How to insulate walls
Wall insulation in this room is not always done, but only if it is impossible to insulate the pediment and the roof of the house to the very bottom.
If the floor in the room was previously lined with insulation, then you can repeat this procedure for the walls.
The scheme for insulating the walls of the attic in a wooden and other house will be similar: behind the racks, where the future walls will be supported, you need to fill wooden slats every 30-40 cm of space.
A layer of thermal insulation will be laid on them.
At the same time, the insulation should enter with difficulty and be a little more free space, because. it will shrink over time.
From above, the heat-insulating layer must be covered with vapor barrier material in the same way as it is done with the ceiling, and then hemmed with slats so that it is stable and does not come off the walls.
The vapor barrier material must fit very tightly to the wall in order to fulfill its function, so the joints of the material must be glued with tape.
For internal insulation of attic walls, polystyrene foam and mineral wool are most often used - both of these materials do their job well and help keep the heat in the room.
But it is not necessary to insulate the walls with foam plastic, although this material is not inferior to mineral wool in terms of heat retention properties, but it has significant disadvantages.
In addition to the fact that this material will take up a significant part of the space of the room, there is a risk that rodents will start in it, and the insulation will become unusable very quickly.
To do this, lay the foam in two layers, choose sheets of 50 mm, not 100 mm, and lay them so that the joints do not match, then it will last longer.
If you are insulating walls with mineral wool, then use chopped material, not a roll, because. mats retain their shape better and do not settle after a while.
Just like polystyrene, mineral wool is laid in two layers.
Video:
Attic insulation with polyurethane foam is the easiest to do. This method is suitable for absolutely any type of wall material: wood, concrete, brick, etc.
Polyurethane foam will create an ideal waterproofing layer in the room, in addition to helping to insulate the room.
PPU foam is applied in the gaps between the rafters and thus fills all the empty space. You can use it not only for walls, but also for gables and floors.
Drywall walls are covered with a final decorative finish, and on this the work of bringing the attic into a residential look can be considered completed.
Sometimes lining is chosen for decorative finishing - wood looks better and more presentable, especially in a wooden house, but such a finish will be somewhat more expensive.
Videos and photos will help you not only insulate the attic yourself, but also make it beautiful and cozy with the help of the final finish.
Photos of the stages of work on the insulation of walls and roofs, as well as a video on how to work with one or another material, will help you understand how to insulate the attic, do the job correctly and get a cozy and warm room that will remain so even in the most severe frosts.
Which insulation for the attic is better to choose
To insulate the attic of a house, you can use any heat-insulating material that has proven itself in practice.
Among the most popular materials: cotton wool, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam and their varieties. It should be remembered that the attic insulation is selected taking into account the factors inherent in a particular house and taking into account the skill level of the one who will install the thermal insulation material.
The characteristics that determine the suitability of the insulation for use in a particular case are given in the table.
| insulation | Rigidity (compressive strength) | Thermal conductivity | Hygroscopicity | Shrinkage | Weight | Installation on a sloping roof | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral wool (basalt insulation) | – | – | + | + | – | + | 100-140 rub/sq.m. |
| Glass wool (synthetic insulation) | – | – | + | + | – | + | 70-80 rub/sq.m. |
| Penofol (foil insulation) | – | – | – | – | – | + | 40-50 rub/sq.m. |
| Ecowool (cellulose insulation) | – | – | + | – | – | + | 23-35 rub/kg |
| Polyurethane foam (PPU foam) | + | – | – | – | – | + | 170-212 rub/kg |
| Styrofoam | + | – | – | – | – | – | 2560-3200 rub/m3 |
| Expanded polystyrene (foam) | + | – | – | – | – | – | 3500-5000 rub/m3 |
The material was prepared for the site www.moydomik.net
How to insulate the roof and other elements
The scheme of how to properly insulate the attic can be different and depends on the type of house.
