Back to manometers
I don’t know about you, but for me the main characteristic of a pressure gauge is accuracy. In second place is reliability. The size of the dial is important, but secondary. If I have an extremely accurate, but small pressure gauge, I will not be too lazy to look at it through a magnifying glass. It's not a problem.
The problem is different. Perhaps I will tell you something new, but any analog pointer device has a measurement error. Moreover, this error is uneven. This error is spread over the scale in such a way that it is maximum at the edges of the scale, and minimum in the middle. This error is so uneven that the values in the first and last quarter of the scale are very inaccurate, and the values in the first and last fifth of the scale can not even be looked at. They most likely will not have anything to do with reality.
And now back to the issue of maximum working pressure. Obviously, pressure gauges for heating and plumbing must be different! For the heating system, the maximum pressure, the end of the scale should be at 4 atmospheres, and for the water supply at 8.
In reality, we see a completely different picture. The vast majority of pressure gauges are designed for a maximum of 10 atmospheres, you can find them at 8. Very rarely, if you look for good suppliers for a long time, you can find them at 6. You can also see pressure gauges for 4 atmospheres, but this is already exclusive.
Why is there such a picture? Again, I express my personal opinion. I suspect making a pressure gauge for a higher maximum pressure is easier and cheaper. It is very possible that the membranes, springs that are used in pressure gauges are easier to make more rigid. That is, we again become a kind of hostages of the economy and marketing. That is, we use not what we need, but what is given. Or you need to understand, search, consult, overpay.
Safety devices
Each OKN to ensure safe
operating conditions is supplied with PU from
increase in pressure above the allowable.
As PU are used: spring
PC; lever-cargo PC; impulse launchers;
membrane PU; other PU, application
which are agreed with RTN.
Spring valves: design
should exclude the possibility of tightening
springs in excess of the established value;
spring must be protected from
unacceptable heating (cooling) and
direct impact of working
environment. Device provided
to check the correct operation
valve in working order
short-term forced
undermining. When the valve is located above
2.5 m remote
drive unit.
Lever weight valves: installation
on mobile objects is not allowed.
The weight is indicated on the load. Cargo motionless
attached to the lever.
The diameter of the passage of the lever-cargo and
spring valves at least 20 mm.
Membrane PU: need
installation and design determines
project organization. Installed:
– instead of lever-load and spring
valves when those valves are in service
conditions of a particular environment cannot be
applied due to their inertness or
other reasons;
– in front of the PC in cases where the PC cannot
work reliably due to harmful
exposure to the working environment (corrosion,
erosion, sticking, freezing. T.
etc.) or possible leaks through a closed
valve of dangerous and harmful substances;
– in parallel with PKPK to increase
throughput of discharge systems
pressure;
– on the output side of the PKPK for
prevent harmful effects
working media from the waste system
and to eliminate the influence of fluctuations
backpressure of this system on accuracy
operation of the PKPK.
On every steam and hot water boiler
must have at least two
PU.
The total throughput of PU,
installed on the steam boiler must
be at least nominal
boiler steam output. Checkpoint
the ability of the launcher is indicated in its
passport.
PU must protect against exceeding
pressure:
Vessels: with pressure up to 3 kgf/cm2 no more than 0.5 kgf/cm2 calculated;
from 3 to 60 kgf/cm2 15% of the calculated value;
over 60 kgf / cm2 10% of the calculated.
When the PC is running, it is allowed to exceed
pressure in the vessel by more than 25% of the working
provided that this is an excess
envisaged by the project and reflected in
passport.
Boilers - no more than 10% of the calculated
(allowed).
Pipelines - no more than 10%
design, at design pressure up to
5 kgf / cm2 - no more than 0.5
kgf/cm2.
For boilers and pipelines
pressure at the full opening of the PC is higher
than 10% of the calculated can be allowed,
if provided for by the
strength.
Vessels and pipelines, design pressure
which are lower than the pressure supplying them
source must have a reducing
device with pressure gauge and safety
valve, which are installed with
side of lower pressure after
reducing device.
If the operation of the object is allowed
at reduced pressure, then the adjustment
PU is produced according to this pressure,
throughput should be
verified by calculation.
Methodology and frequency of regulation
PU and the pressure of the beginning of their opening should
be specified by the manufacturer
in the installation and operating instructions
object.
PU is delivered to the customer with a passport,
including a characteristic of its throughput
capabilities. Attached to the passport
user manual.
PU is installed on nozzles or
pipelines, directly
attached to the object.
The selection of the working medium from the nozzles on
which are installed PU is not allowed.
Installation of shutoff valves between
objects and PU, as well as behind it is not allowed.
PU must have discharge pipelines,
equipped with drains
condensate. Installation of locking devices
drains are not allowed.
