How will we connect
The scheme for connecting radiators can be different. The level of heat transfer and the comfort of being in the apartment depend on which option will be preferred. Incorrectly selected wiring can reduce the power of the heating system by 50%.
The most widespread is the one-sided side scheme, which has the highest heat transfer rate. In this case, the pipe supplying the coolant is connected to the upper branch pipe, and the outlet pipe to the lower one.
If you do the opposite, the efficiency of space heating will decrease by almost 7%. To connect multi-section radiators, such a scheme is not always justified, since insufficient heating of the last sections is possible. This can be avoided by installing a water flow extension.
In an apartment with pipes hidden in the floor or passing under the plinth, a bottom connection is used.
This is the most aesthetic option, in which the pipes for supplying and discharging the coolant are located below in the floor, and therefore the lower holes are used for connection.
Diagonal
Installation of batteries with twelve or more sections is carried out in a diagonal pattern.
The coolant is supplied through the upper branch pipe located on one side of the radiator, and is discharged through the lower one on the other side.
Sequential
Such a connection scheme assumes the presence in the heating system of pressure sufficient for the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
In this case, it is worthwhile to provide for a Mayevsky crane, designed to remove excess air.
It is important to remember that the implementation of repair and maintenance work will be accompanied by a shutdown of the entire heating system.
Parallel
Parallel wiring assumes the presence of a special heat pipe built into the heating system, through which the coolant is supplied and discharged outside.
The presence of special taps at the inlet and outlet makes it possible to replace individual radiators without turning off the heat supply. However, the scheme can cause insufficient heating of the pipes at reduced pressure in the system.
Dimensions of heating radiators
The standard height of the most popular models of heating devices with a center distance along the eyeliners is 500 millimeters. It was these batteries that in most cases could be seen about two decades ago in city apartments.
Cast iron radiators. A typical representative of these devices is the MS-140-500-0.9 model.
The specification for it includes the following overall dimensions of cast iron heating radiators:
- length of one section - 93 mm;
- depth - 140 millimeters;
- height - 588 millimeters.
It is not difficult to calculate the dimensions of a radiator from several sections. When the battery consists of 7-10 sections, add 1 centimeter, taking into account the thickness of the paronite gaskets. If the heating battery is to be installed in a niche, it is necessary to take into account the length of the flushing valve, since cast-iron radiators with side supply always require flushing. One section provides a heat flow of 160 watts at a temperature difference between the hot coolant and the air in the room equal to 70 degrees. The maximum working pressure is 9 atmospheres.
Aluminum radiators. For aluminum heaters on the market today, with the same interaxal spacing of the connections, there is a significant variation in the parameters (in more detail: “Dimensions of aluminum heating radiators, section volume, preliminary calculations“).
Typical are the following dimensions of aluminum heating radiators:
- the length of one section is 80 millimeters;
- depth 80-100 millimeters;
- height - 575-585 millimeters.
The heat transfer of one section directly depends on the area of its fins and depth.Usually it is in the range from 180 to 200 watts. The working pressure for most models of aluminum batteries is 16 atmospheres. Heating devices are tested with a pressure one and a half times greater - this is 24 kgf / cm².
Aluminum radiators have the following feature: the volume of coolant in them is 3, and sometimes 5 times less than in cast iron products. As a result, the high speed of movement of hot water prevents silting and the formation of deposits. Bimetal radiators. The steel core in such devices in no way affects their appearance and dimensions of heating radiators, but the maximum working pressure increases significantly. Unfortunately, the increase in the strength of the bimetallic battery leads to a high cost. And the price of such a product is already inaccessible to a wide range of consumers.
Bimetallic heating radiators section dimensions are as follows:
- length 80-82 mm;
- depth - from 75 to 100 millimeters;
- height - a minimum of 550 and a maximum of 580 millimeters.
In terms of heat transfer, one bimetallic section is inferior to aluminum about 10-20 watts. The average value of the heat flux is 160-200 watts. Due to the presence of steel, the working pressure reaches 25-35 atmospheres, and during testing - 30-50 atmospheres.
When arranging the heating structure, pipes should be used that are not inferior in strength to radiators. Otherwise, the use of durable devices loses all meaning. For bimetallic radiators, only steel eyeliner is used.
