502 bad gateway
A few general but important notes In order to be able to talk about the correct operation of the heating system and its setup and adjustment, first you need to make sure that your country house heating system is correctly designed, installed, and heating equipment is correctly selected. This approach is dictated by the fact that often in private homes, heating systems are “sculpted” by teams of “shabashniks”. And how, what, and on the basis of what they do, often remains a big secret for homeowners.
Therefore, I have to draw the reader's attention to a few, in general, common truths, without understanding which it is not serious to talk about tuning and adjustment. Stage number 1 The first thing to make sure is that the parameters of the boilers correspond to the parameters of the heating system
The arithmetic here is simple.
Temperature norms
 The requirements for the temperature of the coolant are set out in the regulatory documents that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State building codes and regulations:
The requirements for the temperature of the coolant are set out in the regulatory documents that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State building codes and regulations:
- DBN (V. 2.5-39 Heat networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning".
For the calculated temperature of the water in the supply, the figure is taken that is equal to the temperature of the water at the outlet of the boiler, according to its passport data.
For individual heating, it is necessary to decide what the temperature of the coolant should be, taking into account such factors:
- 1 Beginning and end of the heating season according to the average daily temperature outside +8 °C for 3 days;
- 2 The average temperature inside the heated premises of housing and communal and public importance should be 20 °C, and for industrial buildings 16 °C;
- 3 The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning" (clause 3.20), the limiting indicators of the coolant are as follows:
- 1 For a hospital - 85 °C (excluding psychiatric and drug departments, as well as administrative or domestic premises);
- 2 For residential, public, as well as domestic buildings (excluding halls for sports, trade, spectators and passengers) - 90 ° С;
- 3 For auditoriums, restaurants and production facilities of category A and B - 105 °C;
- 4 For catering establishments (excluding restaurants) - this is 115 °С;
- 5 For production premises (categories C, D and D), where combustible dust and aerosols are released - 130 ° C;
- 6 For stairwells, vestibules, pedestrian crossings, technical premises, residential buildings, industrial premises without flammable dust and aerosols - 150 °С.
Depending on external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 ° C, dust and paintwork begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit more heating.
To calculate the optimal indicators, special graphs and tables can be used, in which the norms are determined depending on the season:
- With an average value outside the window of 0 °С, the supply for radiators with different wiring is set at a level of 40 to 45 °С, and the return temperature is from 35 to 38 °С;
- At -20 °С, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °С, while the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °С;
- At -40 ° C outside the window for all heating devices set the maximum allowable values. At the supply it is from 95 to 105 ° C, and at the return - 70 ° C.
Heating standards for apartment buildings heated centrally
These norms are the most "ancient".They were calculated at a time when they did not save on fuel for heating the coolant, the batteries were hot. But the houses were built mainly from materials that were “cold” in terms of heat-saving qualities, that is, from concrete panels.
Times have changed, but the rules remain the same. According to the current GOST R 52617-2000, the air temperature in residential premises should not be lower than 18 ° C (for corner rooms - at least 20 ° C). At the same time, the organization - the supplier of thermal energy has the right to reduce the air temperature by no more than 3 ° C at night (0-5 hours). Separately, heating standards are set for various rooms of the apartment: for example, in the bathroom it should be at least 25 ° C, and in the corridor - at least 16 ° C.
For a long time and at times not without success, society has been fighting to change the procedure for determining heating standards, tying them not to the air temperature in the premises, but to the average temperature of the coolant. This indicator is much more objective for consumers, although unprofitable for the heat supplier. Judge for yourself: the temperature in residential premises often depends not only on the operating system, but on the nature of human life and living conditions.
For example, the thermal conductivity of a brick is much lower than that of concrete, so a brick house at the same temperature will have to spend less heat energy. In rooms such as the kitchen, the heat generated during cooking is not much less than from radiators.
Much also depends on the design features of the heating devices themselves. Say, panel heating systems at the same air temperature will have a higher heat transfer than cast iron batteries. Thus, heating norms tied to air temperature are not entirely fair. This method takes into account the outdoor temperature below 8°C. If this value is fixed for three consecutive days, the heat generating organization must unconditionally supply heat to consumers.
For the middle band, the calculated values of the temperature of the coolant, depending on the temperature of the outside air, have the following values (for convenience of using these values, using household thermometers, the temperature indicators are rounded):
Outside air temperature, °С
Temperature of network water in the supply pipeline, °С
Using the above table, you can easily determine the temperature of the water in the panel heating system (or in any other), using a conventional thermometer at the moment a part of the coolant is drained from the system. For the direct branch, the data of columns 5 and 6 are used, and for the return line, the data of column 7. Note that the first three columns set the outlet temperature of the water, that is, without taking into account losses in the transmission main pipelines.
