We warm the house. Which is better outside or inside
When insulating housing construction, there are two main types of it - internal and external. Each of them has a number of advantages and disadvantages. Statistics say that in 8 out of 10 cases a person chooses the internal and here's why:
- Work can be done regardless of the weather;
- The technology of internal insulation is significantly cheaper;
- Wall insulation makes it possible to eliminate defects.
Of the shortcomings, the following can be considered obvious:
- Heat preservation works exclude the possibility of living in the house for the duration of their implementation;
- The choice of low-quality insulation can affect the health of those who will subsequently live here;
- Warming from the inside shifts the dew point into the interior, and this, without certain countermeasures, will provoke the formation of mold and fungus;
- Excessive amount of material to achieve thermal comfort can significantly reduce the volume of rooms.
In addition to the main function, the insulation also has additional functions. For example, it increases sound insulation, allows walls to "breathe", and in some cases can even be a decorative finish.
With all of the above, we quite intelligibly indicated the importance of not only how to mount the current, but also what to mount. This is what our story will go below.
Presentation on theme: "What is Thermal Conductivity? HEAT CONDUCTIVITY - the transfer of energy from more heated parts of the body to less heated ones as a result of thermal movement and interaction. transcript
1
What is thermal conductivity?
2
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY - the transfer of energy from more heated parts of the body to less heated ones as a result of thermal motion and interaction of microparticles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). It leads to equalization of body temperature. Not accompanied by transfer of substance! This type of transfer of internal energy is characteristic of both solids and liquids, gases. The thermal conductivity of various substances is different. There is a dependence of thermal conductivity on the density of a substance.
3
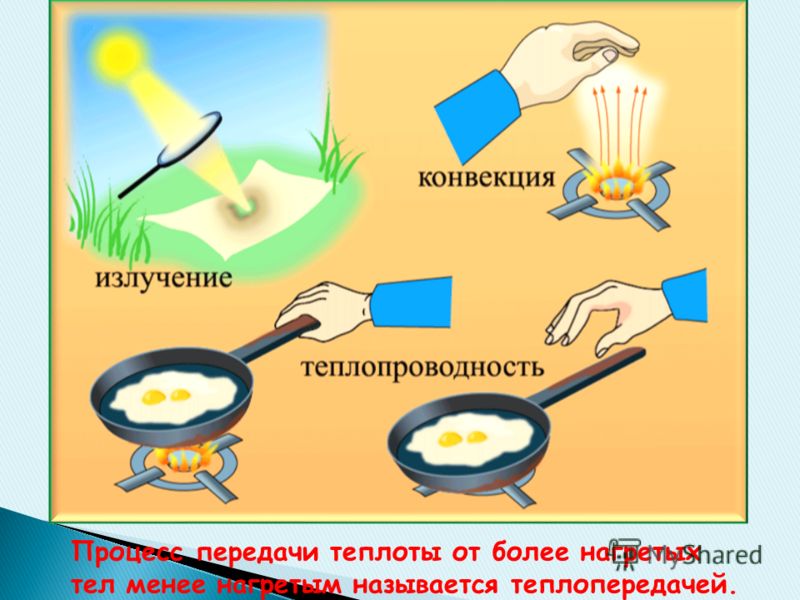
The process of transferring heat from hotter bodies to less hot ones is called heat transfer.
4
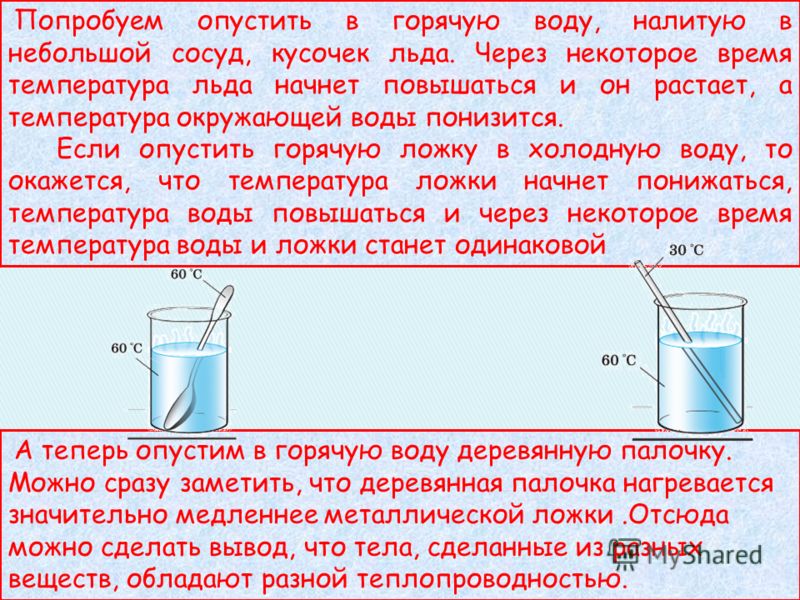
Let's try to lower a piece of ice into hot water poured into a small vessel. After some time, the temperature of the ice will begin to rise and it will melt, and the temperature of the surrounding water will drop. If you lower a hot spoon into cold water, it turns out that the temperature of the spoon will begin to drop, the temperature of the water will rise, and after a while the temperature of the water and the spoon will become the same. Now let's put a wooden stick in hot water. You can immediately notice that a wooden stick heats up much more slowly than a metal spoon. From this we can conclude that bodies made of different substances have different thermal conductivity.