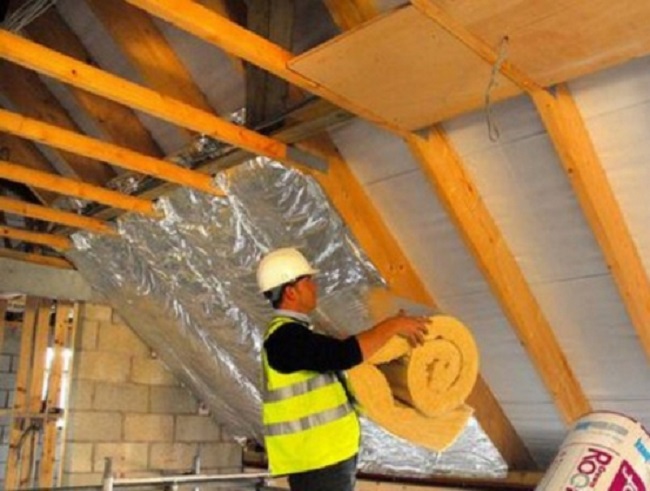
Insulation of the attic roof is the most important stage, because. It is she who occupies most of the room.
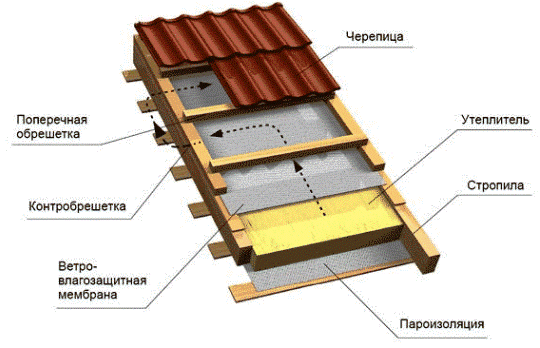
Since the roof is sloping, only those materials that do not change their size and shape over time are suitable as insulation.
If you have chosen basalt wool for insulation, then it is better to purchase it in tiled form, and not in a continuous sheet, because. in this case, it will be easier to lay it, and the plates can be easily connected to each other during the installation process.
The insulation must lie in a continuous layer, so if there are gaps between the plates, then they must be closed with a strip of material, which should be slightly larger than the required space, because. cotton wool tends to shrink over time.
Details for closing the gaps are driven into the space between the slab and the rafters with force. The laying pattern of this material is available on video and photos - watch them before starting work.
Thermal insulation is also required by complex roof elements - skates, overhangs and valleys.
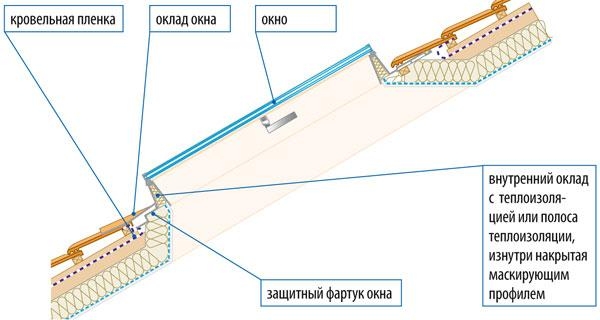
In a private house where the shape of the roof changes, it is important to tightly connect the parts of the insulation so that it does not move away and performs its function, holding warm air. A particularly problematic place in the room is the junction of walls with a roof and window openings.
To prevent these places from freezing in winter, the windows of the room are also insulated. The scheme of window insulation is shown in the photo below.
A particularly problematic place in the room is the junction of walls with a roof and window openings. To prevent these places from freezing in winter, the windows of the room are also insulated. The scheme of window insulation is shown in the photo below.
The material for insulating the ceilings of the attic roof depends on their type.
Expanded polystyrene is most suitable for reinforced concrete structures and self-leveling or tiled floors - it is durable and also has good sound insulation, which is very important in this type of room.
For reinforced concrete floors with wooden floors on logs, insulation from the outside with wool with basalt fiber is usually used.
At the same time, ventilation holes must be made in the corners of the attic, and so that the ceiling does not let in unnecessary sounds, sound-absorbing pads are installed on the logs.
Warming the gables is another important step that should not be missed. The layout of the insulation depends on the type of construction of the house.
If it is erected by means of layered masonry, then the insulation must be laid inside the masonry. At the same time, there is a facing material outside the structure, and a load-bearing wall on the inside.
If the house uses a ventilated facade, then the gable is insulated with basalt fiber slabs. When laying, a space of 4-15 cm should remain between the material and the cladding layer.
To ensure that cold air does not penetrate into the attic from the outside of the gables.
To protect the insulation from moisture, a membrane must be installed on top of it, which will resist wind or rain on it.
