1 What is a thermal energy metering unit
Thermal unit - a set of equipment, the installation of the project of which is provided in order to provide basic accounting and regulation of energy, the volume of the coolant, as well as the registration and control of its parameters.

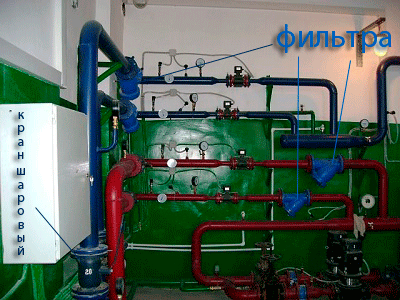
Thermal energy metering unit
Heat energy metering unit - an automatic module, which is installed to the pipeline system to provide accounting data for the project of operation and regulation of heating resources.
1.1 Where are the heating units installed?
Installation of thermal units and their maintenance, as a rule, is carried out in typical apartment buildings, with communal heating systems.
In turn, heat energy metering units are installed in an apartment building to perform the following tasks:
- verification and regulation of the operation of the coolant and thermal energy;
- testing and regulation of hydraulic and heating systems;
- records of fluid data such as temperature, pressure and volume.
- the product of the monetary calculation of the consumer and the supplier of thermal energy, after the verification of the received data is carried out.
Installation of heat energy metering units
When implementing the installation project of heating equipment should be taken into account. that the consumption of resources supplied to the central heating in an apartment building incurs certain financial costs for users (in this case, residents of an apartment building).
The apartment building will be able to reduce costs, as well as maintain the performance of the unit built according to the previously designed scheme for a long time, if competent checks of accounting equipment and its maintenance are provided in a timely manner, including high-quality installation of equipment and pipelines.
Automation of the process of regulating the heat supply of MKD
The existing system of transportation and distribution of thermal energy is far from ideal. Its imperfection is especially acutely felt during the off-season. It often happens - the weather is consistently warm outside, the batteries stubbornly heat the already warm rooms. This situation is due to the fact that the only link in the chain of enterprises, communications and coolant supply devices
, which has the ability to influence the process of heat supply, is a boiler house or a CHP. But even they do not have the possibility of flexible regulation, they do not have mechanisms that allow them to instantly respond to changes in the weather.
Individual metering of heat supply allows the consumer to carry out regulation of the amount of heat energy consumed
. This can be achieved by setting a lower temperature in rooms that are not in use, raising it as needed.
The regulation of the heat supply can be implemented by closing the taps on the radiators. In addition, you can entrust the regulation process to automation. Modern industry offers various devices that allow you to control the temperature of the room. The most common of them are radiator thermostats. These are devices consisting of a thermostatic head and a valve. The sensor measures the room temperature and controls the valve. Depending on the presettings, the valve increases or decreases the flow of the coolant by adjusting the heating level.
Thanks to the possibility of fine tuning, this device allows you to adjust the microclimate inside the building, maintain a comfortable atmosphere, and save energy. There are various types of radiator thermostats. Most of them allow you to set the temperature value that the owner of the room wants to receive.There are more complex models. Some of them allow you to set the temperature for different times of the day, for example, they can limit the heat supply during the day when there is no one in the apartment, and in the late afternoon warm the room to a comfortable level.
Waterproofing of pipeline passages
The waterproofing of the pipeline has its own characteristics and difficulties. When performing such work, it is necessary to take into account not only the strong pressure of water from the outside, but also the response pressure of internal fluids, as well as the constant temperature difference. Ordinary sealants will not be able to withstand such a significant load for a long time. Therefore, for the entrances, passages and inlets of the pipeline, the principle of a three-component hydraulic seal is used.
Such a hydraulic seal consists of non-shrinking concrete mixtures and a polyurethane composition. The use of such a design is especially effective in buildings where significant drying and movement of the structure is expected. As a polyurethane filler used:
- Akvidur TS-B,
- Akvidur ES,
- Akvidur TS-N.
Node characteristics and features of work
According to the diagrams, it can be understood that the elevator in the system is needed to cool the superheated coolant. In some designs there is an elevator that can also heat water. Especially such a heating system is relevant in cold regions. The elevator in this system starts only when the cooled liquid is mixed with hot water coming from the supply pipe.