Examination:
The correctness of the action is checked
short-term forced detonation.
Staff:
– for boilers and pipelines – as for
pressure gauges;
- for vessels - the order and terms in
depending on the technological process
specified in the instruction manual.
PU approved by the owner in the established
okay.
Test results, information about them
setting are recorded in the shift log
persons performing these operations.
GOST 12.2.085–82 “Safety valves.
Safety requirements".
Gauge scale units
I suggest everyone to focus on bars. This is a non-systemic unit of pressure. It shows the value closely approximated to the physical and technical atmosphere and is the most convenient. Consider a bar (0.1 MPa) as an abstract atmosphere and don't worry. Why are physical and technical atmospheres different? Because getting attached to a water column is dangerous. The real water column also depends on atmospheric pressure. But, I repeat, approximately all three units are equal to each other. If the pressure gauge scale is graduated in kgf/cm2, then it must be borne in mind that 1 kgf/cm2 is exactly equal to one technical atmosphere, or 10 m of water column. More information about pressure units can be found in a special article about plumbing.
I strongly advise against paying attention to such a unit as Psi, or pounds per square inch. This is not our unit and you should not even try to get used to it
Although, if desired, of course, you can get used to inches and pounds and feet. But you need a great desire and a lot of practice.
Briefly speaking
- Technical atmosphere (1 at) \u003d 10 m of water column \u003d 1 kgf / cm2
- bar - has an intermediate value = 10.197 m of water column = 0.1 MPa
- Physical atmosphere (1 atm) = 10.33 m of water column
For the purposes of determining the pressure in the water supply, all these pressures (5 different units of measurement) are approximately equal. The extreme differences are 33 cm of water column or somewhere a bucket of water. Not by weight, mind you, but by height. Since we measure in meters, we neglect 30 centimeters.
Thermomanometer
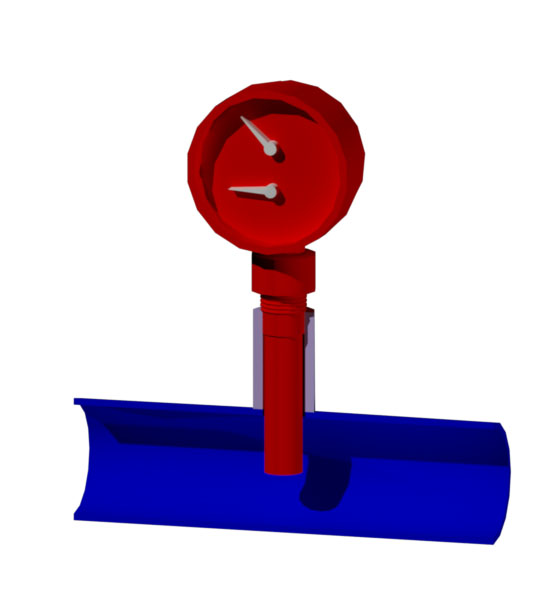
thermomanometer in 3d
We had places where we needed local instruments for measuring temperature and pressure, in order to save space, it was decided to put a thermomanometer instead of a thermometer and a manometer. The delivery set of the thermomanometer includes a valve so that it can be dismantled without depressurization of the system.
The price of a manometer and a thermometer at the same ROSMA 350 + 685 = 1035 rubles, the price of a thermomanometer = 1110 rubles. Considering that fittings will be required 2 times more, I see no reason to put a thermometer and a pressure gauge separately.
Were ordered:
- Thermomanometer ROSMA TMBR - 31P2 (0-140 ° C) (0-0.25 MPa) G1 / 2
- Boss No. 2 BP-BT-30-G½ (for BT thermometer)
Conclusion
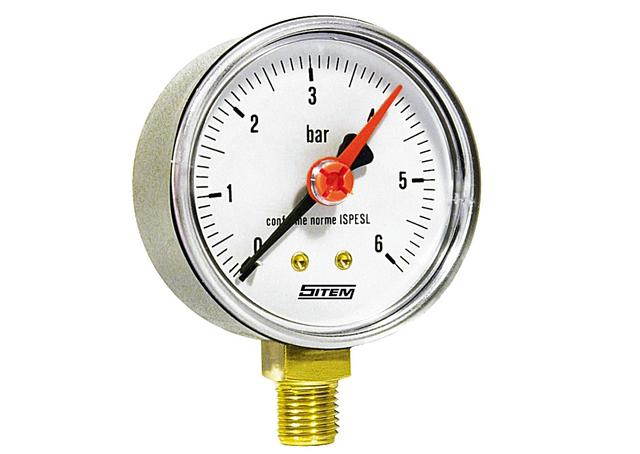
Manometer with a convenient scale and an additional pointer arrow
This pressure gauge would be ideal for plumbing. And there is only one scale. And in bars. It is possible that the creators were thinking about the end consumer. The red arrow pointer is useful for marking the turn-on pressure of the pump.