Video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=toBUp4SITcQ
If the facade is plaster, then expanded polystyrene or stone wool slabs are used to insulate the gables. If you use cotton wool, you will have to adjust it to the desired size of the gables.
Whatever type of insulation you choose, it is better to first follow the stages of work on photos and videos, and only then proceed to finish the attic.
If it is impossible to insulate the walls of the gables, then you will have to insulate the walls from the inside. We will talk about this below.
Best Answers
Sergey Parfilov:
Of course it is possible.Just keep an eye on tightness
Vladimir Petrov:
If you want to properly insulate, then do this with 100 mm of cotton wool from the side of the house, further from the street, bars, then 50 minutes of cotton wool for wind and moisture protection and siding. Just as you wrote above, do not forget about the ventilation gap from the faces and the ventilation gap from the house after the vapor barrier and the fine upholstery of the house
Roman Shved:
It is possible, only taking into account that the staples from the stapler will be closed with a bar, that is, beacons for siding.
Alexander:
Good thermal insulation will allow you to maintain the appropriate temperature in the attic in the house both in winter and in summer. Roof slopes must be well insulated. Only a thick (20–25 cm) layer of thermal insulation will make it possible to achieve heat transfer resistance R = 5–6.25 (m2·K)/W. It is most convenient to place heat-insulating material between the rafters. But usually the height of the rafters does not exceed 18 cm, so it will not be possible to completely lay the insulation between them. Part of the required thickness of thermal insulation, which does not fit between the rafters, is laid in the second layer, between the bars of the inner crate nailed to the rafters from the side of the attic. If a ceiling is made in the attic of the house, then the insulating material covering part of the attic can be laid in the roof pie at the level of the ceiling.
Alexei:
Well, in principle, we didn’t even cover with bars, only the joints were wound into a tube so that it wouldn’t blow through
Pavel Kharlamov:
No. Warming is done outside.
What material to choose for insulation
Attic insulation from the inside can be carried out in many ways using various materials, and in order to choose them, you need to consider the pros and cons that each of them has.
It directly depends on the insulation how warm the room will be, as well as how much you have to spend on heating, because if the warm air leaves quickly, then much more energy will be needed to heat the room.
Video:
The better to insulate the attic depends on the thermal conductivity of the material: the lower it is, the thinner the layer of insulation you will need.
Another important factor to consider is moisture resistance.
The worse the material absorbs water, the less likely it is that condensation will appear on the attic ceiling and the room will become damp.
From constant dampness in the room, mold, fungus can appear, and the microclimate can simply be disturbed.
Since attics are usually insulated for living, the insulation must also be safe for humans, environmentally friendly and refractory.
The most economical way to insulate a room is to use mineral, ecowool or glass wool insulation.
They are divided into three types:
- cotton wool, which consists of a fibrous material;
- mats that are made from quilted cotton;
- slab-wool - such material is fastened with the help of special impregnation and plates of various sizes are made from it.
At the moment, these materials have lost their relevance, because. new ones have appeared that have more significant advantages and better retain the heat of the ceiling and walls in the rooms.
At the moment, the most popular attic insulation is foam plastic, more precisely, one of its varieties - polystyrene foam.
It is easy to work with this material and it has significant advantages, for example, it serves both as a vapor and heat insulator, which allows you to make insulation faster and at a lower cost.
They also perform two functions: a vapor barrier layer is located inside the material, and a waterproofing layer is located outside.
Attic insulation with polyurethane is a modern and effective way to maintain heat in the room.
It is good in that you can create a monolithic coating from a heater, because. the process of warming involves applying the agent to the space of gables, partitions, ceilings and roofs, and guarantees complete tightness.
Video:
At the same time, the thermal conductivity of the material is minimal, so the heat will be stored in the room for a long time.
Insulation of the attic from the inside with polyurethane foam is recommended for those rooms where the roof is rather low and it is very important to preserve the maximum living space, because. this material is thinner than mineral wool or polystyrene and will not take up the required attic area
In addition to the insulation itself, you will also need tools and additional materials that are best purchased in advance.
You also need to calculate how much insulation will be needed for the entire attic area.