5
The thermal conductivity of various substances is different. Metals have the highest thermal conductivity, and different metals have different thermal conductivity. Liquids have less thermal conductivity than solids, and gases less than liquids. When heating the upper end of a test tube closed with a finger with air inside, you can not be afraid to burn your finger, because. the thermal conductivity of gases is very low.
6
Substances with low thermal conductivity are used as heat insulators. Thermal insulators are substances that conduct heat poorly. Air is a good heat insulator, which is why window frames are made with double panes so that there is a layer of air between them. Wood and various plastics have good thermal insulation properties.
You can pay attention to the fact that the handles of teapots are made from these materials in order not to burn your hands when the teapot is hot.
7
To create warm clothes, substances that conduct heat poorly, such as felt, fur, cotton wool, feathers and down of various birds, are widely used.These clothes help keep the body warm. Felt and cotton mittens are used when working with hot objects, for example, in order to remove hot pots from the stove. All metals, glass, water conduct heat well and are poor heat insulators. Under no circumstances should hot objects be removed with a cloth soaked in water. The water contained in the rag will instantly heat up and burn your hand. Knowing about the ability of different materials to transfer heat in different ways will help in the campaign. For example, in order not to burn yourself on a hot metal mug, its handle can be wrapped with insulating tape, which is a good heat insulator. In order to remove a hot pot from the fire, you can use felt, cotton or canvas mittens.
8
In the kitchen, when lifting hot dishes, so as not to burn yourself, you can use only a dry rag. The thermal conductivity of air is much less than that of water! And the fabric structure is very loose, and all the gaps between the fibers are filled with air in a dry rag, and water in a wet one.
9
Partridges, ducks and other birds do not freeze in winter because the temperature of their paws can differ from body temperature by more than 30 degrees. The low temperature of the paws greatly reduces heat transfer. Such are the body's defenses! IF you put a piece of foam (or wood) and a mirror on the table next to it, the sensations from these objects will be different: the foam will seem warmer, and the mirror colder. Why? After all, the ambient temperature is the same! Glass is a good conductor of heat (it has a high thermal conductivity), and will immediately begin to “take away” heat from the hand. The hand will feel cold! Styrofoam conducts heat worse. It will also, heating up, “take away” heat from the hand, but more slowly, and therefore it will seem warmer.
Archive 24228 dated December 17, 2013
2013
Archive 2019
Archive 2018
Archive 2017
Archive 2016
Archive 2015
Archive 2014
Archive 2013
Archive 2012
Archive 2011
Archive 2010
Archive 2009
Archive 2008
Archive 2007
Archive 2006
Archive 2005
Archive 2004
Keep warm in summer
New projects can change the energy market. Thermochemical batteries are ideal for combined heat and power plants. The desire to save heat efficiently was unrealistic for a long time. The Lüneburg University project focuses on natural resources and shows how easily and cost-effectively this can be achieved. It looks like some kind of witchcraft: in the summer, when the sun is constantly shining, people do not need warmth. But there are no systems that could store this heat and use it in winter. Doesn't exist yet... For now, Professor Wolfgang Rook, together with his team, has developed a system that can "reshape" the entire energy market anew. Nevertheless, even a child can understand the principle of action. Leuphana University researchers use heat to carry out a chemical reaction that saves energy. It sounds complicated, but it really isn't. The basic principle of heat preservation is based on the separation and combination of storage material (eg calcium chloride, potash or magnesium chloride) and water. “When the material is charged, the salt crystalline hydrate is separated by heat into salt and water. After the discharge reaction, heat is again generated, which can be used. Thus, a reversible reaction can be repeated an unlimited number of times,” explains Prof. Rook. Compared to physical heaters, such as water heaters, a thermochemical heat accumulator has a much higher energy density index. While a water heater with a volume of 800 liters can save 46 kWh, a new thermochemical heater with a volume of 1 cubic meter saves up to 80 kWh. The trick is also that due to poor insulation, a water heater can lose up to 3 kW / h per day, Lüneburg researchers do not have such energy losses.
