even layer.
Experts recommend preparing such a solution, but it will take a little longer to prepare.
The ratio of ingredients
To prepare the correct solution, you need to calculate the amount of ingredients. For a solution, sand is taken in the middle fraction, the brand of the solution may be different, but it is the sand fraction that affects the proportions. For instance:
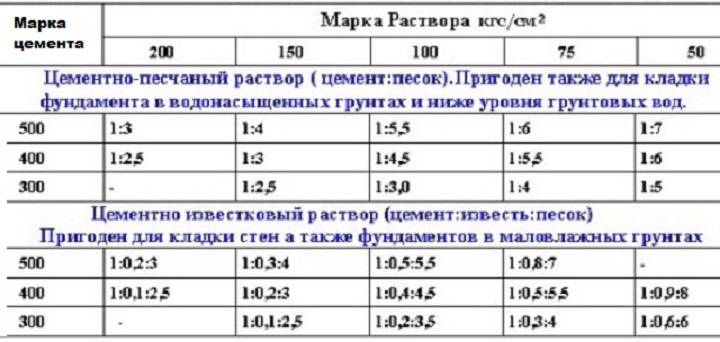
- We use cement M-500, the proportions will be as follows: 1 part of cement for 2/10 lime take 3 parts of sand;
- We use cement grade 400, the proportions will be as follows: 1 part of cement for 1-3/10 parts of lime for 2.5-4 parts of sand;
- We use cement grade 300, 1 part of cement is taken for 2/10 lime for 3.5 sand.
All components of the solution must be mixed well.
This example is for a cement-limestone mixture and for a cement-sand mixture.
Solution proportions:
- When using cement grade 500, take 1 part of cement to 3 parts of sand;
- for cement grade 400, take 1 part of cement to 2.5 parts of sand.
Categories of sand as a building material
This building material is usually divided into the following categories:
 Diagram of deep sea sand mining.
Diagram of deep sea sand mining.
- Ravine. This material is mined in an open way without the formation of a quarry. Usually the sizes of elementary particles range from 0.15 to 3 mm. Their surface is rough, and the shape is angular. Advantage: the solution with the use of such sand becomes very strong. Disadvantage: contains a lot of impurities.
- River. It is considered the most profitable, since it is mined from the bottom of the river and does not require cleaning. Sand grains can be of different sizes. Typically, such sand is used for laying facing bricks, but can also be used as a filler for concrete production. In addition, it is customary to include it in the composition of asphalt mixtures when laying roads, as well as in the formation of drainage and as a filler for dyes and grouts.
- Career. This is sand that lies underground, but at a shallow depth from the surface, so its extraction requires the formation of a quarry as a way to develop a mineral deposit.
In addition, there is a classification according to the size of the grains of sand. Distinguish:
- small - up to 0.2 cm;
- medium - from 0.2 to 0.28 cm;
- large - from 0.29 cm and more.
Physical and mechanical characteristics
Volume weight
It shows the mass of 1 m3 of sand in its natural state (wet, with all impurities). On average, the volumetric weight of this material is from 1500 to 1800 kg.
The composition of building sand is evaluated according to the following parameters:
- Granulometric;
- Mineral;
- Chemical.
Granulometric shows the percentage of grains of different sizes. To determine it, the sand is sieved through calibrated sieves (from 0.16 mm to 10 mm).
A sieve with a hole size of 5 and 10 mm reveals gravel granules. GOST allows the presence of grains 1 cm in size. At the same time, their number should be no more than 0.5% of the total mass of sand.
Granules larger than 5 mm are normalized in this way:
- The maximum content is up to 10% in natural;
- up to 15% in crushed;
- up to 5% in enriched sand.
Mineral composition
According to the content of minerals, sands are divided into quartz, dolomite, feldspar and limestone. Quartz sand is the most valuable for construction, since other types are not strong enough and unstable to chemical attack.
Chemical composition
It plays an important role in determining the suitability of bulk material in various areas of construction. Red, yellow, and orange shades indicate the presence of oxidized metals. Green and blue colors are characteristic of river sand, which contains aluminum salts.
Properties and origin
So what is the best sand to use? It is impossible to give a universal answer to this question, since goals and situations are very different. Most often, river or quarry is used, which is extracted from sources corresponding to the name, with medium-sized particles.
River in its structure is more homogeneous and much cleaner, because all its fractions are purified by water to almost perfect smoothness, which, in turn, enhances the beauty of its appearance. However, such a chic appearance can reduce adhesion - the ability of grains of sand to adhere to cement to form a monolithic mortar. The career option does not have a similar drawback and at the same time it costs an order of magnitude cheaper, but it needs washing and screening.
Therefore, for the construction of load-bearing walls and the production of rough work, processed quarry-type material is best suited, and for decorative cladding, river material is needed, as it looks better.
That's all, my dear readers, until we meet again on our construction portal. Visit our website, because only here you can find out a huge amount of useful information related to construction, which will be useful not only to you, but also to all your friends and acquaintances.
What is lime mortar
In lime milk, which must be filtered through a sieve, sifted fine dry sand is added, and then everything is mixed well. If necessary, you can add water in small portions.
In this case, it is imperative to observe the exact proportions and monitor the uniformity of the composition itself. For strength, cement must be added to such a solution. In some situations, for example, when building stoves or fireplaces, it may be necessary to make a cement-clay composition.