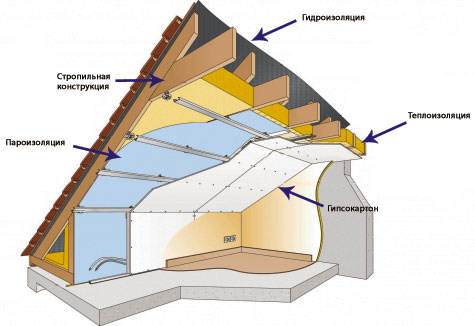
Insulation of the attic gable from the inside
Insulation of the attic gable can be external and internal. External insulation of the attic pediment is done as a continuation of the layers of insulation and decorative plaster from the facade to the pediment.
If the installation of an external plaster system is not planned, then the pediment is insulated from the inside using ECOVER-type basalt thermal insulation slabs using a special technology. Insulation plates are placed between the wooden beams of the frame, on the previously fixed hydro-vapor barrier. If the thickness of the beams and insulating plates do not match, then the frame beams are built up with strips of the required thickness, attaching them with screws.
It is forbidden to compress the insulation layer! After laying the heat-insulating boards, the wall is completely covered with a polyethylene film for vapor barrier. Instead of a film, you can use penofol - foamed polyethylene with a layer of foil. The shiny layer should be located inside the room. Penofol is fixed with wooden slats, pressing down to the frame. The inner lining will then be mounted on the rails. During installation, it is necessary to create this air layer in order to prevent the formation of moisture on the insulation boards. The vapor barrier layer should create a continuous coating on the gable and roof slopes, it should not have gaps. At the joints, the strips are laid with an overlap of 10 cm and glued with construction tape.
The “warm cake” when insulating the gable of the attic should look like this: a wall, wind and waterproofing, a horizontal frame mesh of bars with a section of at least 25x25 mm in increments of 600 mm, insulation plates between the frame beams, vapor barrier and sheathing made of lining or drywall. It is most convenient to create a heat-insulating system when insulating the attic gable using basalt wool materials that hold the shape. Such mats are easy to mount, using a minimum of fasteners. You can use mineral wool. It is cut in width slightly larger than the gap between the beams. Slightly compress and straighten in the space intended for it. After straightening, the mineral wool fills the place tightly and holds tightly.
Insulation of the attic gable can be done using polyurethane foam by spraying. Pressurized foam insulation is supplied from a small installation and fills the space without gaps. It turns out a monolithic insulating layer that does not require the use of vapor barrier. Styrofoam boards can also be used for insulation. But they have less thermal protection than cotton wool, and over time, mice can settle in such a sheathing.
The thickness of the insulation layer, and therefore the amount of material, is determined by the thermal conductivity of the material used. Insulation of the attic pediment can be done by laying heat-insulating boards in two layers, placing the boards apart. A vapor barrier layer is required, as it protects the insulation from moisture. The use of penofol for this purpose has a double effect - insulation and vapor barrier. The foil is an excellent reflective thermal insulation, and the gap between it and the inner side of the skin creates a full-fledged reflective effect.
When performing work, remember that all supporting structures must be strong and withstand the weight of the insulation and finishes. The choice of materials should be made in favor of as light as possible in order to reduce the load on the foundation.
How to insulate the attic from the inside
Features of the use of heaters of different types and types.
Soft thermal insulation materials:
attic insulation with mineral wool requires a competent choice and application of films. Thus, it is possible to eliminate the main disadvantage of cotton wool - its hygroscopicity. The second, less significant minus - slight rigidity, is eliminated by reliable fixation of cotton wool, as well as the use of its denser varieties. Thus, sagging of cotton wool is excluded. Nevertheless, due to the environmental friendliness of the components, attic insulation with mineral wool from the inside continues to hold a leading position;
attic insulation with glass wool is rarely performed due to the fact that glass wool is an unsafe material from the point of view of environmental friendliness. Plus, it creates difficulties in installation;
insulation of the attic with penofol. It is used if it is necessary to insulate without significant losses in the height of the room. In order for penofol to perform its functions, the material must be oriented with a foil layer inside the room.