It does not matter if such a heater is in the basement or on the street. “Energy is associated with its chemical carrier,” explains Wolfgang Rook.
Similarly, energy is stored in oil and wood. Another advantage: the drive covers a wide range of temperatures and can operate up to 1000 degrees. Specific applications are currently being researched and the project will enter the market in the near future. The goal now is to develop and successfully test a compact, efficient, energy-lossless heater with an energy content of 80 kWh and a volume of 1 cubic meter, in order to then start serial production of a product for fixed installation in 1 or 2 family houses together with a combined heat and power plant. For private homes, this technology may not yet be of interest, since current is generated only when heat is used. This can change modern heat-accumulators beyond recognition. Since heat can be stored for a long time, combined heat and power plants can operate in the summer. Thus, these heaters can give off all the heat of the summer in winter. But the Lüneburg researchers have much greater prospects. “Soon we will have no problems with electricity. We use not only the available heat.”
Author's translation of an article from the magazine Bauen und Wohnen
The principle of operation of a thermochemical accumulator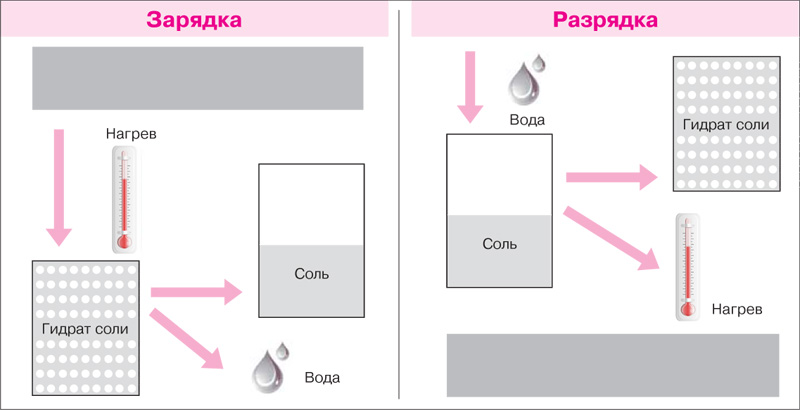
published an analytical article "Opportunities for eco-energy in
Russia”, where it was proposed to accumulate kinetic and thermal energy
environment (wind, solar, etc.) not in electrical
batteries, but in the form of a metastable, energy-intensive substance, to
which includes not only crystal hydrates of salts, but also various types
fuel and even explosives.
For companies offering modern energy-efficient technologies, there are special conditions for publishing in the Ulyanovsk Real Estate magazine. Contact tel. 73-05-55.