In this case, it is better to use fine material so that the strength and reliability of the masonry is higher. In principle, the entire production procedure differs from the lime version only in that lime is replaced by clay
Therefore, it is very important to choose this component correctly and do everything using the manual for the application of this technology. In this case, the clay must have high plasticity and not have lumps, as well as other foreign substances.
What sand is better to choose for laying bricks
Each type of sand, depending on its characteristics, has its own purpose and can be used in any range of construction from laying the foundation to finishing. The table provides information on how to choose the material and for what work it is better to use:
| Type of sand | Application methods |
|---|---|
| Quarry and ravine | Draft masonry |
| Foundation pouring | |
| Create load-bearing walls | |
| River | Facing |
| decorative masonry |
Criteria for the material that is needed for brickwork:

- Uniformity. Sand granules must be the same in size, because the viscosity and stability of the solution under loads depend on this.
- Purity. The quality of the mixture deteriorates from impurities, its plasticity decreases. Because of this, the alignment of the brick row becomes more difficult.
- Medium sand. A look with larger particles can be used in rough masonry, and for finishing work - a sample with small fractions.
How to calculate volume
In order to plan the brickwork budget in advance, it is advisable to calculate how much and what will be required. The main guidelines in this case are the volume of the walls being constructed and the type of mortar used, which affects the proportions of the ingredients.
Calculation of the volume of brickwork
Let's say you need to build a simple building, where the walls are 700 cm long, with a ceiling height of 300 cm. There is one opening in the wall for doors 210x130 cm, and a pair of windows 180x120 cm. For the wall thickness, you can take 2.5 bricks (64 cm). To calculate the volume of masonry, the number of walls is multiplied by their height and thickness. After rounding, it turns out 54 m3. The volume of door and window openings (4.5 m3) is subtracted from the result obtained. The result is 49.5 m3 directly on the walls, free areas are not taken into account here.
Mixture calculation
To determine how much the finished mixture will require, you need to know how much mortar per 1 m3 of masonry. The consumption of mortar per masonry cube is usually in the range of 20-30%. For the calculation, we select the average indicator of 0.25, which is multiplied by the number of the total volume (49.5). As a result, we obtain 12.4 m3 of solution. It is also necessary to calculate how much cement is required, since it is the most expensive component. As you know, each brand of mortar has its own ratio between sand and cement. If the proportion of sand and cement is 1:4, then it is necessary to purchase cement in the amount of 2.5 m3. Focusing on the average density of this material (1300 kg / m3), it is easy to calculate its weight (3250 kg).
At the last stage, the exact number of bags is calculated. Usually cement is packaged in 50 kg, so 65 bags are required. They try to buy building materials with some margin, so it's better to take 66-67 bags.
Helpful information
Masonry methods
Brick is laid according to special rules so that the building structure is monolithic and durable.
All dosages in the manufacture of masonry mixture must be observed exactly.
Water consumption:
- Concrete grade 100, take 1 part of cement from 1/2 to 7/10 parts of water;
- Cement-sand mortar. 8/10 parts of water are used on a part of cement.
- Mark M100 - 300-250 kg per m3;
- M150 - 400-330 kg per m3;
- M200 - 490-410 kg per m3;
- M300 - 600-510 kg per m3.
Solution mobility
The mobility of the solution is an important characteristic. This value depends on what ingredients are mixed into the solution.
To check the mobility of the solution, a cone is used, the angle of which is 30 degrees, the height is 15 cm and the weight is 300 grams. Immerse the cone in the prepared solution. The number of centimeters the cone plunged is the number showing the mobility of the train.
The mortar mixture is considered the basis for the construction of walls made of bricks and other building materials. Whatever the solution, it always includes fine aggregate, usually sand, less often clay.
Sand can be considered an indispensable component for brickwork, and there are reasons for this, which lie in the properties of the material. It is relatively inert, homogeneous in structure, has a fine fraction and the required specific gravity. In addition, the considered natural material is well wetted by water, has a significant bearing capacity, is inexpensive and affordable. There are several main types of sand in nature, and all of them are used to prepare mortars and concrete mixes. In order to figure out which sand is better for laying river or quarry bricks, let's deal with its subspecies.
Quarry sand usually lies at a shallow depth from the surface of the earth, is mined using bucket loaders or excavators. The rock consists of small particles of quartz with impurities of clay and various minerals. This type of sand is used for laying walls or building a foundation, but before preparing a mortar or concrete, it is recommended to clean it from foreign impurities by washing or sifting.Quarry sand is also used for backfilling the construction site and leveling access roads.
Ravine sand is considered another equally common type of raw material; it is also mined in an open way. The particle size of this raw material usually ranges from 0.3 to 3 millimeters, it is rough in its structure, which improves adhesion to the brick surface. The value of the rock is reduced due to the presence of various impurities in its composition, but the admixture of clay has almost no effect in the case of using ravine sand for laying brick walls. If this sand is cleaned of foreign impurities, then it can be successfully used for the preparation of most mortars and concrete.
River sand is considered the purest of all the considered raw materials for solutions. It is extracted from the river bottom and used for the preparation of all masonry mortars, concretes and other purposes. This natural material does not need additional purification. River sand can be divided into fractions:
- from 3 to 5 millimeters - large;
- from 2 to 2.9 millimeters - medium;
- less than 2 millimeters - small.
It is believed that sand of medium fraction, river or quarry washed and sifted, is best suited for bricklaying.