Rigid thermal insulation materials:
insulation of the attic with foam. An excellent and easy-to-install option, which has such a drawback as the incomplete fit of the sheets to the crate. In view of this, a space unfilled with a heater appears and the efficiency of insulation decreases. In addition, polystyrene is combustible and releases toxic substances when burned. And in conclusion, rigid heaters do not pass steam well. The popularity of foam is due to its low price;
insulation of the attic with expanded polystyrene (foam) is similar to insulation with foam
The difference lies in the presence of a tongue-and-groove fastening system, which, in fairness, does not play an important role in attic insulation. And also in the greater density of the material itself
Note that breathable soft insulation will be a good option, if necessary, insulate a wooden attic.
Sprayed thermal insulation materials:
- attic insulation with ecowool. The material is 80% cellulose and 20% wood. It contains a natural antiseptic. This is a completely eco-friendly material;
- attic insulation with polyurethane foam (PPU).

The widespread distribution of sprayed heaters is hindered by their high price, as well as the need to attract specialists and use special equipment. At the same time, as evidenced by consumer reviews, the price is justified by a high level of thermal insulation. After all, the sprayed material fills the smallest gaps and eliminates sources of heat loss.
The thickness of the attic insulation depends on: the type of roofing material, the height of the room, the presence of a heating system, the location of the insulation and its type.
Recommendation. If a chimney passes through the mansard roof, basalt wool should be used. It begins to melt at a temperature of 1000 ° C, and does not smolder like ecowool and does not melt like rigid insulation (polystyrene, foam plastic).
Waterproofing and vapor barrier under insulation
Since wool is the leader among materials for attic insulation, and at the same time it is hygroscopic, it becomes necessary to take care of the wool itself, protecting it with a film of hydro and vapor barrier. Otherwise, the wool will get wet and lose its thermal insulation properties.
For insulation insulation are used:
isospan (20-25 rubles / sq.m.). The vapor barrier film (membrane) has a double layer and surface roughness, due to which condensate is retained;
polyethylene film (3 rubles / sq.m.). The most affordable waterproofing material in terms of price. But this film does not have the ability to pass steam;
waterproofing membrane (30-45 rubles / sq.m.). Many manufacturers offer membranes for roofing, which are distinguished by the ability to simultaneously retain moisture and pass steam.
penofol (40-50 rubles / sq.m.). Foil insulation.

The difference between external and internal gable insulation
To determine the difference between these types of insulation, let's turn to the term "dew point", since the efficiency of insulation work depends on it. The dew point (TP) is the air temperature at which the moisture in it reaches its maximum saturation and, as a result, condenses on the surface of the wall (or other plane).
Insulation of the attic pediment from the inside is as effective as from the outside, but the insulation procedure must be performed taking into account the smallest nuances. Poorly insulated areas are more prone to condensation on their surface than others
Particular attention should be paid to corner and butt joints, since these are the places most susceptible to moisture settling. To determine the “dew point”, a special technique can be used using special physical and mathematical functions, but not everyone has a technical mindset, so the following table was created to simplify this procedure:
| t˚C air | HVV, Rh | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.95 | |
| -10 | -23.2°С | -20.4°С | -17.8°C | -15.8°C | -14.1°C | -12.6°C | -10.6°C | -10 °C |
| -5 | -18.9°C | -15.8°C | -13.3°С | -10.9°С | -9.3°C | -8.1°С | -6.5°С | -5.8°С |
| -14.5°С | -11.3°C | -8.7°C | -6.2°С | -4.4°С | -2.8°С | -1.3°С | -0.7°С | |
| 5 | -10.5°C | -7.3°С | -4.3°С | -2.2°С | -0.1°С | +1.6°C | +3.3°C | +4.1°С |
| 10 | -6.7°C | -3.2°С | -0.3°С | +2.2°С | +4.4°C | +6.4°С | +8.2°C | +9.1°C |
| 15 | -2.9°C | +0.8°C | +4.0°C | +6.7°C | +9.2°C | +11.2°С | +13.1°С | +14.1°С |
| 20 | +1.0°С | +5.2°C | +8.7°C | +11.5°С | +14.0°С | +16.2°С | +18.1°С | +19.1°С |
| 30 | +9.5°C | +13.9°C | +17.7°С | +21.3°С | +23.8°C | +26.1°С | +28.1°С | +29.0°С |
| 40 | +17.9°С | +22.6°С | +26.9°С | +30.3°С | +33.0°С | +35.6°С | +38.0°С | +39.0°С |
In this regard, the insulation of the attic gable from the outside is a more acceptable method, since the “dew point” is already, by definition, located outside, where, when exposed to winds and sunlight, excess moisture will evaporate and not accumulate on the wall surface.
