What should be the operating pressure in the heating system
But to answer this question in a nutshell is quite simple. A lot depends on which house you live in. For example, for an autonomous or apartment, 0.7-1.5 atm is often considered normal. But again, these are approximate figures, since one boiler is designed to operate in a wider range, for example, 0.5-2.0 atm, and the other in a smaller one. This must be seen in the passport of your boiler. If there is none, stick to the golden mean - 1.5 atm. The situation is quite different in those houses that are connected to central heating. In this case, it is necessary to be guided by the number of storeys. In 9-story buildings, the ideal pressure is 5-7 atm, and in high-rise buildings - 7-10 atm. As for the pressure under which the carrier is supplied to buildings, most often it is 12 atm. You can reduce the pressure with the help of pressure regulators, and increase it by installing a circulation pump. The latter option is extremely relevant for the upper floors of high-rise buildings.
The advantage of using automatic balancing valves is also the possibility of dividing the system into separate zones that do not depend on pressure, and the implementation of their stage-by-stage commissioning. Among the advantages of automatic balancing valves are easier and faster system setup, fewer valves, and minimal system maintenance. Modern automatic balance valves are characterized by high reliability and improved control characteristics. Some of them are modular in design, meaning they can be upgraded or extended in functionality.
Where is the return
In short, the heating circuit consists of several important elements: a heating boiler, batteries and an expansion tank. In order for heat to flow through the radiators, a coolant is needed: water or antifreeze. With proper construction of the circuit, the coolant is heated in the boiler, rises through the pipes, increasing its volume, and all the excess enters the expansion tank.
Based on the fact that the batteries are filled with liquid, hot water displaces cold water, which, in turn, enters the boiler again for subsequent heating. Gradually, the degree of water increases and reaches the desired temperature. The circulation of the coolant in this case can be natural or gravitational, carried out using pumps.
Based on this, the return can be considered a coolant that has passed the entire circuit, giving off heat, and already cooled, it again entered the boiler for subsequent heating.
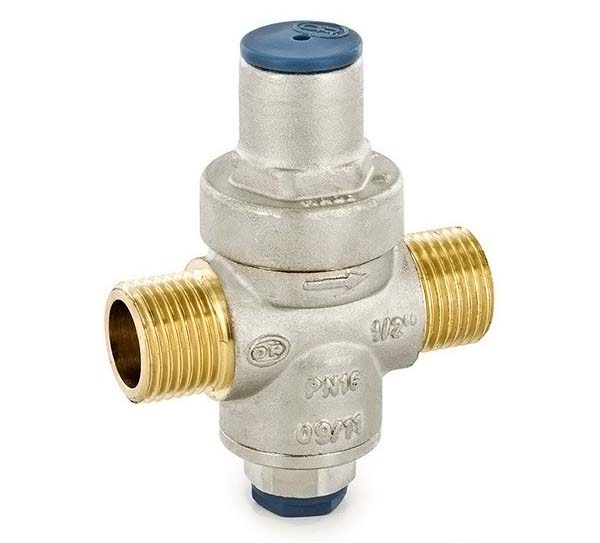
pressure regulator
The operation of the batteries and the pump is disrupted due to high or low pressure levels. Correct control in the heating system will help to avoid this negative factor. The pressure in the system plays a significant role, it ensures that water enters the pipes and radiators. Heat loss will be reduced if the pressure is standard and maintained. This is where water pressure regulators come in handy. Their mission is, first of all, to protect the system from too much pressure. The principle of operation of this device is based on the fact that the valve of the heating system, located in the regulator, works as a force equalizer. From the type of pressure, regulators are classified into: static, dynamic. It is necessary to choose a pressure regulator based on throughput. This is the ability to pass the required volume of coolant, in the presence of the necessary constant pressure drop.
Operating pressure in the heating system
The working pressure is considered to be the value of which ensures the optimal operation of all heating equipment (including the heating source, pump, expansion tank).In this case, it is taken equal to the sum of pressures:
- static - created by a column of water in the system (in the calculations, the ratio is taken: 1 atmosphere (0.1 MPa) per 10 meters);
- dynamic - due to the operation of the circulation pump and the convective movement of the coolant when it is heated.