If the actual temperature of the heat carrier does not correspond to the standard, this is the basis for a proportional reduction in the payment for the provided district heating services.
There is another option with the installation of heat meters, but it works only when all apartments in the house are served by a central heating system. In addition, such meters are subject to an annual mandatory inspection.
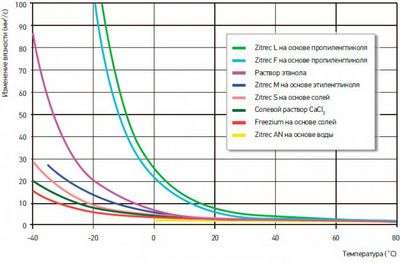
Antifreeze as a coolant
Higher characteristics for the efficient operation of the heating system have such a type of coolant as antifreeze. By pouring antifreeze into the heating system circuit, it is possible to reduce the risk of freezing of the heating system in the cold season to a minimum. Antifreeze is designed for lower temperatures than water, and they are not able to change its physical state. Antifreeze has many advantages, since it does not cause scale deposits and does not contribute to corrosive wear of the interior of the heating system elements.
Even if the antifreeze solidifies at very low temperatures, it will not expand like water, and this will not cause any damage to the heating system components. In the event of freezing, the antifreeze will turn into a gel-like composition, and the volume will remain the same. If, after freezing, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system rises, it will turn from a gel-like state into a liquid, and this will not cause any negative consequences for the heating circuit.
Many manufacturers add various additives to antifreeze that can increase the life of the heating system.
Such additives help to remove various deposits and scale from the elements of the heating system, as well as eliminate pockets of corrosion. When choosing antifreeze, you need to remember that such a coolant is not universal. The additives that it contains are only suitable for certain materials.
Existing coolants for heating systems-antifreezes can be divided into two categories based on their freezing point. Some are designed for temperatures up to -6 degrees, while others are up to -35 degrees.
Properties of various types of antifreeze
The composition of such a coolant as antifreeze is designed for a full five years of operation, or for 10 heating seasons. The calculation of the coolant in the heating system must be accurate.
Antifreeze also has its drawbacks:
- The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15% lower than that of water, which means that they will give off heat more slowly;
- They have a rather high viscosity, which means that a sufficiently powerful circulation pump will need to be installed in the system.
- When heated, antifreeze increases in volume more than water, which means that the heating system must include a closed-type expansion tank, and radiators must have a larger capacity than those used to organize a heating system in which water is the coolant.
- The speed of the coolant in the heating system - that is, the fluidity of antifreeze, is 50% higher than that of water, which means that all connectors of the heating system must be very carefully sealed.
- Antifreeze, which includes ethylene glycol, is toxic to humans, so it can only be used for single-circuit boilers.
In the case of using this type of coolant as antifreeze in the heating system, certain conditions must be taken into account:
- The system must be supplemented with a circulation pump with powerful parameters. If the circulation of the coolant in the heating system and the heating circuit is long, then the circulation pump must be outdoor installation.
- The volume of the expansion tank must be at least twice as large as the tank used for a coolant such as water.
- It is necessary to install volumetric radiators and pipes with a large diameter in the heating system.
- Do not use automatic air vents. For a heating system in which antifreeze is the coolant, only manual type taps can be used. A more popular manual type crane is the Mayevsky crane.
- If antifreeze is diluted, then only with distilled water. Melt, rain or well water will not work in any way.
- Before filling the heating system with coolant - antifreeze, it must be thoroughly rinsed with water, not forgetting about the boiler. Manufacturers of antifreezes recommend changing them in the heating system at least once every three years.
- If the boiler is cold, then it is not recommended to immediately set high standards for the temperature of the coolant to the heating system. It should rise gradually, the coolant needs some time to heat up.
If in winter a double-circuit boiler operating on antifreeze is turned off for a long period, then it is necessary to drain water from the hot water supply circuit.If it freezes, the water can expand and damage pipes or other parts of the heating system.