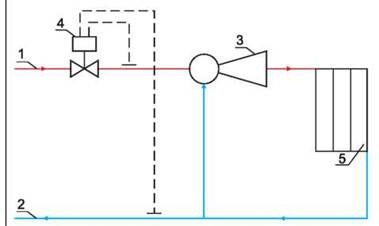
According to this scheme, it can be understood that the node significantly increases the efficiency of the entire heating system in the house. It works simultaneously as a circulation pump and a mixer. As for the cost, the node will cost quite cheaply, especially the option that works without electricity.
But any system has its drawbacks, the collector unit is no exception:
- Separate calculations are required for each element of the elevator.
- Compression drops should not exceed 0.8-2 bar.
- Inability to control high temperature.
The cost of sealing the passages of engineering communications
The cost of waterproofing the passages of engineering communications and the period of work in each case are determined individually - they depend on the volume and complexity. Our specialists will be happy to come to your site at a convenient time for you to assess the situation. They will choose the most optimal option for sealing technological openings and advise certain materials for waterproofing, make an estimate. We are always happy to help you!
The passage of the pipe through the foundation is carried out in accordance with the norms of SNiP. The technology for connecting the engineering systems of a cottage depends on the type of foundation:
According to the requirements of SNiP, the entrance of the pipeline to the building is insulated: waterproofing and thermal insulation.
- monolithic slab - first, two water supply lines, two sewage pipelines (one working, the second backup) are mounted, then sleeves with branch pipes coming out of them are mounted in the places of risers, reinforced concrete is poured;
- - the technology is similar to the previous one, only the sleeves are mounted in the vertical walls of the base at a depth below the freezing mark;
- prefabricated strip foundation - technological gaps are left between the blocks, laid with red brick, into which sleeves / pipes are embedded.
Schemes of thermal units
If we talk about schemes of heat points, it should be noted that the following types are the most common:
Thermal unit - a scheme with a parallel one-stage connection of hot water. This scheme is the most common and simple. In this case, the hot water supply is connected in parallel to the same network as the heating system of the building.The coolant is supplied to the heater from the external network, then the cooled liquid flows in the reverse order directly into the heat pipeline. The main disadvantage of such a system, in comparison with other types, is the high consumption of network water, which is used to organize hot water supply.
Scheme of a heat point with a serial two-stage connection of hot water. This scheme can be divided into two stages. The first stage is responsible for the return pipeline of the heating system, the second - for the supply pipeline. The main advantage that thermal units connected according to this scheme have is the absence of a special supply of network water, which significantly reduces its consumption. As for the disadvantages, this is the need to install an automatic control system to adjust and adjust the heat distribution. Such a connection is recommended to be used in the case of a ratio of the maximum heat consumption for heating and hot water supply, which is in the range from 0.2 to 1.
Thermal unit - a scheme with a mixed two-stage connection of a hot water heater. This is the most versatile and flexible connection scheme in settings. It can be used not only for a normal temperature graph, but also for an increased one. The main distinguishing feature is the fact that the connection of the heat exchanger to the supply pipeline is carried out not in parallel, but in series. The further principle of the structure is similar to the second scheme of the heat point. Thermal units connected according to the third scheme require additional consumption of network water for the heating element.
How is the thermal unit arranged
In general, the technical device of each heat point is designed separately, depending on the specific requirements of the customer. There are several basic schemes for the execution of heat points. Let's look at them in turn.
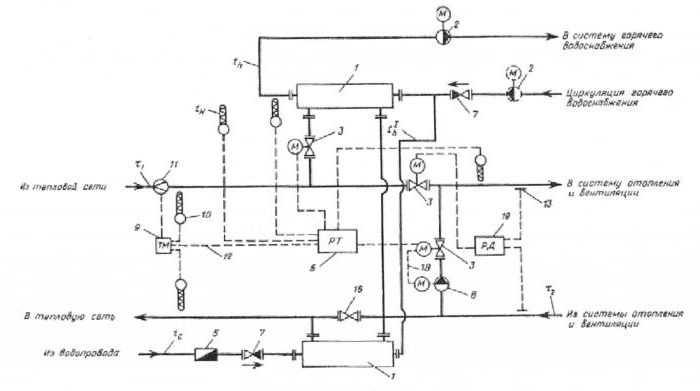
Thermal unit based on the elevator.