It is clear that in different heating schemes the value of the working pressure will be different. So, if natural circulation of the coolant is provided for the heat supply of the house (applicable to individual low-rise construction), its value will exceed the static indicator by only a small amount. In forced schemes, it is taken as the maximum allowable to ensure higher efficiency.
Numerically, the value of the working head is:
- for one-story buildings with an open circuit and natural water circulation - 0.1 MPa (1 atmosphere) for every 10 m of the liquid column;
- for low-rise buildings with a closed circuit - 0.2-0.4 MPa;
- for multi-storey buildings - up to 1 MPa.
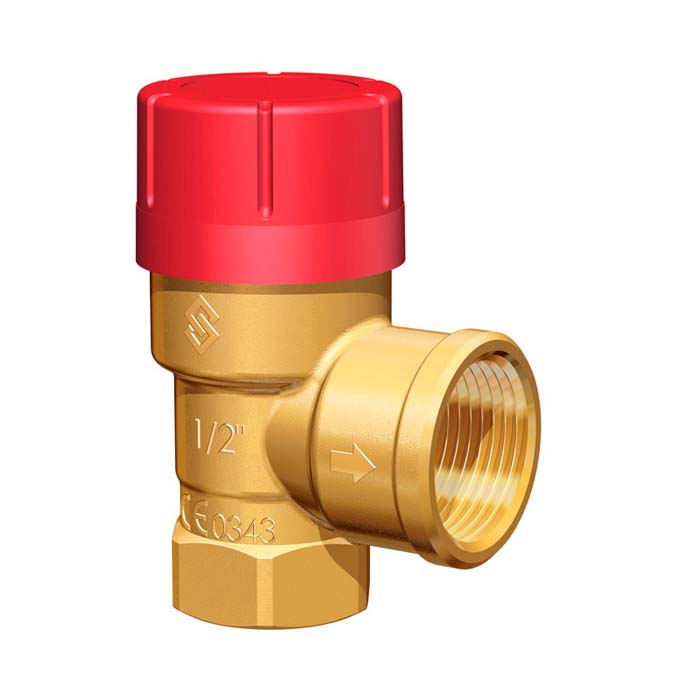
Safety valves
Any boiler equipment is a source of danger. Boilers are considered explosive, as they have a water jacket, i.e. pressure vessel. One of the most reliable and common safety devices that reduces the risk to a minimum is the safety valve of the heating system. The installation of this device is due to the protection of heating systems from excessive pressure. Often this pressure occurs as a result of boiling water in the boiler. The safety valve is placed on the supply pipe, as close as possible to the boiler. The valve has a fairly simple design. The body is made of good quality brass. The main working element of the valve is the spring. The spring, in turn, acts on the membrane, which closes the passage to the outside. The membrane is made of polymeric materials, the spring is made of steel. When choosing a safety valve, it should be taken into account that full opening occurs when the pressure in the heating system rises above the value by 10%, and full closure occurs when the pressure drops below the actuation by 20%. Due to these characteristics, it is necessary to choose a valve with a set pressure higher than 20-30% of the actual one.
Features of the heating system of apartment buildings
When installing heating equipment in multi-storey buildings, it is imperative to comply with the requirements established by the regulatory documentation, which includes SNiP and GOST. These documents state that the heating structure should provide a constant temperature in the apartments within the range of 20-22 degrees, and the humidity should vary from 30 to 45 percent.
To achieve the required parameters, a complex design is used that requires high-quality equipment. When creating a project for the heating system of an apartment building, specialists use all their knowledge to achieve an even distribution of heat in all sections of the heating main and create a comparable pressure on each tier of the building. One of the integral elements of the work of such a design is the work on a superheated coolant, which provides for the heating scheme of a three-story house or other skyscrapers.
