Varieties of the Senerji facade
- Senergy PPS.
Senardzhi PPS - ideal for low-rise buildings
PPS is used for the facade, walls, roofs of small rooms, cottages with a maximum of 3 floors. The system is used in buildings where fire resistance reaches the 5th degree, observing all standards for protecting the heat of the room, improving the appearance of the structure. PPS material - expanded polystyrene, is not afraid of moisture, retains thermal insulation characteristics. The indicator of the mechanical strength of the material is ten times lighter than mineral wool. Therefore, it does not need to be fixed with anchors. Also, the advantage is the price of products, a simple installation procedure.
- Senergy PPS-3.
Senardzhi PPS-3 is used in reconstructions
It has found application in newly erected buildings, reconstructions, premises for any degree of resistance to fire, as well as protection against fires of a functional, constructive type. The list excludes fire hazard premises - F1.1, which are: kindergarten, nursing home, nursing home, etc. Structures of the F4.1 type are also excluded: a school, an educational institution of the middle class, etc. The material is in demand in construction work. It has an average density, has an excellent property of heat and sound insulation. Senerzhi PPS-3 is easy to install and is cheap. Expanded polystyrene is often used to insulate the roof, ceiling, wall, floor.
- Senergy MVS.
Senardzhi MvS - wet facade based on mineral wool
The MVS system is used for structures of varying degrees of fire resistance and fire hazard. The advantages of this material can be called resistance to alkalis. Senergy MVS is not afraid of corrosion in contact with metals, has stable volumes, shapes, and high delamination strength. It is possible to create the exact size of the material for laying, ease of processing through cutting. The material must be protected during transportation, storage, installation from the harmful effects of the external environment.
Ventilated insulation system
The principal constructive solution of one of the variants of the hinged ventilation facade: 1 - the main part of the wall; 2 - leveling plaster layer; 3 - gasket; 4 - bearing bracket; 5 - support bracket; 6 - clamping tongue; 7 - dowel-anchor axis for attaching the bracket to the main part of the wall; 8 - vertical support profile; 9 - rivet axis and rivet; 10 - non-combustible effective insulation; 11 - wind protection; 12 - dowel-anchor; 13 - ordinary clamp; 14 - end clamp; 15 - rivet; 16 - sealing gasket; 17 - facing plate (from porcelain stoneware).
In general, a hinged system ventilated by outside air, or a hinged ventilated facade (ventilated facade), consists of three main elements:
- outer cladding (rain screen);
- cladding frame (sub-facing structure);
- effective thermal insulation from, as a rule, mineral wool.
Installation of a ventilation façade. Aluminum profile cladding frame
In a ventilation facade with a wooden frame (it is used mainly in low-rise buildings), low-density thermal insulation is advisable, protected from blowing and flaking with windproof material. It allows water vapor diffusing in cold weather through the wall into the ventilated gap, but does not allow external moisture to pass into the insulation. In the case of a metal (galvanized or stainless steel, aluminum) frame, in some cases, thermal insulation of a relatively high density (rigid plates) is advisable. In this case, wind protection may be absent. Moreover, in any case, water vapor without much interference enters the ventilated gap from the room.
In the ventilated facade, due to the ventilation of the air gap, the insulation is in more favorable conditions compared to non-ventilated systems. Thanks to the gap, the temperature and humidity conditions of the premises are improved, and the actual thermal conductivity of the insulation is lower than in walls without a ventilated gap. In addition, the ventilation facade eliminates overheating of the wall.
Due to the absence of "wet" processes, it is possible to install a ventilation facade at any time of the year. Control of work progress is simple and reliable. Ventfasad has a high degree of maintainability. Before its installation, it is not always necessary to level the surface of the main part of the wall. The service life of the ventilation facade without major repairs is approximately up to 50 years.
How much does the heating system cost?
The cost of a heating system depends on many factors. If we proceed from ensuring the value of the normative resistance to heat transfer of the outer wall at 3.2 m2 × ° С / W, then the approximate prices of not the most expensive insulation systems in Belarus are as follows (with a heater thickness of up to 15 cm):
- light plaster systems - 35–50 US dollars per 1 m2;
- heavy plaster systems - 30–45 US dollars per 1 m2;
- ventilated systems - 50-90 US dollars per 1 m2;
Of course, the lower the quality of the elements of insulation systems, the lower not only their cost, but also reliability and durability.
Are cellular concrete walls warm?