Advantages of bimetallic heating radiators
The popularity of batteries of this variety is explained very simply. Cast iron radiators are quite reliable, but do not look too aesthetically pleasing. In addition, they are difficult to install. Aluminum batteries look modern and attractive. However, this metal does not tolerate contact with oxygen in the coolant very well. Therefore, aluminum radiators quickly fail and begin to leak. Steel batteries last longer. However, at the same time, they do not look so aesthetically pleasing.
Bimetal models combine the advantages of aluminum and steel radiators. In a modern interior, such batteries fit just perfectly. The sections are made of aluminium. At the same time, they serve for a long time, since the pipes through which the coolant flows through them are made of steel.
Calculations depending on the volume of the room
More accurate data can be obtained if the sections of heating radiators are calculated taking into account the height of the ceiling, i.e., by the volume of the room. The principle here is about the same as in the previous case. First, the total heat demand is calculated, then the number of radiator sections is calculated.
According to the recommendations of SNIP, 41 W of thermal power is required to heat each cubic meter of a dwelling in a panel house. Multiplying the area of the room by the height of the ceiling, we get the total volume, which we multiply by this standard value. For apartments with modern double-glazed windows and external insulation, less heat will be needed, only 34 W per cubic meter.
For example, let's calculate the required amount of heat for a room of 20 sq.m. with a ceiling height of 3 meters. The volume of the room will be 60 cubic meters (20 sq.m. X 3 m.). The calculated thermal power in this case will be equal to 2460 W (60 cubic meters X 41 W).
And how to calculate the number of heating radiators? To do this, you need to divide the data obtained by the heat transfer of one section specified by the manufacturer. If we take, as in the previous example, 170 W, then the room will need: 2460 W / 170 W = 14.47, i.e. 15 radiator sections.
Manufacturers tend to indicate overestimated heat transfer rates of their products, assuming that the temperature of the coolant in the system will be maximum. In real conditions, this requirement is rarely met, so you should focus on the minimum heat transfer rates of one section, which are reflected in the product passport. This will make the calculations more realistic and accurate.
Requirements for the selection of radiators
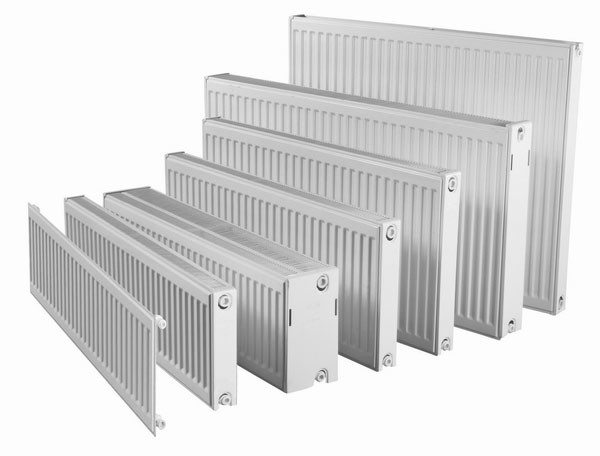

When choosing the dimensions of radiators for placement under a window, it is necessary to build on the values of the width of the window opening and the estimated distance of the edges of the elements to the window sill and the floor surface. Before leaving for the store, it is necessary to make all the necessary measurements and focus on them when considering options. The standard opening width is 110-120 cm. The size of the purchased battery must be at least 70-75% of this value. If we are talking about a sectional device made of aluminum, you will need a radiator of 10-12 elements (the width of one is usually about 8 cm).
When choosing the size of radiators, the height of the window sill must be taken into account. Between it and the upper edge of the radiator elements there should be a distance of 6-12 cm
The installation height of heaters above the floor must be at least 8 cm. In this case, heat transfer is achieved that is as close as possible to that declared by the manufacturer.
Also in the conditions of the private sector, the volume of liquid placed in the section is of great importance. If in apartment buildings whose residents use central heating, this parameter does not play a role, then when using your own system, it is needed to calculate the volume when you want to find out the efficiency of a pump or boiler.
The most important indicator when choosing heating equipment is thermal power. It is far from always advisable to choose high-power options. In dwellings with high-quality thermal insulation, a model with an average value of this parameter is sufficient.