The scheme of a thermal point based on an elevator unit is the simplest and cheapest. Its main drawback is the inability to regulate the temperature of the coolant in the pipes. This causes inconvenience for the end user and a large overconsumption of thermal energy in case of thaws during the heating season. Let's look at the figure below and understand how this circuit works:
In addition to what is mentioned above, a pressure reduction reducer can be included in the thermal unit. It is installed at the feed in front of the elevator. The elevator is the main part of this scheme, in which the cooled coolant from the "return" is mixed with the hot coolant from the "supply". The principle of operation of the elevator is based on the creation of a vacuum at its outlet. As a result of this rarefaction, the coolant pressure in the elevator is less than the coolant pressure in the "return" and mixing occurs.
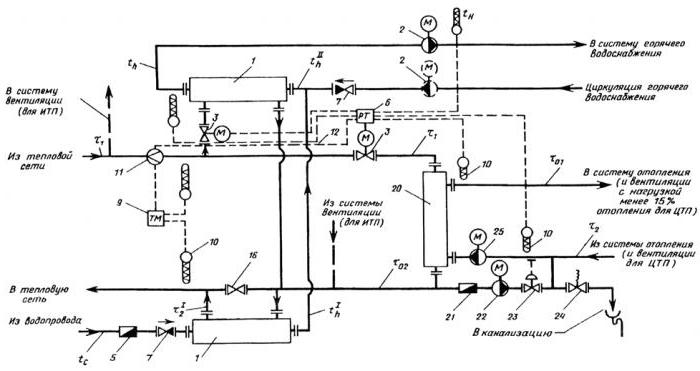
Thermal unit based on a heat exchanger.
A heat point connected through a special heat exchanger allows you to separate the heat carrier from the heating main from the heat carrier inside the house. Separation of heat carriers allows its preparation with the help of special additives and filtration. With this scheme, there are ample opportunities in regulating the pressure and temperature of the coolant inside the house. This reduces heating costs. In order to have a visual representation of this design, look at the figure below.

The mixing of the coolant in such systems is done using thermostatic valves. In such heating systems, in principle, aluminum heating radiators can be used, but they will last for a long time only if the quality of the coolant is good. If the PH of the coolant goes beyond the limits approved by the manufacturer, then the service life of aluminum radiators can be greatly reduced. You cannot control the quality of the coolant, so it is better to play it safe and install bimetallic or cast iron radiators.
Domestic hot water can be connected in this way via a heat exchanger. This offers the same benefits in terms of hot water temperature and pressure control. It is worth saying that unscrupulous management companies can deceive consumers by lowering the temperature of hot water by a couple of degrees. For the consumer, this is almost not noticeable, but on the scale of the house it allows you to save tens of thousands of rubles a month.
Commissioning of the metering unit. Adjacent heating networks, jumpers
Resource supply of housing and communal services > Heat supply > Commercial metering of thermal energy. Decree 1034
RULES FOR COMMERCIAL ACCOUNTING OF THERMAL ENERGY, HEAT CARRIER
Commissioning of the metering station installed at the consumer, on adjacent heat networks and on jumpers
61. The mounted metering unit, which has undergone trial operation, is subject to commissioning.62. Commissioning of the metering unit installed at the consumer is carried out by a commission consisting of: a) a representative of the heat supply organization; b) a representative of the consumer; c) a representative of the organization that carried out the installation and commissioning of the metering unit being put into operation.63. The commission is created by the owner of the metering unit.64. To put the metering station into operation, the owner of the metering station submits to the commission a project of the metering station, agreed with the heat supply organization that issued the technical specifications and the certificate of the metering station or the draft passport, which includes: and diameters of pipelines, shut-off valves, control and measuring devices, mud collectors, drains and jumpers between pipelines; b) certificates of verification of instruments and sensors to be verified with valid verification marks; c) a database of tuning parameters entered into the measuring unit or heat calculator ;d) a scheme for sealing measuring instruments and equipment that is part of the metering unit, excluding unauthorized actions that violate the reliability of commercial metering of thermal energy, coolant; e) hourly (daily) statements of continuous operation of the metering unit for 3 days (for objects with hot water supply - 7 days j).65. Documents for putting the metering unit into operation are submitted to the heat supply organization for consideration at least 10 working days before the expected day of commissioning.66. When accepting the metering unit for operation, the commission checks: a) compliance of the installation of the components of the metering unit with project documentation, technical conditions and these Rules; b) the availability of passports, certificates of verification of measuring instruments, factory seals and brands; c) compliance of the characteristics of measuring instruments with