How it works? Water comes directly from the thermal power plant and is heated to 130-150 degrees. In addition, the pressure is increased to 6-10 atmospheres, so the formation of steam is impossible - high pressure will drive water through all floors of the house without loss. The temperature of the liquid in the return pipeline in this case can reach 60-70 degrees. Of course, at different times of the year, the temperature regime can change, since it is directly related to the ambient temperature.
Design features of the heating circuit
In modern buildings, additional elements are often used, such as collectors, heat meters for batteries and other equipment.In recent years, almost every heating system in high-rise buildings is equipped with automation to minimize human intervention in the operation of the structure (read: "Weather-dependent automation of heating systems - about automation and controllers for boilers with examples"). All the described details allow to achieve better performance, increase efficiency and make it possible to distribute heat energy more evenly throughout all apartments.
Types of heating systems
The amount of heat that a heating radiator will radiate depends not least on the type of heating system and the type of connection chosen. To choose the best option, you must first understand what kind of heating systems are and how they differ.
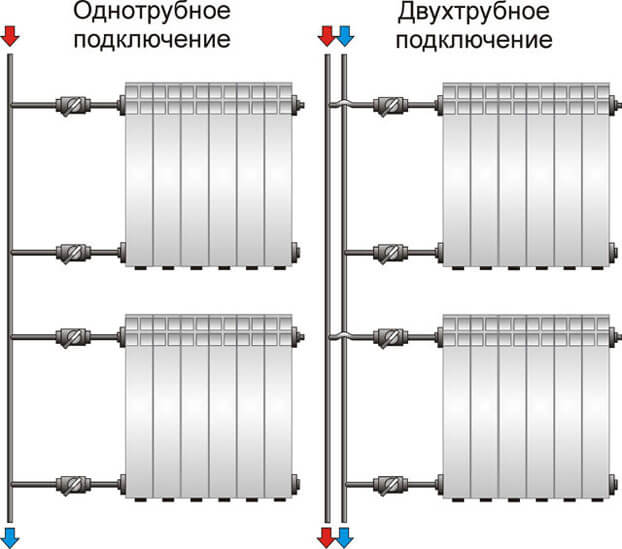
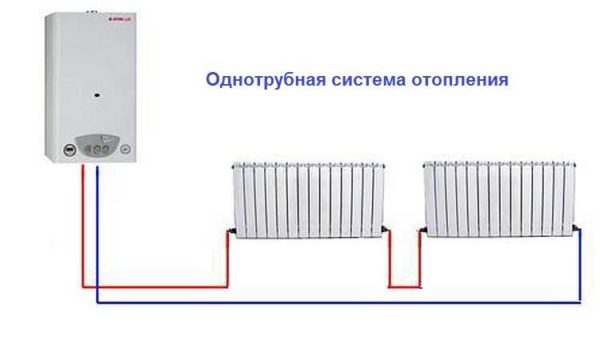
Single pipe
A single-pipe heating system is the most economical option in terms of installation costs. Therefore, it is this type of wiring that is preferred in multi-storey buildings, although in private such a system is far from uncommon. With such a scheme, the radiators are connected in series to the line and the coolant first passes through one heating part, then enters the second one, and so on. The output of the last radiator is connected to the input of the heating boiler or to the riser in high-rise buildings.
Example of a one-pipe system
The disadvantage of this wiring method is the impossibility of adjusting the heat transfer of radiators. By installing a regulator on any of the radiators, you will regulate the rest of the system. The second significant drawback is the different temperature of the coolant on different radiators. Those that are closer to the boiler heat up very well, those that are further away become colder. This is a consequence of the series connection of heating radiators.