Comments 1
Andrey
12/13/2017 at 07:51 | #
Dear Sirs! I purchased in the fall from, through dealers, convectors built into the window sill - 3 pcs (one 3m, the other 2 1.2m each). I installed them in a window sill whose depth is 50 cm, the heating season began and it turned out that they did not even heat up. We have a townhouse of 4 floors, I live on the fourth floor, it is supposed to be another 5th floor, there is a boiler, it is heated with coal. My heating is water in the floor. The floor is warm enough, but as for the convectors, they are a little warm and, accordingly, do not cut off the cold air. The temperature in the comb reaches a maximum of 51 degrees, and as your dealers explained to me, that this temperature is not enough for a convector, at least 70 degrees is needed, but unfortunately if our boiler supplies 80 degrees, then it will be very hot in the lower floors. In this regard, I wanted to ask you for your opinion on what can be done in my case. Can I get convectors and change them to electric ones, although the repair has already been done? Then how much more expensive will it be when paying a check for electricity? Is it possible to install an electric boiler on convectors although I have very little space in the boiler room and how much will the electricity bill increase? maybe just install wall mounted radiators? Don't misunderstand me, I was advised to put built-in convectors in the window sill, as the window sill is deep, and I, in turn, refused wall-mounted radiators. At the moment, my convectors do not heat and there are no radiators, which, you see, is very insulting. I am writing to you in the hope of an answer and help. Thank you.
We assume that the coolant in the riser complies with the building regulations. It remains to find out what is the norm for the temperature of the heating batteries in the apartment. The indicator takes into account:
- outdoor air parameters and time of day;
- the location of the apartment in terms of the house;
- living or utility room in the apartment.
Therefore, attention: it is important, not what is the degree of the heater, but what is the degree of air in the room. During the day in the corner rooms, the thermometer should show at least 20 ° C, and in the centrally located rooms 18 ° C is allowed. At night, the air in the dwelling is 17 ° C and 15 ° C, respectively.
Theory of Linguistics The name "battery" is an everyday one, denoting a number of identical objects. In relation to the heating of housing, this is a series of heating sections. The temperature standards of heating batteries allow heating no higher than 90 ° C. According to the rules, parts heated above 75 ° C are protected
At night, air in the dwelling is allowed to be 17 ° C and 15 ° C, respectively. Theory of Linguistics The name "battery" is an everyday one, denoting a number of identical objects. In relation to the heating of housing, this is a series of heating sections. The temperature standards of heating batteries allow heating no higher than 90 ° C. According to the rules, parts heated above 75 ° C are protected.
Heat meters
Let us recall once again that the heat supply network of an apartment building is equipped with heat energy metering units that record both the consumed gigacalories and the cubic capacity of water passed through the house line.
In order not to be surprised by bills containing unrealistic amounts for heat at temperatures in the apartment below the norm, before the start of the heating season, check with the management company whether the meter is in working order, whether the verification schedule has been violated.
Many manufacturers of boiler equipment require that at the inlet to the boiler there be water not lower than a certain temperature, since the cold return has a bad effect on the boiler:
-
- the efficiency of the boiler is reduced,
- condensation on the heat exchanger increases, which leads to boiler corrosion,
- due to the large temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger, its metal expands in different ways - hence the stress and possible cracking of the boiler body.
The first method is ideal, but expensive.
Esbe
offers a ready-made module for adding to the boiler return and controlling the load of the heat accumulator (relevant for solid fuel boilers) - the LTC 100 device is an analogue of the popular Laddomat unit (Laddomat).
Phase 1. The beginning of the combustion process. The mixing device allows you to quickly increase the temperature of the boiler, thus starting the circulation of water only in the boiler circuit.
Phase 2: Start loading the storage tank. The thermostat, opening the connection from the storage tank, sets the temperature, which depends on the version of the product. High, guaranteed return temperature to the boiler, maintained through the entire combustion cycle
Phase 3: The storage tank is in the process of being loaded. Good management ensures efficient loading of the storage tank and proper stratification in it.
Phase 4: The storage tank is fully loaded. Even at the end of the combustion cycle, the high quality of the regulation ensures good control of the return temperature to the boiler while simultaneously fully loading the storage tank
Phase 5: End of the combustion process. By completely closing the top opening, the flow is directed directly to the storage tank, using the heat in the boiler
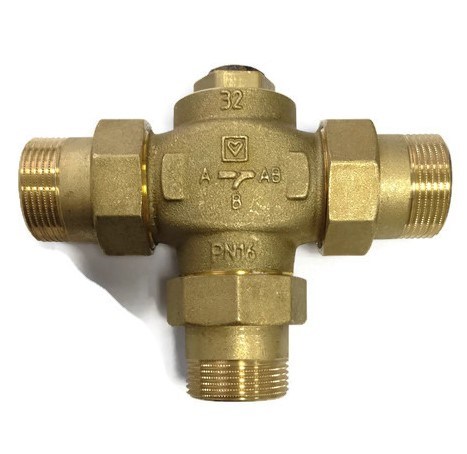
The second method is simpler, using a high quality three-way thermal mixing valve.