the characteristics specified in the passport data of the metering unit; d) compliance of the measurement ranges of parameters allowed by the temperature schedule and the hydraulic mode of operation of heat networks with the values of the specified parameters determined by the contract and the conditions for connecting to the heat supply system.67. In the absence of comments on the metering unit, the commission signs the act of commissioning the metering unit installed at the consumer.68. The act of commissioning the metering unit serves as the basis for conducting commercial accounting of thermal energy, heat carrier according to metering devices, quality control of thermal energy and heat consumption modes using the received measurement information from the date of its signing.69. When signing the act on commissioning of the metering unit, the metering unit is sealed.70. The sealing of the metering unit is carried out: a) by a representative of the heat supply organization if the metering unit belongs to the consumer; b) by the representative of the consumer who has the metering unit installed.71. Places and devices for sealing the metering station are prepared in advance by the installation organization.The places of connection of primary converters, connectors of electrical communication lines, protective covers on the adjustment and adjustment devices of devices, power supply cabinets of devices and other equipment, interference in the operation of which may lead to distortion of measurement results, are subject to sealing.72. If the members of the commission have comments on the metering unit and identify deficiencies that impede the normal functioning of the metering unit, this metering unit is considered unsuitable for commercial metering of thermal energy, coolant. In this case, the commission draws up an act on the identified deficiencies, which provides a complete list of the identified deficiencies and deadlines for their elimination. The specified act is drawn up and signed by all members of the commission within 3 working days. Re-acceptance of the metering unit for operation is carried out after the complete elimination of the identified violations.73. Before each heating period and after the next verification or repair of metering devices, the readiness of the metering unit for operation is checked, about which an act of periodic inspection of the metering unit at the interface between adjacent heat networks is drawn up in the manner established by paragraphs 62 - 72 of these Rules.
_______________________________________
Hermetic partition of the heating main. Sealing of engineering communications inputs
Insufficiently high-quality waterproofing of the entry points of various engineering communications, in particular, pipes, cables, is one of the most common mistakes of builders and designers. Due to the fact that the so-called cold joint remains at the “concrete-metal” or “concrete-plastic” joints, water enters through them into the basement recessed rooms
That is why it is very important to carry out complete sealing of pipe entries, using modern waterproofing technologies.
Pipe entries are one of the most vulnerable places, since they are in direct contact with various building structures. In the event of a leak, significant damage can be done to the entire building, walls and ceilings will be damaged. In addition, due to leaks, efflorescence and stains, fungus appear on the moist surface of the walls, finishing coatings peel off, and all this invariably leads to additional costs for cosmetic repairs. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to carry out sealing of pipe and communications inlets in a quality and timely manner.
Sealing of pipe entries can be carried out at various stages, including:
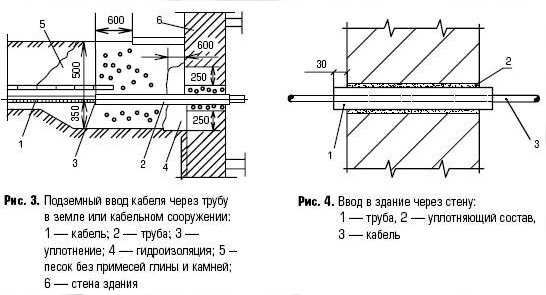
- Sealing of pipe entries at the construction stage. For this, various hydraulic gaskets, waterstops and hydraulic cords can be used. The technology for sealing pipe inlets in this way is carried out in the following sequence: before pouring concrete, a ring (or two rings) of hydrophilic rubber is mounted on the pipe (butt, without breaks or overlap). The ring is attracted to the pipe or glued with a swelling sealant.
- Sealing of pipe entries at the stage of installation and repair. There are several options for waterproofing joints, depending on the material from which the buried part of the building is built. If these are FBS blocks, then the pipe inlets are sealed in such a way that the ring of the hydraulic cord is in the middle of the wall thickness. If it is brickwork, then it is possible to seal the pipe entries by filling the hole in the wall with cement mortar. Regardless of the design of the wall, it is possible to perform waterproofing of the inputs using the injection method.