N1(205) dated January 16
N2(206) dated January 29
N3(207) dated February 12
N4(208) dated February 27
N5(209) dated March 13
N6(210) dated March 26
N7(211) dated April 09
N8(212) dated April 23
N9(213) dated May 14
N10(214) dated May 28
N11(215) dated June 11
N12(216) dated June 25
N13(217) dated 09 July
N14(218) dated July 23
N15(219) dated August 13
N16(220) dated August 27
N17(221) dated September 10
N18(222) dated 24 September
N19(223) dated 08 October
N20(224) dated October 22
N21(225) dated 06 November
N22(226) dated November 19
N23(227) dated 03 December
N24(228) dated December 17
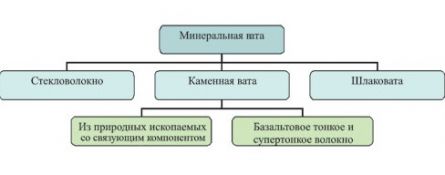
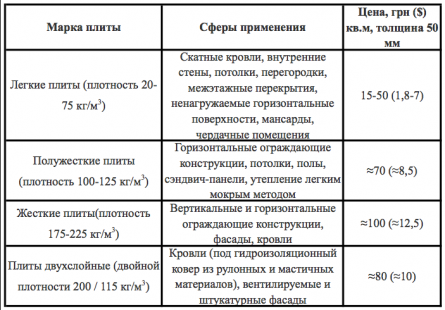
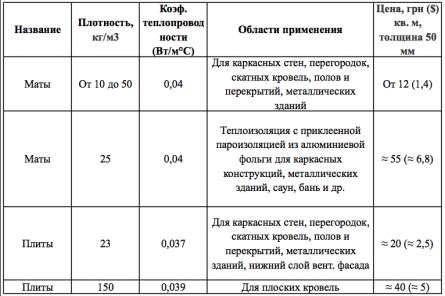
Inorganic materials and products fibrous heat-insulating materials
Mineral wool
Any fibrous insulation obtained from mineral raw materials (marls, dolomites, basalts, etc.) Mineral wool is highly porous (up to 95% of the volume is occupied by air voids), therefore it has high thermal insulation properties. This diagram will help you understand the names of the materials:
The fiber, which is obtained from the melt, is fastened into the product with the help of a binder (most often it is a phenol-formaldehyde resin). There are products called stitched mats - in them the material is sewn into fiberglass and stitched with threads.
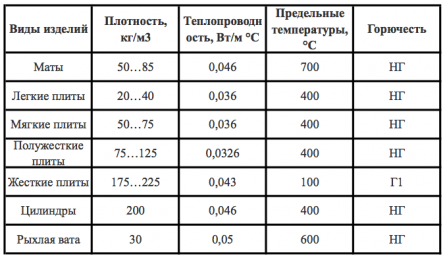
Table 1. Types of thermal insulation products and their characteristics
Mineral wool occupies one of the first places among thermal insulation, this is due to the availability of raw materials for its production, simple production technology, and, as a result, an affordable price. Its thermal conductivity is mentioned above, I will note the following of its advantages:
- Does not burn;
- It is slightly hygroscopic (when moisture gets in, it immediately gives it away, the main thing is to provide ventilation);
- Extinguishes noise;
- Frost-resistant;
- Stability of physical and chemical characteristics;
- Long service life.
Flaws:
- When moisture enters, it loses its heat-insulating properties.
- Requires a vapor barrier and waterproofing film during installation.
- Inferior in strength (for example, foam glass).
Basalt wool mats and slabs
• High heat-insulating properties;
• Maintains high temperatures, without losing the heat-insulating properties;
Basalt wool
Table 2. Basalt wool application and pricing
The average prices for cotton wool produced in Europe were taken as a basis.
glass wool
It is produced from fiber, which is obtained from the same raw materials as glass (quartz sand, lime, soda).
glass wool
They are produced in the form of rolled materials, plates and shells (for pipe insulation). In general, its advantages are the same (see mineral wool). It is stronger than basalt wool, dampens noise better.
The disadvantage is that the temperature resistance of glass wool is 450 ° C, lower than that of basalt wool (we are talking about the wool itself, without a binder). This characteristic is important for technical insulation.
Table 3. Characteristics of glass wool and its pricing
The average prices for European-made glass wool were taken as a basis.
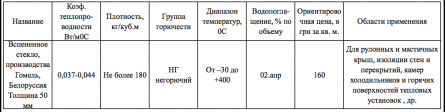
Foam glass (cellular glass)
It is produced by sintering glass powder with blowing agents (for example, limestone). The porosity of the material is 80-95%. This causes high thermal insulation properties of foam glass.
Foam glass
Advantages of foam glass:
- Very durable material;
- Waterproof;
- Incombustible;
- Frost-resistant;
- Easy to machine, you can even drive nails into it;
- Its service life is practically unlimited;
- Rodents "do not like" him
- It is biologically stable and chemically neutral.
Vapor resistance of foam glass - since it does not “breathe”, this must be taken into account when arranging ventilation. Also, its “minus” is the price, it is expensive. Therefore, it is used mainly at industrial facilities for flat roofs (where strength is needed, and where the cash costs for such thermal insulation are justified). Produced in the form of blocks and plates.
Table 4. Characteristics of foam glass
In addition to the listed materials, there are a number of other materials that also belong to this group of inorganic heat-insulating materials.
Heat-insulating concretes are: gas-filled (foam concrete, cellular concrete, aerated concrete) and based on lightweight aggregates (expanded concrete, perlite concrete, polystyrene concrete, etc.).