Ask an expert
Senergy installation basics
Senergy technology includes many layers. Therefore, the installation of elements is carried out by fixing one to the other, creating layers:
- Insulation - mineral wool or expanded polystyrene;
- Then glue, a primer are applied, dowels are used for fasteners;
- Reinforcement - creates a powerful adhesion of the elements of thermal insulation and topcoat;
- Installation of a reinforcing mesh is also carried out to exclude the appearance of crevices, cracks, splits;
- Application of a top coat that increases protection against the negative effects of precipitation and other things.
Layers of insulation, reinforcement, decorative coating are produced in a period of several days. The warming procedure should be carried out by a professional master. It is necessary to ensure high-quality preparation of the wall, roof, floors, materials, the correct choice of the thickness of the insulation elements.
Given the above facts, we can conclude that Senerzhi's wet facade technology allows both to insulate the building and improve the aesthetic beauty of the building.
Installation steps
- Preparatory work on cleaning, getting rid of dust, repair work (if necessary), creating a smooth surface of facades.
- In some cases, a layer is applied to strengthen (primer).
- The adhesive composition is applied to the thermal insulation material, then glued to the base.
- Installation of a heat-insulating plate by means of a dowel, an anchor.
- Aluminum perforated corners are mounted on the facade (at the corner or slope).
- Installation of the grid, drowning it in the adhesive composition.
- Re-opening with adhesive or applying water-repellent type plaster.
- Product of protective, decorative finishing. Textured, finely dispersed plasters are used, covered with facade paints or without coating.
Wet facade materials
The first include the use of polystyrene foam board as the basis for insulation. Also in the composition there is organic reinforcement and plaster, as a decorative layer. The mineral type involves the use of mineral plates, reinforcement with a mineral mixture, silicate, mineral plaster. Combined insulation options include both types of materials.
Recommendation! Work on the installation of wet facades should be carried out after the roof, windows, doors have already been installed, wiring has been laid, and primary finishing inside the building has been completed.
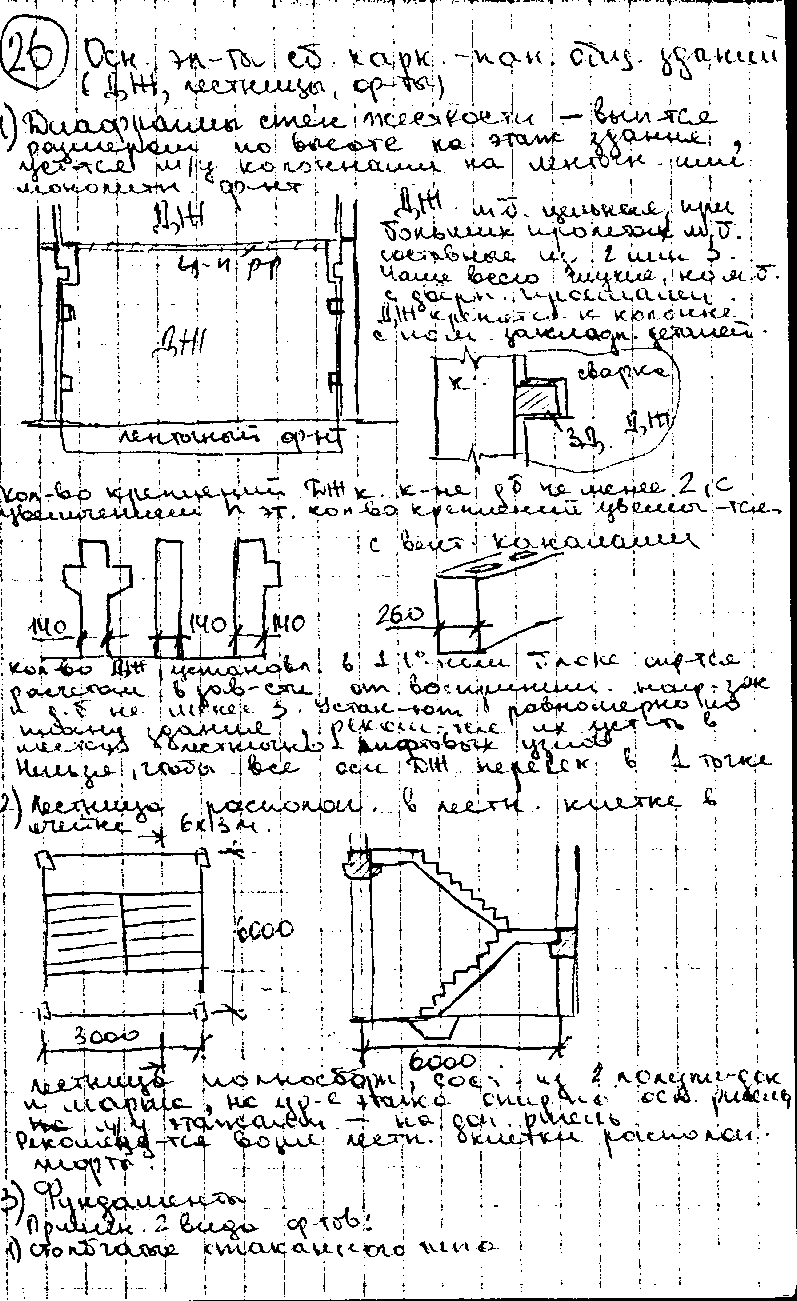
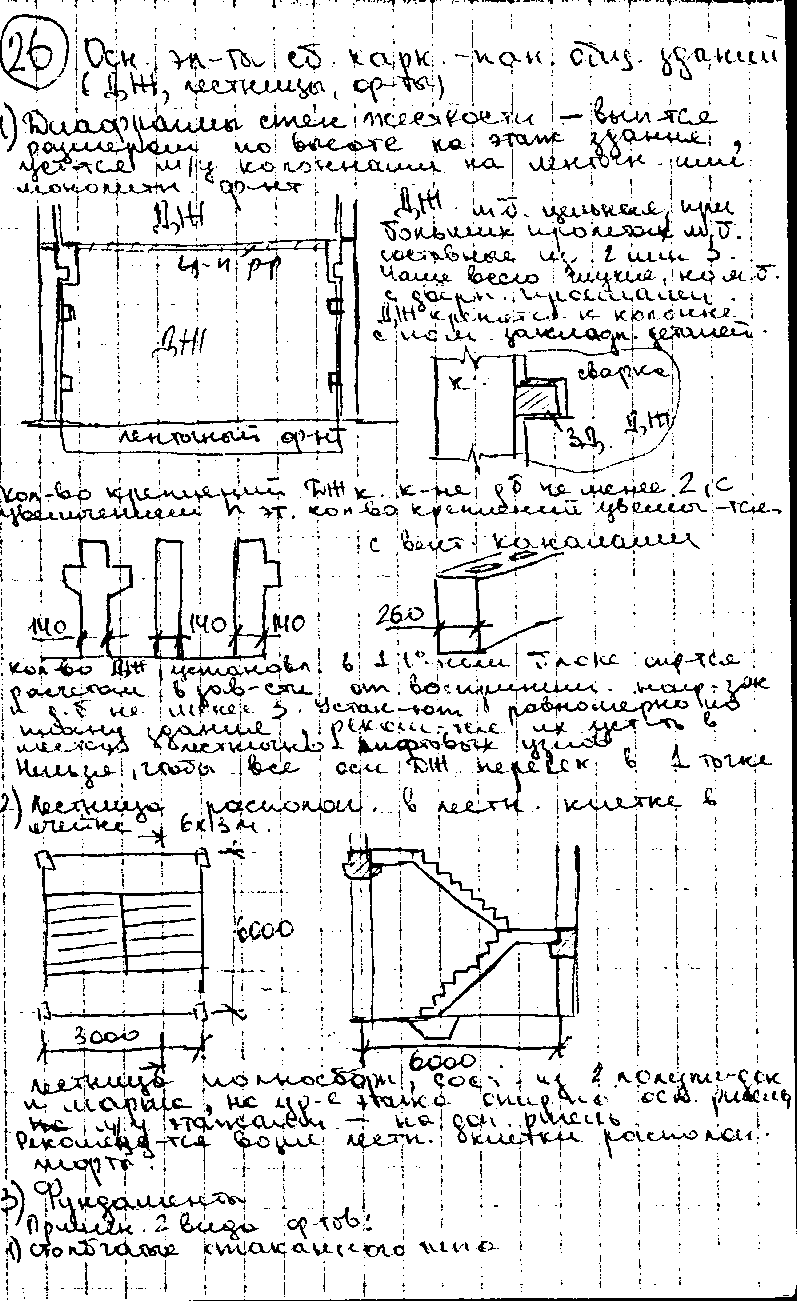
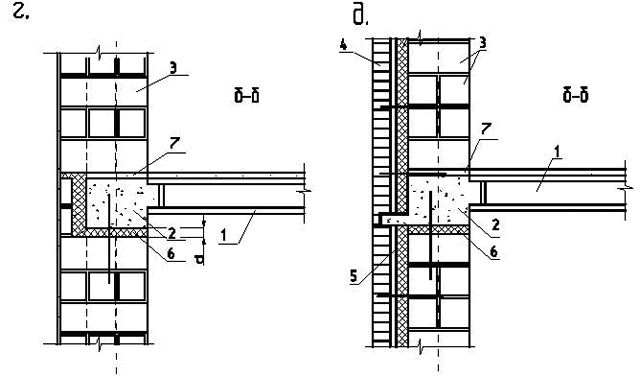
Structural elements of frame-panel buildings series 1. 020-1, their types and purpose.