At whatever stage of the building operation you carry out sealing of engineering communications (pipes, etc.), you cannot do without the use of special materials, such as hydraulic seals, swelling cords and sealants, multicomponent polyurethane and acrylate materials that can harden by binding physically and chemically water, and not leak unbound water.
When sealing pipe entries and communications, it should be remembered that the service life of wall structures subject to moisture, due to corrosion of metal and concrete, destruction of bricks, is greatly reduced
Therefore, waterproofing work is very important to carry out in a timely manner.
One of the most vulnerable points of any communications is the place where a cable or wire enters the wall of a building, into a switchgear, an actuator, etc. Today, there are many options for protecting cable passages from moisture, we tried to collect the most effective of them for readers site in this article. So, let's figure out now how the sealing of cable entries into a building, an ASU cabinet, etc. can be performed.
What are the rules and requirements?
The regulatory documents PUE 2.1.58 and SNiP 3.05.06-85 describe the requirements for cable passages:
According to the above requirements, it turns out that the cable gland in the building must be able to retain water, not support combustion and prevent the spread of fire. With all this, be able to re-replace the cable or wire, if necessary.
Sealing methods
To seal the input in a private house or cottage, fire-retardant polyurethane foam is most often used, evenly distributing it in the pipe around the cable. After hardening, the mounting foam is cut off and partially rammed, pressing into the pipe. The resulting recesses are plastered with cement mortar. An example of such an option for sealing a cable line is shown in the photo below:
Setting the temperature in an apartment building on the return and supply
Installation of the heating system regulator will depend on its general device
. If the CO is installed individually for a particular room, the improvement process takes place due to the following factors:
- system works from a boiler of individual power
; - set special three-way valve
; -
coolant pumping
going on by force
.
In general, for all COs, power adjustment work will consist of installation of a special valve
to the battery itself.
With it, you can not only adjust the heat level
in the right places, but exclude the heating process altogether in those areas that are poorly used
or not functioning.
There are the following nuances in the process of adjusting the heat level:
- Central heating systems to be installed in multi-storey buildings
, are often based on coolants, where feed is strictly vertical from top to bottom.
In such houses, it is hot on the upper floors, and cold on the lower ones, so it will not be possible to adjust the heating level accordingly. - If used in homes single pipe network
, then heat from the central riser is supplied to each battery and returned back, which ensures uniform heat on all floors of the building. In such cases, it is easier to install heat control valves - installation takes place on the supply pipe
and the heat continues to spread evenly. -
For two pipe system
there are already two risers mounted - heat is supplied to the radiator and in the opposite direction, respectively, the adjustment valve can be install in two places - on each of the batteries.
Types of regulating valves for batteries
Modern technologies are far from standing still and allow for each heating radiator to install quality and reliable faucet
, which will control the level of heat and heat. It is connected to the battery with special pipes, which will not take much time.
By types of adjustment, I distinguish two types of valves
:
-
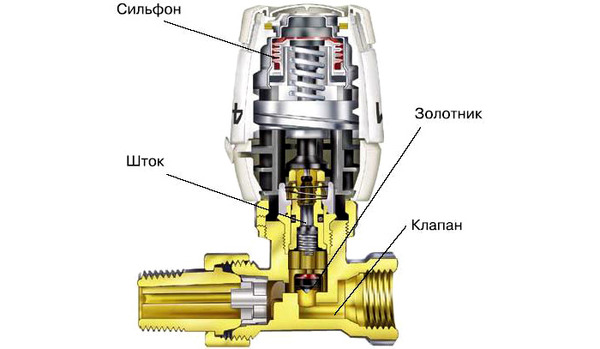
Conventional thermostats with direct action.
Installed next to the radiator, it is a small cylinder, inside which is hermetically located siphon based on liquid or gas
, which quickly and competently responds to any temperature changes. If the temperature of the battery rises, the liquid or gas in such a valve expands, there will be pressure on valve stem
a heat regulator that will move and block the flow. Accordingly, if the temperature drops, the process will be reversed.
Photo 1. Scheme of the internal device of the thermostat for the battery. The main parts of the mechanism are indicated.
-
Temperature controllers based on electronic sensors.
The principle of operation is similar to conventional regulators, only the settings differ - everything can be done not in manual mode, but in electronic mode - to set functions in advance, with a possible delay in time and temperature control.
How to adjust heating radiators
Standard process for temperature control of heating radiators consists of four stages
- bleeding air, adjusting pressure, opening valves and pumping coolant.