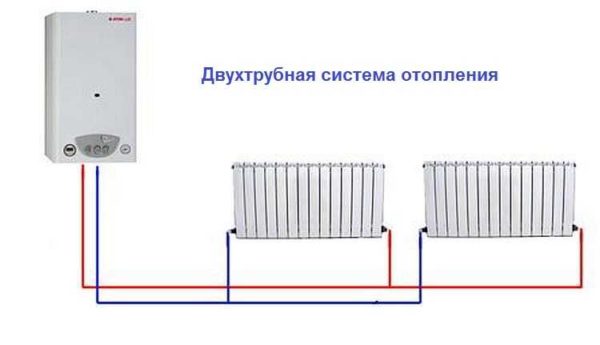
Two-pipe wiring
A two-pipe heating system is distinguished by the fact that it has two pipelines - supply and return. Each radiator is connected to both, that is, it turns out that all radiators are connected to the system in parallel. This is good in that a coolant of the same temperature enters the inlet of each of them. The second positive point is that you can install a thermostat on each of the radiators and use it to change the amount of heat that it emits.
The disadvantage of such a system is that the number of pipes when distributing the system is almost twice as large. But the system can be easily balanced.
How to fix the situation with a drop
Everything is extremely simple here. First, you need to take a look at the pressure gauge, which has several characteristic zones. If the arrow is in green, then everything is fine, and if it is noticed that the pressure in the heating system is dropping, then the indicator will be in the white zone. There is also a red one, it signals an increase. In most cases, you can manage on your own. First you need to find two valves. One of them is used for injection, the second - for bleeding the carrier from the system. Further, everything is simple and clear. If there is a lack of carrier in the system, it is necessary to open the discharge valve and follow the pressure gauge installed on the boiler. When the arrow reaches the required value, close the valve. If bleeding is needed, everything is done in the same way with the only difference being that you need to take a vessel with you, where the water from the system will drain. When the gauge needle shows the norm, tighten the valve. Often this is how the pressure drop in the heating system is “treated”. Now let's go further.
They are widely used in constant flow systems. The main advantage of manual balance valves is their low cost. As a major disadvantage, it can be noted that each change in the installation must rebuild the system, which is time consuming and costly.
Automatic balance valves Automatic balance valves allow you to flexibly change the parameters of the piping system depending on pressure fluctuations and the flow of the working medium. They are proportional regulators that maintain a constant system differential pressure and minimize disturbance caused by control valves. They are characterized by high performance, which allows them to maintain the established hydraulic conditions in systems, compensating for disturbances caused by the control valve.
Pressure rate
Efficient transfer and even distribution of the coolant, for the performance of the entire system with minimal heat loss, is possible at normal operating pressure in the pipe lines.
The coolant pressure in the system is divided according to the method of action into types:
- Static. The force of action of a stationary coolant per unit area.
- Dynamic. The force of action in motion.
- Ultimate pressure. Corresponds to the optimal value of the liquid pressure in the pipes and is able to maintain the operation of all heating devices at a normal level.
According to SNiP, the optimal indicator is 8–9.5 atm, pressure reduction to 5–5.5 atm. often leads to interruptions in heating.
For each particular house, the indicator of normal pressure is individual. The following factors influence its value:
- power of the pumping system supplying the coolant;
- pipeline diameter;
- remoteness of the premises from the boiler equipment;
- wear of parts;
- head.
Manometers mounted directly into the pipeline allow you to control the pressure.
The diameter of the pipes, as well as the degree of their wear
It must be remembered that the size of the pipe must also be taken into account. Often, residents set the diameter they need, which is almost always slightly larger than standard sizes. This leads to the fact that the pressure in the system decreases somewhat, due to the large amount of coolant that will fit into the system. Do not forget that in the corner rooms the pressure in the pipes is always less, since this is the most remote point of the pipeline. The degree of wear of pipes and radiators also affects the pressure in the heating system of the house. As practice shows, the older the batteries, the worse. Of course, not everyone can change them every 5-10 years, and it’s not advisable to do this, but it won’t hurt to carry out preventive maintenance from time to time. If you are moving to a new place of residence and you know that the heating system is old there, then it is better to change it right away, so you will avoid many troubles.
Hydraulic balance of hot water supply systems. The temperature of hot water in hot water systems decreases significantly with low or no consumption. This leads to several problems: long waits for hot water, water overflow, and the possibility of unwanted bacteria growing. To keep the water temperature at the required level, it is usually a constant circulation of water in the systems, through a circulation pump and a circulation pipe. Maintaining the hydraulic balance in these systems is usually done with direct acting temperature controllers.