For example valves from ESBE or or VTC300. These valves differ depending on the capacity of the boiler used. VTC300 is used with boiler power up to 30 kW, VTC511 and VTC531 - with more powerful boilers from 30 to 150 kW
The valve is mounted on the bypass line between the boiler supply and return.
The built-in thermostat opens input "A" when the temperature at the output "AB" is equal to the thermostat setting (50, 55, 60, 65, 70 or 75°C). Inlet "B" closes completely when the temperature at inlet "A" exceeds the nominal opening temperature by 10°C.
When the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the valve "AB" is less than 61°C, the inlet "A" is closed, hot water flows through the inlet "B" from the boiler supply to the return. If the temperature of the coolant at the outlet "AB" exceeds 63°C, the bypass inlet "B" is blocked and the coolant from the return of the system through the inlet "A" enters the return of the boiler. Bypass outlet "B" reopens when the temperature at outlet "AB" drops to 55°C
When the coolant passes through outlet “AB” with a temperature of less than 61°C, inlet “A” from the return of the system is closed, and hot coolant is supplied to outlet “AB” from bypass “B”. When the outlet “AB” reaches a temperature of more than 63°C, the inlet “A” opens, and the water from the return is mixed with the water from the bypass “B”. To equalize the bypass (so that the boiler does not work constantly on a small circle of circulation), a balancing valve must be installed in front of the input "B" on the bypass.
Providing heat to apartment buildings centralized heating system
At the same time, deviations from the specified regime of the temperature of the water entering the heating network at the heat source are provided for no more than +/- 3%;
By virtue of clause 9.2.1 of Rules N 115, the deviation of the average daily temperature of the water supplied to the heating, ventilation, air conditioning and hot water supply systems must be within 3% of the established temperature schedule. The average daily temperature of the return network water should not exceed the temperature set by the temperature chart by more than 5%.
The pressure and temperature of the coolant supplied to the heat-consuming power plants must correspond to the values established by the technological regime (clause 4 of Rules N 115).
In accordance with paragraph 107 of the Rules on the commercial accounting of thermal energy, coolant, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 18, 2013 N 1034 (hereinafter referred to as Rules N 1034), the following parameters characterizing the thermal and hydraulic regime of the heat supply system of heat supply and heat network organizations are subject to control of the quality of heat supply:
a) when connecting the heat-consuming installation of the consumer directly to the heat network:
pressure in the supply and return pipelines;
the temperature of the heat carrier in the supply pipeline in accordance with the temperature schedule specified in the heat supply contract;
b) when connecting a consumer's heat-consuming installation through a central heating point or when directly connected to heating networks:
pressure in the supply and return pipelines;
differential pressure at the outlet of the central heating point between the pressure in the supply and return pipelines;
compliance with the temperature schedule at the inlet of the heating system during the entire heating period;
pressure in the supply and circulation pipeline of hot water supply;
temperature in the supply and circulation pipeline of hot water supply;
c) when connecting the heat-consuming installation of the consumer through an individual heating point:
pressure in the supply and return pipelines;
compliance with the temperature schedule at the inlet of the heating network during the entire heating period.
The following parameters characterizing the thermal and hydraulic regime of the consumer are subject to quality control of heat supply (clause 108 of Rules N 1034):
a) when connecting the heat-consuming installation of the consumer directly to the heat network:
return water temperature in accordance with the temperature schedule specified in the heat supply contract;
heat carrier consumption, including the maximum hourly consumption, determined by the heat supply agreement;
make-up water consumption, determined by the heat supply agreement;
b) when connecting a consumer's heat-consuming installation through a central heat point, an individual heat point or with direct connection to heat networks:
temperature of the heat carrier returned from the heating system in accordance with the temperature schedule;
coolant flow in the heating system;
make-up water consumption according to the heat supply contract.
Heat supply of a multi-storey building
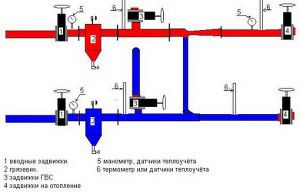
Distribution unit for heating an apartment building
The distribution of heating in a multi-storey building is important for the operational parameters of the system. However, in addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of heat supply
An important of them is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
In overwhelming cases, they make a connection to the central heating system. This reduces running costs. in the budget for heating of a multi-storey building. But in practice, the level of quality of such services remains extremely low. Therefore, if there is a choice, preference is given to autonomous heating of a multi-storey building.
Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
In modern multi-storey residential buildings, it is possible to organize an independent heat supply system. It can be of two types - apartment or common house. In the first case, an autonomous heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out in each apartment separately. To do this, they make an independent wiring of pipelines and install a boiler (most often a gas one). General house implies the installation of a boiler room, to which special requirements are imposed.
The principle of its organization is no different from a similar scheme for a private country house. However, there are a number of important points to consider:
- Installation of several heating boilers. One or more of them must necessarily perform a duplicate function. In case of failure of one boiler, another must replace it;
- Installation of a two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, as the most efficient;
- Drawing up a schedule for scheduled maintenance and preventive maintenance.This is especially true for heating heating equipment and security groups.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the heating scheme of a particular multi-storey building, it is necessary to organize an apartment heat metering system. To do this, for each incoming branch pipe from the central riser, you need to install energy meters. That is why the Leningrad heating system of a multi-storey building is not suitable for reducing current costs.
Centralized heating of a multi-storey building
Scheme of the elevator node
How can the heating layout in an apartment building change when it is connected to the central heating supply? The main element of this system is the elevator unit, which performs the functions of normalizing the coolant parameters to acceptable values.
The total length of the central heating mains is quite large. Therefore, in the heating point, such parameters of the coolant are created so that heat losses are minimal. To do this, increase the pressure to 20 atm. which leads to an increase in the temperature of hot water up to +120°C. However, given the characteristics of the heating system in an apartment building, the supply of hot water with such characteristics to consumers is not allowed. To normalize the parameters of the coolant, an elevator assembly is installed.
It can be calculated for both two-pipe and single-pipe heating systems of a multi-storey building. Its main functions are:
- Reducing pressure with an elevator. A special cone valve regulates the amount of coolant inflow into the distribution system;
- Lowering the temperature level to + 90-85 ° С. For this purpose, a mixing unit for hot and cooled water is designed;
- Coolant filtration and oxygen reduction.
In addition, the elevator unit performs the main balancing of the single-pipe heating system in the house. To do this, it provides shut-off and control valves, which in automatic or semi-automatic mode regulates pressure and temperature.
You also need to consider that the estimate for centralized heating of a multi-storey building will differ from the autonomous one. The table shows the comparative characteristics of these systems.
Heating system
Why do you need an expansion tank
Accommodates excess expanded coolant when it is heated. Without an expansion tank, the pressure can exceed the tensile strength of the pipe. The tank consists of a steel barrel and a rubber membrane that separates air from water.
Air, unlike liquids, is highly compressible; with an increase in the volume of the coolant by 5%, the pressure in the circuit due to the air tank will increase slightly.
The volume of the tank is usually taken to be approximately equal to 10% of the total volume of the heating system. The price of this device is low, so the purchase will not be ruinous.
Proper installation of the tank - eyeliner up. Then no more air will get into it.
Why does pressure decrease in a closed circuit?
Why does pressure drop in a closed heating system?
After all, the water has nowhere to go!
- If there are automatic air vents in the system, the air dissolved in the water at the time of filling will exit through them. Yes, it makes up a small part of the volume of the coolant; but after all, a large change in volume is not necessary for the pressure gauge to note the changes.
- Plastic and metal-plastic pipes can be slightly deformed under the influence of pressure. In combination with high water temperature, this process will accelerate.
- In the heating system, the pressure drops when the temperature of the coolant decreases. Thermal expansion, remember?
- Finally, minor leaks are easy to see only in centralized heating by rusty traces. The water in a closed circuit is not so rich in iron, and the pipes in a private house are most often not steel; therefore, it is almost impossible to see traces of small leaks if the water has time to evaporate.
What is the danger of a pressure drop in a closed circuit
Boiler failure. In older models without thermal control - up to the explosion. In modern older models, there is often automatic control of not only temperature, but also pressure: when it falls below the threshold value, the boiler reports a problem.
In any case, it is better to maintain the pressure in the circuit at about one and a half atmospheres.
How to slow down the pressure drop
In order not to feed the heating system over and over again every day, a simple measure will help: put a second larger expansion tank.
The internal volumes of several tanks are summarized; the greater the total amount of air in them, the smaller the pressure drop will cause a decrease in the volume of the coolant by, say, 10 milliliters per day.
Where to put the expansion tank
In general, there is no big difference for a membrane tank: it can be connected to any part of the circuit. Manufacturers, however, recommend connecting it where the water flow is as close to laminar as possible. If there is a tank in the system, it can be mounted on a straight pipe section in front of it.
We hope that your question has not gone unnoticed. If this is not the case, you may be able to find the answer you need in the video at the end of the article. Warm winters!