-
Air bleeding
. Each radiator has a special valve, by opening which you can release excess air and steam, which prevents the battery from heating. within half an hour
after such a procedure, the required heating temperature must be reached. -
Pressure regulation
. In order for the pressure in the CO to be evenly distributed, you can turn the shut-off valves of different batteries attached to one heating boiler by a different number of revolutions. This adjustment of the radiators will heat the room as quickly as possible. -
Opening valves
. Installation of special three-way valves
on radiators will allow you to remove heat in unused rooms or limit heating, for example, during your absence from the apartment during the day. It is enough just to close the valve completely or partially.
Photo 2. A three-way valve with a thermostat that allows you to easily adjust the temperature of the heating radiator.
-
Coolant pumping.
If CO is forced, the coolant is pumped using control valves, with the help of which a certain amount of water is drained to give the heating radiator the opportunity to heat up.
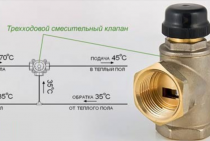
Dependent scheme with a three-way valve and circulation pumps

Dependent scheme for connecting a heating substation of a heating system to a heat source with a three-way valve for a heat flow regulator and circulation-mixing pumps in the supply pipeline of the heating system.
This scheme in ITP is used under the following conditions:
1 The temperature schedule of the heat source (boiler room) is greater than or equal to the temperature schedule of the heating system. The heat point connected according to this concept can work both with admixture to the flow from the return pipeline, and without it, that is, let the coolant from the supply pipeline of the heating network directly into the heating system.
For example, the calculated temperature curve of the heating system 90/70°C is equal to the temperature curve of the source, but the source, regardless of external factors, always works with an outlet temperature of 90°C, and for the heating system, it is necessary to supply a coolant with a temperature of 90°C only at the calculated outside air temperature (for Kiev -22°C). Thus, at the heating point, the cooled coolant from the return pipeline will be mixed with the water coming from the source until the outside air temperature drops to the calculated value.
2 The heating substation is connected to a non-pressure collector, a hydraulic arrow or a heating main with a pressure difference between the supply and return pipelines of not more than 3 m of water.
3 The pressure in the return pipeline of the heat source in static and dynamic modes exceeds the height from the point of connection of the heat point to the top point of the heating system (building statics) by at least 5 m.
4 The pressure in the supply and return pipelines of the heat source, as well as the static pressure in the heating networks, do not exceed the maximum allowable pressure for the heating system of the building connected to this IHS.
5 The connection scheme of the heat point should provide automatic high-quality control by the heating system according to the temperature or time schedule.
Description of the operation of the ITP circuit with a three-way valve
The principle of operation of this scheme is similar to the operation of the first scheme, except that the three-way valve can completely block the extraction from the return pipeline, in which all the coolant coming from the heat source without admixture will be supplied to the heating system.
In the case of a complete shutdown of the supply pipeline of the heat source, as in the first scheme, only the coolant that has left it and is taken from the return will be supplied to the heating system.

Dependent scheme with a three-way valve, circulation pumps and a differential pressure regulator.
It is used when the pressure drop at the point of connection of the IHS to the heating network exceeds 3 m of water. The pressure drop regulator in this case is selected for throttling and stabilizing the available pressure at the inlet.
Supply and regulation of heat in a two-pipe scheme
This option is more complex, but allows you to significantly expand the capabilities of the mechanisms regulation of heat supply to each consumer
. The difference between the system is that the coolant that has given up part of the energy does not continue to move through the same pipe to the next consumer, it flows into the second pipe, the “return”. Due to this, the coolant has approximately the same temperature all the way, at each radiator.
This solution makes it possible to regulation of heat supply in an apartment building
using each individual radiator. You can regulate the temperature both manually, with a valve, and automatically, using temperature controllers.
Regardless of how the heat supply is implemented, the system must include devices for automatic metering and regulation of heat supply in an apartment building. This allows not only to provide housing with the heat necessary for life, but also to significantly save energy resources.
In apartments or private houses, residents often encounter the phenomenon uneven heating of radiators
heating in different parts of the home. Such situations are typical in cases where the premises are connected to autonomous heating systems.
How optimize the system
heating (CO), stop overpaying and how the installation of a thermostat for batteries will help - we will consider further.