barometric formula. Boltzmann distribution.
At
derivation of the basic equation
molecular kinetic theory of gases
and Maxwellian distribution of molecules
the speed was assumed to be
that external forces do not act on molecules
gas, so the molecules are uniformly
distributed by volume. But molecules
of any gas are in potential
the gravitational field of the earth. Gravity, s
one side, and thermal motion
molecules, on the other hand, lead the gas to
some steady state
at which the gas pressure with height
decreases.
Let's derive
the law of change in pressure with height,
assuming that the mass of all
molecules is the same, the gravitational field
homogeneous and the temperature is constant.
Fig.1
If
atmospheric pressure at altitude h is
p (Fig. 1), then at height h + dh it is equal to p + dp
(for dh>0 dp2:
where
ρ is the gas density at height h (dh is so
little that when changing the height in this
interval, the gas density can be considered
constant). Means,
(1)
Knowing
ideal gas equation of state
pV=(m/M) RT (m is the mass of gas, M is the molar mass
gas), we find that
Substituting
is the expression in (1), we get
or
WITH
height change from h1 before
h2 pressure
changes from r1 before
R2 (rice.
67), i.e.
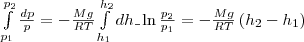
or
(2)
Expression
(2) calledbarometric
formula.
It allows you to calculate the atmospheric
pressure depending on altitude or,
measuring pressure, find height: Since
heights are considered relative to the level
seas where the pressure is considered normal,
then expression (2) can be represented
as
(3)
where
p is the pressure at altitude h.
device
to determine the height above the ground
surface is calledaltimeter (oraltimeter).
His work is based on the application
formulas (3). From this formula it follows that
the heavier the gas, the higher the pressure
decreases the faster.
barometric
formula (3) can be transformed if
use the formula p=nkT:
where
n is the concentration of molecules at height h,
n-
the same, at height h=0. Since M=mNA (NA –
Avogadro constant, m -
mass of one molecule), a R=kNA,
then
(4)
where
mgh=P
is the potential energy of the molecule in
gravitational field, i.e.
(5)
Expression
(5) calleddistribution
Boltzmann for
external potential field. Out of him
It can be seen that at constant temperature
the density of the gas is greater where it is less
potential energy of its molecules.
If
particles are in a state of chaos
thermal motion and have the same
mass and , then the Boltzmann distribution
(5) applicable in any external potential
field, and not just in the field of gravity.
How is the efficiency of a gas turbine determined?
Here are a couple of simple formulas to show what the efficiency of a gas turbine plant is:
Turbine internal power:
Nt = Gex * Lt, where Lt is the operation of the turbine, Gex is the flow rate of exhaust gases;
GTU internal power:
Ni gtu \u003d Nt - Nk, where Nk is the internal power of the air compressor;
GTU effective power:
Nef \u003d Ni gtu * Efficiency mech, efficiency mech - efficiency associated with mechanical losses in bearings, can be taken 0.99
Electric power:
Nel \u003d Ne * Eg efficiency, where efficiency eg is the efficiency associated with losses in the electric generator, we can take 0.985
Available heat of fuel:
Qsp = Gtop * Qrn, where Gref - fuel consumption, Qrn - the lowest working calorific value of the fuel
Absolute electrical efficiency of a gas turbine plant:
Efficiency \u003d Nel / Q dist
combined cycle CHP
The CCGT efficiency is higher than that of the GTU, since the combined-cycle plant uses the heat from the exhaust gases of the GTU. A waste heat boiler is installed behind the gas turbine, in which heat from the exhaust gases of the gas turbine is transferred to the working fluid (feed water), the generated steam is sent to the steam turbine to generate electricity and heat.
CCGT efficiency is usually represented by the ratio:
PGU efficiency \u003d GTU efficiency * B + (1-GTU efficiency * B) * PSU efficiency
B is the degree of binarity of the cycle
Efficiency PSU - Efficiency of a steam power plant
B = Qks/(Qks+Qku)
Qks is the heat of fuel burned in the combustion chamber of a gas turbine
Qku - heat of additional fuel burned in the waste heat boiler
At the same time, it is noted that if Qku = 0, then B = 1, i.e., the installation is completely binary.
Influence of the degree of binarity on the CCGT efficiency
| B | GTU efficiency | PSU efficiency | CCGT efficiency |
| 1 | 0,32 | 0,3 | 0,524 |
| 1 | 0,36 | 0,32 | 0,565 |
| 1 | 0,36 | 0,36 | 0,590 |
| 1 | 0,38 | 0,38 | 0,612 |
| 0,3 | 0,32 | 0,41 | 0,47 |
| 0,4 | 0,32 | 0,41 | 0,486 |
| 0,3 | 0,36 | 0,41 | 0,474 |
| 0,4 | 0,36 | 0,41 | 0,495 |
| 0,3 | 0,36 | 0,45 | 0,51 |
| 0,4 | 0,36 | 0,45 | 0,529 |
Let's sequentially present tables with the characteristics of the efficiency of gas turbines and after them the indicators of CCGT with these gas engines, and compare the efficiency of an individual gas turbine and the efficiency of CCGT.