Where to put radiators
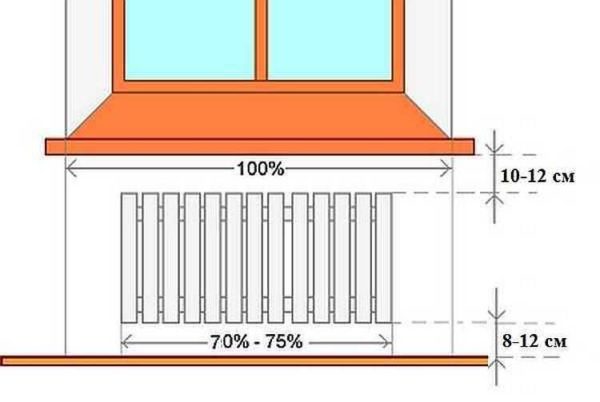
Traditionally, heating radiators are placed under the windows and this is not accidental. The upward flow of warm air cuts off the cold air that comes from the windows. In addition, warm air heats the windows, preventing condensation from forming on them. Only for this it is necessary that the radiator occupies at least 70% of the width of the window opening. Only in this way the window will not fog up. Therefore, when choosing the power of radiators, select it so that the width of the entire heating battery is not less than the specified value.
How to place a radiator under a window
In addition, it is necessary to correctly choose the height of the radiator and the place for its placement under the window. It must be placed so that the distance to the floor is in the region of 8-12 cm. If lowered, it will be inconvenient to clean, if raised higher, the feet will be cold. The distance to the window sill is also regulated - it should be 10-12 cm. In this case, warm air will freely go around the barrier - the window sill - and rise along the window glass.
And the last distance that must be maintained when connecting heating radiators is the distance to the wall. It should be 3-5 cm. In this case, ascending currents of warm air will rise along the rear wall of the radiator, the heating rate of the room will improve.
About Leak Testing
It is imperative to check the system for leaks. This is done to ensure that the heating operation is efficient and has no failures. In multi-storey buildings with central heating, the cold water test is most often used. In this case, if the heating system drops by more than 0.06 MPa in 30 minutes or 0.02 MPa is lost in 120 minutes, it is necessary to look for places of gusts. If the indicators do not go beyond the norm, then you can start the system and start the heating season. The hot water test is carried out immediately before the heating season. In this case, the media is supplied under pressure, which is the maximum for the equipment.
Their purpose is to maintain temperature and minimize water consumption in hot water circulation systems.
An important feature of these valves is the presence of periodic disinfection of the DHW pipeline network. Tags: balancing valves Manual balancing valves
Autonomous heating systems
You may not be asking for cold today, but your heating system will do it for you. If you haven't paid enough attention during the summer season, a nasty surprise can be expected at the beginning or during the heating season. Do you have a house in the cold because your radiators are as good as ever before? An error in maintenance or poor adjustment of some parts of your heating system may be a malfunction. The best time to use the summer months is to maintain the heating system, but many people only start doing it when they need to flood for the first time.
Operating pressure control in heating circuits
For normal trouble-free operation of the heat supply system, it is necessary to regularly monitor the temperature and pressure of the coolant.
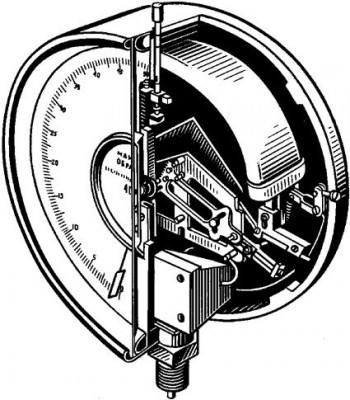
To check the latter, deformation manometers with a Bourdon tube are usually used. To measure small pressures, their varieties can be used - diaphragm devices.