Low and flat radiators
 Cast iron model with center distance less than 40 cm
Cast iron model with center distance less than 40 cm
Low is considered to be models that have a center index of less than 40 cm. This segment is distinguished by a wide variety of products, since miniature batteries are made from different materials. Among Russian buyers, they are not in such great demand, since the radiator cannot be replaced with an accordion without making costly modifications to the design of the heating system.
Among cast iron products, subminiature models are not found. The extreme option is a Bolton radiator with an interaxal measurement of 220 mm and a mounting height of 33 cm. For other small cast iron appliances, these parameters are in the region of 300-350 mm and 35-40 cm, respectively.
For aluminum devices, the minimum center value is 200 mm. There are many options in this size on the market. We can recall the companies Global, Sira and the domestic "Rifar". The same firms produce low bimetal models (with a height of around 25 cm). Slightly larger aluminum models (300-400 mm) are found in any manufacturer that produces heating appliances. Miniature, but powerful and expensive batteries made of copper or its alloy with aluminum usually have a height of 20-22 cm, but there are instances that go beyond the low category.
Miniature non-flat radiators are made from steel by Purmo. This includes two panel models with a center distance of 15 cm. The same or slightly larger (by 1-3 cm) indicator for a number of tubular products. And yet, for most steel batteries, this value exceeds 25 cm. On the market, you can find low, but long designs (up to 2 meters in length).
 The lowest aluminum radiators
The lowest aluminum radiators
In some conditions, placing even a miniature radiator in a room is impractical and contrary to safety standards. As an example, escape route corridors can be given - they are not supposed to mount devices that extend beyond the wall surface at a height of less than 2 meters. For such cases, as well as to save space in the room, the output will be a convector that is built into the floor structure. Such a device can be called the lowest radiator. They are available in a wide range of power ratings.They are used as the only source of heating or in addition to another method. Also, convectors are installed for heating solid glazing.
There are cases when the critical (with respect to minimization) parameter is depth rather than height. Then it is necessary to consider the segment of flat models. Bimetallic and cast iron samples are not suitable in this case due to the large depth. The Russian version of aluminum is a product of the Zlatoust company with an indicator of 52 mm. Models are produced to replace the accordion and low ones with a center distance of 30 cm. They have a high thermal power. Panel batteries with a depth of 6 cm are also suitable.
Advantages and disadvantages
Aluminum batteries differ from cast iron batteries in a number of ways:
- High heat transfer, which means less boiler wear and the ability to reduce heating costs.
- Easily mounted and fit into any interior.
- Well suited for autonomous heating systems, and can also be installed in apartment buildings.
- They can be mounted both in a system with old cast-iron pipes, and in modern plastic and metal-plastic networks.
There is not a single heating device, not a single element of engineering networks, which would be ideal and completely devoid of shortcomings. Aluminum radiators are no exception to this rule.
Among the important shortcomings, it is worth noting:
- High risk of leakage at the joints of the sections.
- Uneven distribution of heat.
- Little convection heat transfer.
- Short service life compared to cast iron batteries.
- High susceptibility to corrosion except for anodized batteries.
- Sensitivity to pressure instability in the system.
These shortcomings can be considered unimportant in autonomous heating systems, but when replacing radiators in a house connected to a central highway, you need to be careful. In such cases, it is better to choose anodized models, not looking at their high cost.
Rules for installing heating radiators
A necessary attribute of each room is a heating radiator, and we are all used to these cast-iron ribbed devices that create warmth and comfort in the house. But time does not stand still, and instead of heavy cast-iron batteries, new generation radiators come. These are fairly light steel or aluminum panels.
They look great, have high heat dissipation, and most importantly, they are easy to install in any room.
Often, the main criterion when choosing a radiator is its appearance, and only then do buyers pay attention to technical characteristics. But in order to achieve maximum heat transfer efficiency of the radiator, you should do exactly the opposite, first carefully study the technical parameters, and only then evaluate the appearance and consider the price
Simple rules for installing heating radiators
The efficiency of the radiator directly depends on its correct location when installed indoors. Determine the areas of greatest heat loss. These include windows and exterior walls. Placing radiators in such places will create the necessary barrier to restrict access to cooled air.
For the correct installation of radiators, it is important to follow a few rules:
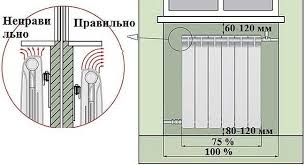
The radiator should not be located too close to the wall, this will reduce air circulation and affect heat dissipation. When installing at the location of the radiator, stick heat-reflecting foil on the wall, which will prevent unwanted heating of the walls
Pay attention to the symmetry of the location of the radiators. Their inaccurate location will spoil the overall look of the room.