frame
according to the series 1.020 communication. Frame-panel
system with a supporting reinforced concrete frame and external
concrete or non-concrete walls
panels. As a horizon diaphragms
rigidity, prefabricated reinforced concrete disks are used
floors, bonded and near-wall
floor slabs are welded with
embedded parts with crossbars and between
themselves, the seams between the plates are filled
concrete, which provides joint
work of all floor slabs, forming
solid hard drive. As
vertical J - transverse and longitudinal
stiffening walls.
Step
columns in the plane of frames L=3;
3.6; 6; 7.2; 9 m, from plane a=3;
3.6; 6; 7.2; 9.0; 12.0 m. Floor height can
be 3.3; 3.6; 4.2; 4.8; 6; 7.2 m
columns:
— extreme (1 console); - medium (2 consoles).
By
building height: - jointless; - for the whole
building height; - butt (lower, middle,
top).
joint
upper and lower columns are performed on
height 600 mm.
By
section: - 300x300; - 400x400.

crossbars:
design tee section with a shelf
on the bottom. Designed for height or
width. Height: 450 (spans up to 7.2 m), 600.
|
single shelf |
two-shelf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
joint |
|
|
|
|
Foundations:
a) columnar glass type. Cup
installed by a foundation crane
preparation (100-200 mm) and concrete (200 mm).

b)
piled on “bushes” of piles, are used
with weak soils. Pile bushes - 3-4 piles,
used under columns. Piles unite
on top of the grillage, on which
glass is installed. Grill size
depends on the diameter of the piles.
Tape
(monolithic) - under stiffening diaphragms,
under brick walls.
P do you
do you
floors
- wall liaison, ordinary,
intercolumn ties. Provide
rigidity and stability. Under the bathrooms
use plumbing ribbed
plates.
For
coatings


|
For |
|
|
|
additional
|
diaphragms
rigidity - solid;
with openings for doors.
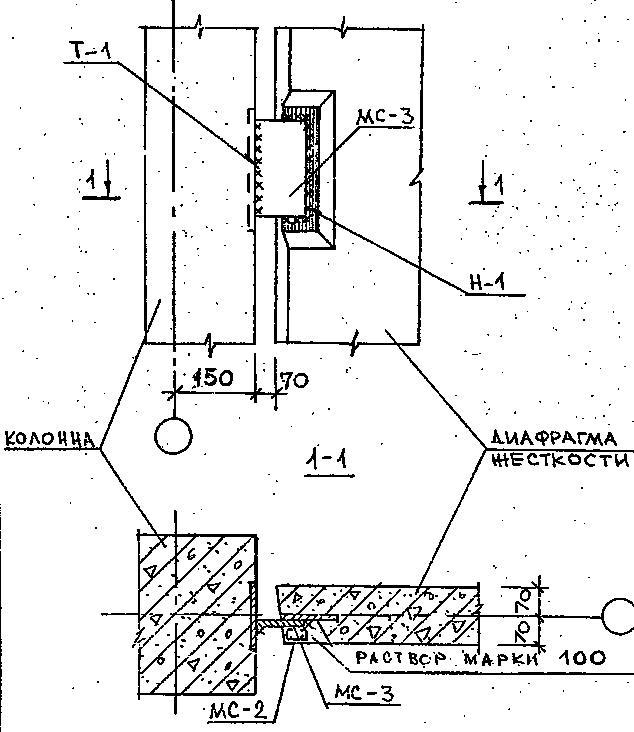
Knot
fixing the J to the column with the help of mortgages
parts (ZD)
General
diaphragm type
ZD
must be at least 2 and depends on the height
floors.