Backfill thermal insulation (expanded clay, perlite, vermiculite). It has high water absorption, is unstable to vibration, can shrink over time, which leads to the formation of voids, requires high installation costs. It also has advantages, for example: expanded clay has a high level of frost resistance and strength. The cost of expanded clay is 350 UAH/m3.
How are waterproofing materials used?

During waterproofing work, it is worth taking into account the fact that each material has some of its own properties, so do not forget to pay attention to the main quality of such materials - breathability
New waterproofing materials are divided into three branches according to the degree of breathability:
- completely pass air;
- partially pass air;
- do not let air through at all.
Materials that protect against moisture and do not allow air to pass through are great for underground structures. For ground structures, for example, for walls, air is very important, since it penetrates through the walls into the room and thus ventilates, although not very much. If a normal flow of free oxygen is not provided for the walls, then this will have a very bad effect on the room. Therefore, ground structures are treated with completely or partially air-permeable waterproofing materials. As a rule, waterproofing materials are divided according to the degree of water resistance, strength, frost resistance, fire resistance, toxicity and durability.
What is thermal conductivity and thermal resistance
When choosing building materials for construction, it is necessary to pay attention to the characteristics of the materials. One of the key positions is thermal conductivity
It is displayed by the coefficient of thermal conductivity. This is the amount of heat that a particular material can conduct per unit of time. That is, the smaller this coefficient, the worse the material conducts heat. Conversely, the higher the number, the better the heat is removed.
Diagram that illustrates the difference in thermal conductivity of materials
Materials with low thermal conductivity are used for insulation, with high - for heat transfer or removal. For example, radiators are made of aluminum, copper or steel, as they transfer heat well, that is, they have a high thermal conductivity. For insulation, materials with a low coefficient of thermal conductivity are used - they retain heat better. If an object consists of several layers of material, its thermal conductivity is determined as the sum of the coefficients of all materials. In the calculations, the thermal conductivity of each of the components of the "pie" is calculated, the found values are summarized. In general, we get the heat-insulating ability of the building envelope (walls, floor, ceiling).
The thermal conductivity of building materials shows the amount of heat that it passes per unit of time.
There is also such a thing as thermal resistance. It reflects the ability of the material to prevent the passage of heat through it. That is, it is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity. And, if you see a material with high thermal resistance, it can be used for thermal insulation. An example of thermal insulation materials can be popular mineral or basalt wool, polystyrene, etc. Materials with low thermal resistance are needed to remove or transfer heat. For example, aluminum or steel radiators are used for heating, as they give off heat well.
Classification of waterproofing materials.
Materials that protect building structures from moisture, in addition to the above properties, are divided into classes according to the field of application, physical state, active waterproofing components and application methods. Basically, we listed the characteristics of waterproofing materials for structures that do not come into close contact with water. And for structures such as reservoirs, pools, fountains and others that are in direct contact with water, there are special waterproofing materials. And finally, the last classification of materials that we consider in this article is the division into materials used for internal work and materials for external work.
According to their physical properties, waterproofing materials are divided into: mastic, powder, roll, film, membrane. If we divide the materials according to the basis from which they are made, then the following classes are obtained: bituminous, mineral, bitumen-polymer, polymer. The division according to the method of application is as follows: painting, plastering, gluing, cast, filling, impregnating, injection (penetrating), mounted. All kinds of waterproofing materials have different quality, different properties, it will be a regular sheet of roofing material or polymeric materials. Therefore, you must understand all the intricacies and choose the right materials.
Table of thermal conductivity of thermal insulation materials
To make it easier for the house to keep warm in winter and cool in summer, the thermal conductivity of walls, floors and roofs must be at least a certain figure, which is calculated for each region. The composition of the "pie" of walls, floor and ceiling, the thickness of the materials are taken in such a way that the total figure is not less (or better - at least a little more) recommended for your region.