Decorating radiators with panels can beautifully complement the interior, but will significantly reduce the efficiency of the heating system.
The following radiator installation parameters will help you achieve maximum heat transfer efficiency.The distance from the wall to the surface of the radiator must be at least 3 centimeters, and from the window sill and the floor at least 10 centimeters. The distance from the main riser to the junction with the radiator must be at least 30 centimeters
Pay special attention to the reliability of fixing radiators to the walls. There must be at least four fasteners, two at the top and two at the bottom.
To avoid annoying mistakes, you should first mark the points of future fasteners so that the radiator plugs coincide with the pipe layout. Only after careful marking of all attachment points, you can proceed to the final installation of the system.
If all the work is done correctly, the new radiators will harmoniously fit into the interior of your home. For efficient heating of the room, it is necessary to observe the proportions of the heated area to the heat transfer characteristics of the radiators. It should be 1000 W of power to 10 square meters of heated space.
The above tips and tricks will help you maximize the efficiency of your heating system, create a cozy atmosphere and modern design in your home.
In our climatic conditions, heat is the most important condition for creating comfort, and the correct installation of radiators will make it possible to achieve significant savings in utility bills, which is important with ever-increasing tariffs. Thus, despite the costs of modernizing the heating system, its efficiency will make it possible to recoup all costs in a relatively short period of time.
Securing batteries

Manufacturers of heating appliances offer a wide range of products that differ in material of manufacture and type of execution:
- Floor. These are units designed to be installed on the floor, for which they are equipped with supports or legs. Supports can be on wheels or without them. The option is easy to install and allows you to provide the desired distance from the window sill to the radiator, while respecting the gap between the lower collector and the floor.
- Mounted. Mounted on the wall, mounted on metal brackets that are screwed into the wall itself. There are adjustable brackets on sale, with which you can adjust the width of the gap not only to the window sill, but also to the wall, as well as align the horizontal level of the installation level.
Terminology
The documentation regarding the dimensions of heating radiators often refers to the center distance. This parameter indicates the length of the gap from the center point of one connection hole to the same location in another. Sometimes this value is called the center or inter-nipple distance. If the pipelines supplying the radiator are in working condition and it is not planned to change them, the new heater purchased must have the same center-to-center ratio as the old one so that changes to the connection are not necessary. Sometimes the names of models - both Russian and foreign - contain three-digit numbers. They indicate this parameter in millimeters (for example, Modern 500).
Linear dimensions include:
- the mounting height of the radiator - it must be selected so as to provide the necessary distances to the window sill and the floor;
- depth;
- width - for models with a sectional design, it, like the previous parameter, also refers to the dimensions of the elements, but if the depth of the radiator and its individual sections is the same, to calculate the total width, you need to multiply the indicator of a single unit by their number and add approximately 1-2 cm, attributable to sealing gaskets.
Calculation of the number of radiator sections
The thermal power of the radiator section depends on its overall dimensions. With a distance between the vertical axes of 350 mm, the parameter fluctuates in the range of 0.12-0.14 kW, with a distance of 500 mm - in the range of 0.16-0.19 kW.According to the requirements of SNiP for the middle band per 1 sq. meters of area, a thermal power of at least 0.1 kW is required.
Given this requirement, a formula is used to calculate the number of sections:
where S is the area of the heated room, Q is the thermal power of the 1st section and N is the required number of sections.
For example, in a room with an area of 15 m 2, it is planned to install radiators with sections of thermal power of 140 W. Substituting the values into the formula, we get:
N \u003d 15 m 2 * 100/140 W \u003d 10.71.
Rounding is done up. Given the standard forms, it is necessary to install a bimetallic 12-section radiator.
Important: when calculating bimetallic radiators, factors that affect heat loss inside the room are taken into account. The result obtained is increased by 10% in cases where the apartment is located on the first or last floor, in corner rooms, in rooms with large windows, with a small wall thickness (no more than 250 mm)
A more accurate calculation is obtained by determining the number of sections not for the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, but for its volume. According to the requirements of SNiP, heating one cubic meter of a room requires a thermal power of 41 watts. Given these rules, get:
where V is the volume of the heated room, Q is the thermal power of the 1st section, N is the required number of sections.