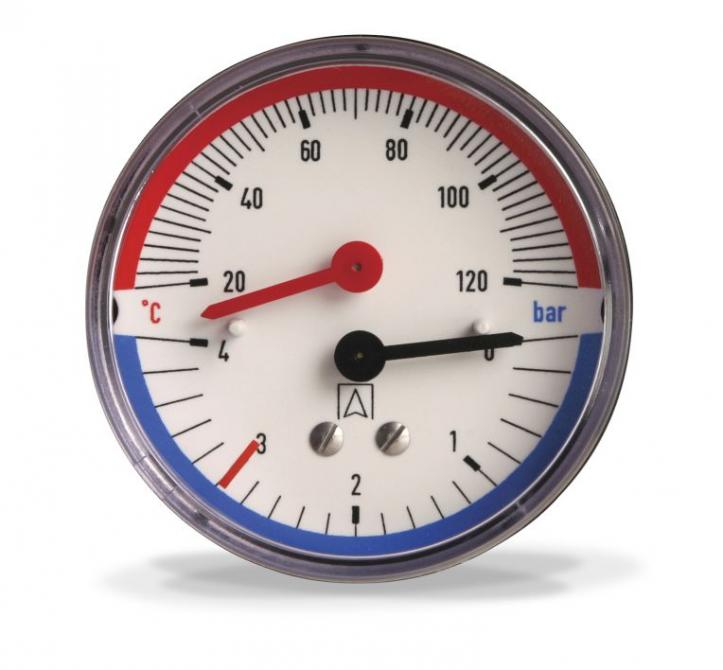
Two devices in one
It is not very convenient to have both a manometer and a thermometer in one device. In addition, the versatility of the device may degrade other characteristics of the device. This pressure gauge is clearly for the heating system.
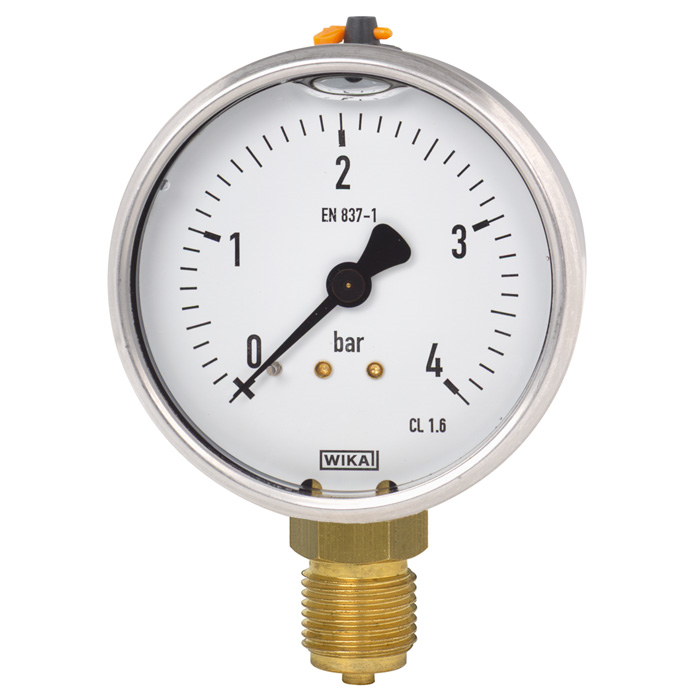
Looks like a device for industrial use
The scale is graduated in kgf / m2 and the upper limit of the scale is 16. This is frankly a lot for a private house.
Manometer with a convenient scale
There she is! The ideal scale for the heating system. Try it, buy one in the store!
Be careful with the choice of pressure gauge. The measured pressure should be as close to the middle of the scale as possible. The pressure gauge must be rated for liquid operation. It is better to choose such pressure gauges that are produced by well-known manufacturers and have indications of measurement error or accuracy class. Under generally equal conditions, a large pressure gauge is better than a small one. The scale should be graduated either in atmospheres or in kgf / cm2, and even better in bars (bar). At worst, MPa will do. All three of these units mean roughly the same thing. The difference between them is insignificant. Probably, it is better to embed the pressure gauge in heating on the return line, because additional heating can introduce an error into the rigidity of the materials that work in the pressure gauge, and the measurement error may increase. But there are pressure gauges designed for high temperatures. Even up to 150 degrees Celsius! I would not install a device in my system that, in addition to measuring pressure, measures something else. Versatility has never been in favor of either instruments or tools.
Big lover of precision instruments Dmitry Belkin
Article created 25.09.2015