Heat transfer coefficient of materials of modern building materials for enclosing structures
When choosing materials, it must be taken into account that some of them (not all) conduct heat much better in conditions of high humidity. If during operation such a situation is likely to occur for a long time, the thermal conductivity for this state is used in the calculations. The thermal conductivity coefficients of the main materials used for insulation are shown in the table.
| Dry | Under normal humidity | With high humidity | |
| Woolen felt | 0,036-0,041 | 0,038-0,044 | 0,044-0,050 |
| Stone mineral wool 25-50 kg/m3 | 0,036 | 0,042 | 0,,045 |
| Stone mineral wool 40-60 kg/m3 | 0,035 | 0,041 | 0,044 |
| Stone mineral wool 80-125 kg/m3 | 0,036 | 0,042 | 0,045 |
| Stone mineral wool 140-175 kg/m3 | 0,037 | 0,043 | 0,0456 |
| Stone mineral wool 180 kg/m3 | 0,038 | 0,045 | 0,048 |
| Glass wool 15 kg/m3 | 0,046 | 0,049 | 0,055 |
| Glass wool 17 kg/m3 | 0,044 | 0,047 | 0,053 |
| Glass wool 20 kg/m3 | 0,04 | 0,043 | 0,048 |
| Glass wool 30 kg/m3 | 0,04 | 0,042 | 0,046 |
| Glass wool 35 kg/m3 | 0,039 | 0,041 | 0,046 |
| Glass wool 45 kg/m3 | 0,039 | 0,041 | 0,045 |
| Glass wool 60 kg/m3 | 0,038 | 0,040 | 0,045 |
| Glass wool 75 kg/m3 | 0,04 | 0,042 | 0,047 |
| Glass wool 85 kg/m3 | 0,044 | 0,046 | 0,050 |
| Expanded polystyrene (polystyrene, PPS) | 0,036-0,041 | 0,038-0,044 | 0,044-0,050 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS, XPS) | 0,029 | 0,030 | 0,031 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete on cement mortar, 600 kg/m3 | 0,14 | 0,22 | 0,26 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete on cement mortar, 400 kg/m3 | 0,11 | 0,14 | 0,15 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete on lime mortar, 600 kg/m3 | 0,15 | 0,28 | 0,34 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete on lime mortar, 400 kg/m3 | 0,13 | 0,22 | 0,28 |
| Foam glass, crumb, 100 - 150 kg/m3 | 0,043-0,06 | ||
| Foam glass, crumb, 151 - 200 kg/m3 | 0,06-0,063 | ||
| Foam glass, crumb, 201 - 250 kg/m3 | 0,066-0,073 | ||
| Foam glass, crumb, 251 - 400 kg/m3 | 0,085-0,1 | ||
| Foam block 100 - 120 kg/m3 | 0,043-0,045 | ||
| Foam block 121- 170 kg/m3 | 0,05-0,062 | ||
| Foam block 171 - 220 kg / m3 | 0,057-0,063 | ||
| Foam block 221 - 270 kg / m3 | 0,073 | ||
| Ecowool | 0,037-0,042 | ||
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) 40 kg/m3 | 0,029 | 0,031 | 0,05 |
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) 60 kg/m3 | 0,035 | 0,036 | 0,041 |
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) 80 kg/m3 | 0,041 | 0,042 | 0,04 |
| Cross-linked polyethylene foam | 0,031-0,038 | ||
| Vacuum | |||
| Air +27°C. 1 atm | 0,026 | ||
| Xenon | 0,0057 | ||
| Argon | 0,0177 | ||
| Airgel (Aspen aerogels) | 0,014-0,021 | ||
| slag wool | 0,05 | ||
| Vermiculite | 0,064-0,074 | ||
| foamed rubber | 0,033 | ||
| Cork sheets 220 kg/m3 | 0,035 | ||
| Cork sheets 260 kg/m3 | 0,05 | ||
| Basalt mats, canvases | 0,03-0,04 | ||
| Tow | 0,05 | ||
| Perlite, 200 kg/m3 | 0,05 | ||
| Expanded perlite, 100 kg/m3 | 0,06 | ||
| Linen insulating boards, 250 kg/m3 | 0,054 | ||
| Polystyrene concrete, 150-500 kg/m3 | 0,052-0,145 | ||
| Cork granulated, 45 kg/m3 | 0,038 | ||
| Mineral cork on a bitumen basis, 270-350 kg/m3 | 0,076-0,096 | ||
| Cork flooring, 540 kg/m3 | 0,078 | ||
| Technical cork, 50 kg/m3 | 0,037 |
Part of the information is taken from the standards that prescribe the characteristics of certain materials (SNiP 23-02-2003, SP 50.13330.2012, SNiP II-3-79 * (Appendix 2)). Those material that are not spelled out in the standards are found on the websites of manufacturers
Since there are no standards, they can differ significantly from manufacturer to manufacturer, so when buying, pay attention to the characteristics of each material you buy.