|
J
|
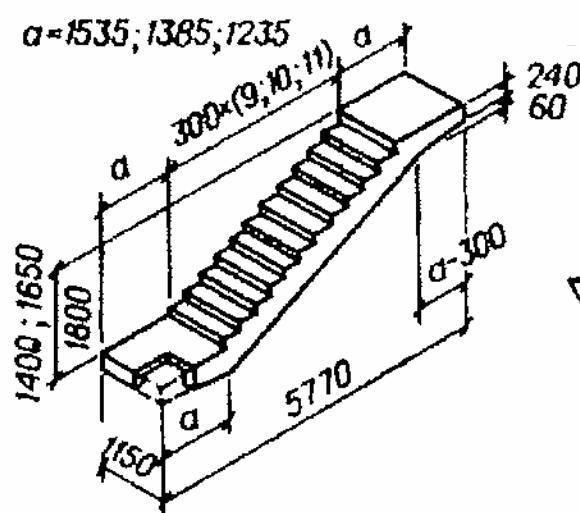
Stair
cells
located in a 3x6m cell. stairs
assembled from monolithic bent
ribbed marching platforms
nominal span 6m, width 1.15m.
Wall
panels - apply:
a) single-layer panels (lightweight or cellular
concrete and have a leveling layer -
improve plaster or tile), b)
multilayer (reinforced concrete shell thickness 50 mm,
inside there is a slab heater,
total thickness panels should not exceed
300mm).
By
location: ordinary - hung
on the frame columns, basement 90cm,
parapet 1.2 or 1.8m); parietal;
corner pas
Neli.

Features of a wet facade using Senergy technology
Like any other plaster system, Senergi includes a heater that is attached to the wall with dowels, anchors, glue, as well as a plaster layer on a reinforcing mesh. A feature is the optimally selected composition of elements to ensure long-term operation of all components as a whole. For facade insulation according to the Senergy system, only certified materials are used. To perform the work, only installers who have been trained in the technology of work are involved. Special requirements for ambient temperature - not lower than +5°C.
The technology of the device is as follows: the components (mineral wool) are glued together, forming plates with no gaps, joints, then fixed with dowels.The latter are driven into concrete up to 4 cm, with a brick version of the walls up to 5 cm, in the case of cinder-concrete structures - 9 cm. After that, the mineral slab is opened with an adhesive. Next, a reinforcing fiberglass mesh is mounted.
The insulation system creates a pleasant microclimate in the room, and also has a number of advantages:
- Excellent temperature conditions in the house, protection of walls from the harmful effects of climate.
- Installing an external type of insulation creates a barrier for cooling the wall, the appearance of condensate in the building itself.
- Accumulative characteristic that allows heat to accumulate even when the heating system is switched off.
Structural solutions for prefabricated monolithic buildings of the b1.020.1-7 series. Carrier structure.
V
depending on the type of carrier
distinguish between two main
constructive
schemes of buildings and structures:
a.
frame b. frameless.
By
method of manufacturing reinforced concrete
frame structures
are separated
on the:
prefabricated;
monolithic;
· prefabricated-monolithic.
V
depending on the method of providing
strength,
rigidity
and building stability frame systems
are separated
on the:
—
frame
—
communication
- frame-bonded.
V
frame frame system vertical
and horizontal
loads
perceived by columns united
with disks
floors.
V
bonded frame system vertical
load
perceived
columns combined with disks
coverings, and
horizontal
- vertical stiffness diaphragms.
V
frame-bonded frame system
vertical and part
horizontal
loads are taken by columns,
combined with
discs
floors, and the rest is horizontal
load -
vertical
stiffness diaphragms.
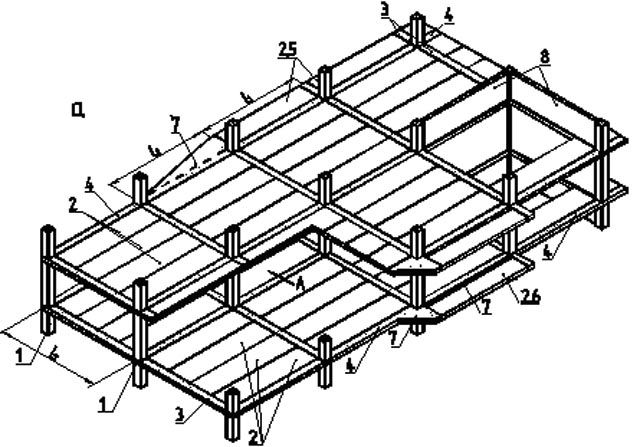
Building
B1.020.1-7 series
include load-bearing prefabricated reinforced concrete
frame-braced frame and floor-supported
cover discs. The frame includes
myself:
-
prefabricated
or monol. columns; -
Prefabricated monoline
floor discs; -
Monolithic
crossbar; -
diaphragms
stiffness.