Picture 1 - Deformation manometer with Bourdon tube
In systems where automatic control and regulation of pressure are provided, various types of sensors are additionally used (for example, electrocontact).
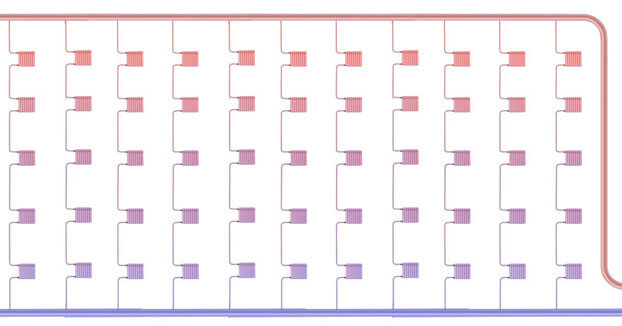
- at the inlet and outlet of the heating source;
- before and after the pump, filters, mud collectors, pressure regulators (if any);
- at the exit of the highway from the CHP or boiler house and at its entrance to the building (with a centralized scheme).
Figure 2 - Section of the heating circuit with installed pressure gauges
How to cut heating
How to refuse heating in an apartment building?
Documentation
We will touch on the documentary part only in part. The problem is very painful; permission to disconnect from the central heating is given by organizations extremely reluctantly, and often it has to be beaten out through the courts. It is quite possible that in your case it will be much more useful not to have a technical article, but to consult a lawyer who is knowledgeable in the Housing Code.
The main steps are:
- We clarify whether there is a technical possibility to disable it. It is at this stage that most of the friction lies: neither the utilities nor the heat suppliers like to lose payers.
- Specifications for an autonomous heating system are being prepared. You need to calculate the approximate consumption of gas (in case you use it for heating) and show that you are able to provide a temperature regime in the apartment that is safe for the building structures.
- The act of fire supervision is signed.
- If you are planning to install a boiler with a closed burner and exhaust of combustion products on the facade of the building, you will need a permit signed by the Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision.
- A licensed installer is hired to complete the project. You will need a complete package of documents - from instructions for the boiler to a copy of the installers' license.
- After the installation is completed, a representative of the gas service is invited to connect the boiler and start it for the first time.
- The last stage: you put the boiler on permanent service and notify the gas supplier about the transition to individual heating.
Technical side
Refusal of heating in an apartment building is due to the fact that you need to dismantle all heating devices without disturbing the operation of the heating system. How it's done?
In houses with bottom bottling, it is worth considering two cases separately:
- If you live on the top floor, you get the consent of the lower neighbors and transfer the jumper between the paired risers to their apartment. Thus, you completely isolate yourself from the Unification Church. Of course, you will have to pay for welding, installation of an air vent, and redecoration of the ceiling at the neighbors.
- On the middle floor, only heating appliances are dismantled, and with welding and cutting of the connections. A jumper of the same diameter as the rest of the pipe cuts into the riser. Then the riser along the entire length is carefully insulated.
Heating check valve

In a complex heating system, there is a fairly large number of auxiliary elements, the task of which is to ensure reliability and uninterrupted operation. One of these elements is the check valve of the heating system. A check valve is installed so that there is no flow in the opposite direction. Its elements have a very high hydraulic resistance. In connection with this circumstance, there are restrictions on the use of check valves in a heating system with natural circulation. There is too little pressure in such a system. At minimum pressure it is necessary to install gravity valves with a butterfly valve, some of them can operate at a pressure of 0.001 bar. The main part of the check valve is the spring used in almost all models. It is the spring that closes the shutter when the normal parameters change. This is the principle of operation of the check valve.
It is necessary to take into account the operating parameters in a particular heating system. In this connection, select a heating system valve that has the necessary spring elasticity. The valves used in heating systems are usually made of the following materials: steel; brass; stainless steel; gray cast iron. Check valves are divided into the following types: poppet; petal; ball; bivalve. These types of valves differ in the locking device.