For example, a calculation for a room with the same area of 15 m 2 and a ceiling height of 2.4 meters. Substituting the values into the formula, we get:
N \u003d 36 m 3 * 41 / 140 W \u003d 10.54.
The increase is again carried out in the big direction. a 12-section radiator is required.
The choice of the width of the bimetallic radiator for a private house is different from the apartment. The calculation takes into account the coefficients of thermal conductivity of each material used in the construction of the roof, walls and floor.
When choosing sizes, the requirements of SNiP for battery installation should be taken into account:
- the distance from the top edge to the window sill must be at least 10 cm;
- the distance from the bottom edge to the floor should be 8-12 cm.
For high-quality space heating, it is necessary to pay attention to the choice of sizes of bimetallic radiators. The dimensions of the batteries of each manufacturer have minor differences, which are taken into account when buying.
Correct calculation will avoid mistakes.
Find out what the correct dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators should be from the video:
Power 1 section cast iron radiator
Another article in the heading - "consumption of an apartment." So, as the heating season has already begun, many are interested in the power of their batteries. After all, the heat in the room and in the apartment as a whole depends on the power (you need to know this when calculating heating radiators at the design level of the heating system). Today I will talk about the power of 1 section of a cast-iron radiator ...
Cast iron radiators come in various brands, but there are not so many of them and they can be listed on the fingers. Everything else is just a variation. Today is the most basic.
The classic and most common radiator is installed in many apartments in our country, as well as in many countries of the post-Soviet space. Section width 140 mm, height (between supply pipes) 500 mm. Additional marking MC 140 - 500. The power of 1 section of this radiator is 175 W of thermal energy.
However, there are many variations of this radiator.
MC 140 - 500 with fins (collector)
The most energy-efficient version of the MS 140 radiator. The thing is that additional cast-iron fins are installed between the sections, which also provide additional heating to the room. The power of such a radiator is 195 W of thermal energy (which is 20 W more than that of the classic MC 140). However, such radiators have a significant disadvantage, you need to monitor the frequency of these fins, if they become clogged (with dust, for example), then the thermal efficiency drops by 30 - 40 W!
MC 140 - 300
As the name implies, this radiator has a width of the same 140 mm, but the height is only 300 mm.This is a compact type of radiators. The power of one section is only 120 W of thermal energy.
MC 90 - 500
A less common radiator, but cheaper than the previous sample. The width of one section is 90 mm (more compact), the height is the same 500 mm, hence the name. Less efficient than the MC 140, the power of one section of such a radiator is about 140 W of thermal energy.
MS 110 - 500
Cast iron radiator 110 mm wide and 500 mm high between pipes. Relatively rare not so often set. Power of one section, about - 150 W
MS 100 – 500
Relatively new development, trace a modified form. The radiator has a section width of 100 mm and a height (between supply pipes of 500 mm). The thermal power of one section is 135 - 140 W.
New cast iron radiators
It is not uncommon now to see modern cast-iron radiators, produced by both imported companies and our domestic ones. They look like aluminum radiators. The power of 1 section of such a radiator ranges from 150 to 220 W, much depends on the size of the radiator.
And that's all, I think I gave you the layout of the usual cast-iron radiators. Of course, power can jump a little from manufacturer to manufacturer, but approximately the power is kept within these limits.
The procedure for determining the installation location
There are strict rules on how to install a heating radiator:
- the supply pipeline to the heaters should be placed with a slope of 0.5 cm per one meter of the pipe in the direction of the coolant circulation. The angle of inclination is calculated taking into account the length of the mounted pipe sections;
- the distance from the plane of the floor covering to the radiator cannot be less than 6-10 centimeters;
- it is required to observe the gap between the lower part of the window sill and the upper line of the battery, equal to 5-10 centimeters:
- the distance between the wall surface and the radiator should be 3-5 centimeters.
Among the mandatory conditions for the installation of devices is the exact observance of horizontal and vertical directions. Batteries in the same room are usually installed at the same level. To increase the efficiency of heat transfer by a radiator, a heat-reflecting shield made of a special material is placed on the wall located behind it. It is possible to coat the surface of the wall with a composition having similar properties.