Carriers
and tie bars provide continuity
cover disks.
diaphragms
stiffness is designed in two directions
to ensure rigidity. D. how
the rule is designed near the elevator shaft
and staircase.
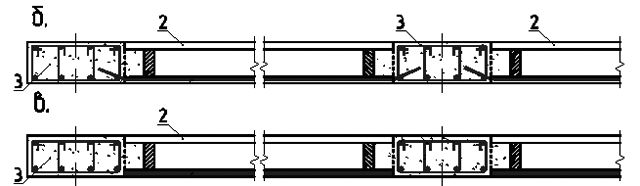
Enclosing
designs
perform in the form of external walls and floor by floor
supported partitions placed in
anywhere on the disc overlap. outdoor
walls are usually made in the form
masonry from various piece products
Building
for this series allows you to create
free planning of apartments and apartments
in two levels.
1
- prefabricated or monolithic reinforced concrete columns,
2 - hollow core slabs, 3 - bearing
monolithic crossbars, 4 - bonded monolithic
crossbars, 5 - consoles for the device
bay windows and balconies, 6 - consoles for
installation of bay windows and balconies, 7 -
monolithic sections of floors, 8 -
vertical diaphragm
rigidity
Facades with a heavy plaster layer
This system consists of heat-insulating stone wool slabs based on ROCKWOOL Fasrock, Fasrock Max basalt fiber, installed on an insulated wall on special movable brackets. In these systems, ROCKWOOL Fasrock, Fasrock Max slabs are protected from atmospheric influences with a layer of mineral plaster more than 20 mm thick on a welded metal mesh with subsequent decorative finishing.
External insulation system with a thick plaster layer: 1 - insulated wall; 2 - fixing anchor; 3 - movable hook; 4 - ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max slabs; 5 - mounting plate; 6 - steel welded mesh; 7 - the main plaster layer; 8 - decorative plaster layer.
External insulation systems with ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max boards and a thick plaster layer can be used both in the construction of new buildings and in the reconstruction of existing residential and public buildings.
In these systems, ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max insulation boards are pierced onto the moving part of the stainless steel brackets. The insulation is attached to the wall without an adhesive solution, which ensures separate operation of the bearing part of the insulated wall and the heat-insulating layer.ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max boards are installed with bandaging of seams (horizontally, at the corners of the building) and are fixed on movable brackets with special steel plates or studs. On the fasteners, a welded steel wire mesh is fixed on top of the ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max plates, on which plaster layers (priming, leveling and decorative) are applied, the total thickness of which is more than 20 mm.
To compensate for temperature deformations in the plaster layer, expansion joints are arranged horizontally and vertically every 12–15 m, as well as vertical joints at the corner of the building. Horizontal joints are more than 6 mm thick and are subsequently sealed with closed-cell sealing tape or sealant. Vertical seams can be left open.
The device of expansion joints: 1 - insulated wall; 2 - fastener; 3 - ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max slabs; 4 - steel welded mesh; 5 - plaster layers
Expansion joints are cut in the plaster layer to the full depth of the plaster to the insulation. After that, a finishing layer is applied, during the construction of which it is necessary to avoid leakage of the mortar into the expansion joints or clear them before the mortar sets.
In systems with a thick plaster layer, an expansion joint should also be provided when adjoining window blocks.
Works on wall insulation from the outside with subsequent plastering on the grid are associated with wet processes, so they must be carried out at an outside air temperature of at least +5 ° C.
PRODUCTION INSTRUCTIONS
1. At the level of the lower edge of the insulation system, a guide steel corner is mounted.
2. Fasteners are installed in holes drilled with a step of not more than 500–600 mm at the rate of 4–5 pcs/m2.
3. Prick ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max stone wool slabs onto the moving part of the brackets. If necessary, fix the insulation plates on the movable hook with steel plates.
4. Install steel wire reinforcing mesh panels over the ROCKWOOL Fasrock or Fasrock Max slabs and fix it on the movable brackets with special plates and studs.
5. Apply the first plaster layer - "spray" with a thickness of 7-10 mm.
6. Apply the main leveling plaster layer 10 mm thick.
7. Arrange vertical and horizontal expansion joints 6–10 mm thick every 12–15 m.
8. Close horizontal seams with sealing materials with closed pores and sealing mastic.
9. A finishing layer with a thickness of 2-5 mm is applied, preventing the mortar from entering the expansion joints or clearing them until the mortar sets.







 J
J