Piping in a multi-storey building
As a rule, in multi-storey buildings, a single-pipe wiring diagram with top or bottom filling is used. The location of the forward and return pipes can vary depending on many factors, including even the region where the building is located. For example, the heating scheme in a five-story building will be structurally different from heating in three-story buildings.
When designing a heating system, all these factors are taken into account, and the most successful scheme is created that allows you to bring all the parameters to the maximum. The project may involve various options for pouring the coolant: from the bottom up or vice versa.In individual houses, universal risers are installed, which ensure the rotation of the movement of the coolant.
Temperature table in the heating pipeline
The heating temperature, including return pipes, directly depends on the indicators of outdoor thermometers. The colder the air outside and the higher the wind speed, the greater the cost of heat.
A normative table has been developed that reflects the temperatures at the inlet, supply and outlet of the heat carrier in the heating system. The indicators presented in the table provide comfortable conditions for a person in a residential area:
| Pace. external, °С | +8 | +5 | +1 | -1 | -2 | -5 | -10 | -15 | -20 | -25 | -30 | -35 | |
| Pace. at the entrance | 42 | 47 | 53 | 55 | 56 | 58 | 62 | 69 | 76 | 83 | 90 | 97 | 104 |
| Pace. radiators | 40 | 44 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 54 | 57 | 64 | 70 | 76 | 82 | 88 | 94 |
| Pace. return lines | 34 | 37 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 58 | 62 | 67 | 69 |
Important! the difference between the supply and return temperatures depends on the direction of movement of the coolant. If the wiring is from above, the differences are no more than 20 ° C, if from below - 30 ° C
Types of radiators for heating apartment buildings
In multi-storey buildings, there is no single rule that allows the use of a specific type of radiator, so the choice is not particularly limited. The heating scheme of a multi-storey building is quite versatile and has a good balance between temperature and pressure.
The main models of radiators used in apartments include the following devices:
- Cast iron batteries. Often used even in the most modern buildings. They are cheap and very easy to install: as a rule, apartment owners install this type of radiator on their own.
- Steel heaters. This option is a logical continuation of the development of new heating devices. Being more modern, steel heating panels demonstrate good aesthetic qualities, are quite reliable and practical. Very well combined with the regulating elements of the heating system. Experts agree that it is steel batteries that can be called optimal when used in apartments.
- Aluminum and bimetallic batteries. Products made of aluminum are highly valued by the owners of private houses and apartments. Aluminum batteries have the best performance compared to previous options: excellent external data, light weight and compactness are perfectly combined with high performance. The only disadvantage of these devices, which often scares off buyers, is the high cost. Nevertheless, experts do not recommend saving on heating and believe that such an investment will pay off pretty quickly.
Conclusion
The correct choice of batteries for a centralized heating system depends on the performance indicators that are inherent in the coolant in the area. Knowing the cooling rate of the coolant and the direction of its movement, it is possible to calculate the required number of radiator sections, its dimensions and material. Do not forget that when replacing heating devices, it is necessary to follow all the rules, since their violation can lead to defects in the system, and then the heating in the wall of the panel house will not perform its functions (read: “Heating pipes in the wall ").
Centralized heating systems demonstrate good qualities, but they need to be constantly maintained in working order, and for this you need to monitor many indicators, including thermal insulation, equipment wear and regular replacement of spent elements.
How is the heating of a residential building arranged? The growth of tariffs encourages the transition to autonomous heating of the apartment; but the refusal of central heating in an apartment building, in addition to a lot of bureaucratic obstacles, also means a number of technical problems. To understand the ways to solve them, you need to imagine the layout of the coolant distribution.
Conclusion
For more information on how the heating systems of residential buildings are arranged, you will find in the video attached to the article. Warm winters!
The reliability and performance of the heating system depends on the efficient operation of all parts included in it.
These include: a boiler for heating the coolant, radiators connected in a certain way to it and to each other, an expansion tank, a circulation pump, shut-off and control valves, a pipeline of the required diameter.
The creation of a highly efficient heating system is possible thanks to special knowledge and experience in this field of activity. The return pipeline plays an important role in the working process of space heating.