Expert answers
Vladimir Petrov:
You don't have the right insulation pie so everything will rot for you. Take only min cotton wool and that will be enough. Plus vapor protection wind and moisture protection and ventilation gaps. Wall thickness 150 mm ceiling 200 mm
Eugene Autumn:
Throw ruberoid to hell, but isover and mineral wool, but it’s better to leave the minplate!
Alexei:
Terrible pie. Warm to soft, dry to wet. Make a thermal calculation on the Internet - there will certainly be waterlogging of the building envelope.
Aa kk:
Ruberoid is not needed, this pie too. Mineral wool is enough (mice love to live in penoplex), and OSB is sheathed.
Denis Garan:
In no case do not insulate from the inside! the transition zone through the dew point in the cold season will be inside, the pediment of the boards will get wet and rot
kes use:
Mineral wool between membranes (windproofing to the outside, vapor barrier to the inside)
Bikeev Pavel:
I would not advise so easy to do everything with penoplex - it may not be very safe in the future.
Anton Loginov:
I would advise using certified and high-quality heaters.
Artem Posokhin:
film is not needed. wood (lining, frame, OSB) must breathe. If you close them with a film, then the dew point in your cake will then rot the entire structure.
Alexei:
Add slats along the OSB, wind-hydroisol along them, and on top of the counter-rail.
It will blow through without windproofing.
Sergey Parfilov:
What tape and why? There is enough wind insulation with ventilation.
Leela Leela:
On the OSB outside, a perforated wind-moisture protective membrane, slats and siding along it, inside insulation into a frame, vapor barrier, crate and lining, or whatever you want to finish the walls with
Alexander:
OSB itself is like a film and nafik it. Steam-permeable wind protection on a liquid crate with the cheapest unedged board and siding on slats. The advantages of the proposed solution: you do not need to make any significant ventilation products, insulate without problems with a heater from the inside. get damp.
Vladimir Petrov:
You need a film of something like Izospan A. And it is necessary to sew not on the OSB, but first the slats standing in increments of 30 - 40 cm, and now on these slats. There must be a vent gap
Valery Popov:
If there is no insulation, then the vapor barrier will be superfluous. See here - xn--jtbgdbpcsdcddj4a2e1goa.xn--p1ai/how-to-insulate-the-pediment-attic-house/
From within
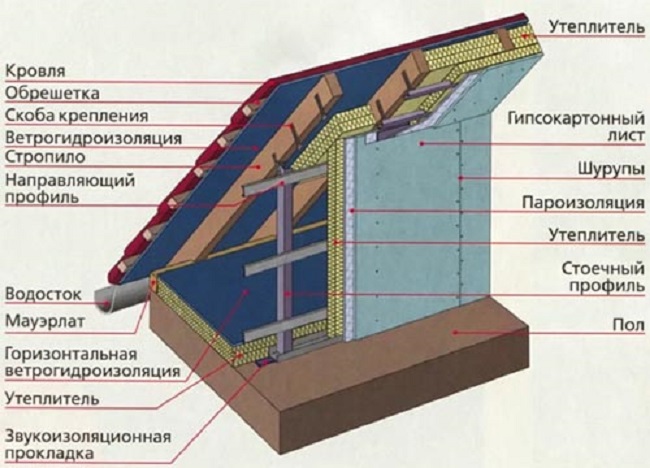
For internal insulation, the usual approach is used to form a sandwich panel or frame-type insulation. The outer boundary is a sheet material made of moisture-resistant chipboard or sheathing along the frame with an edged board. From the outside, the shield is protected by a windscreen and a vapor-permeable membrane; an external finish is attached to the crate. From the inside, a frame of wooden beams or a metal profile is attached, between which the insulation will be fixed.
It is best to use the same insulation as for the roof, or mineral wool without tricks. For materials such as polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, the external and internal finishing of the gable should be waterproof, not forgetting the installation of ventilation ducts for the under-roof space. The latter option is not applicable in the presence of roof support structures as part of the gable. If these are wooden beams, then they need to be provided with ventilation to remove moisture, therefore it is preferable to use vapor-permeable materials.
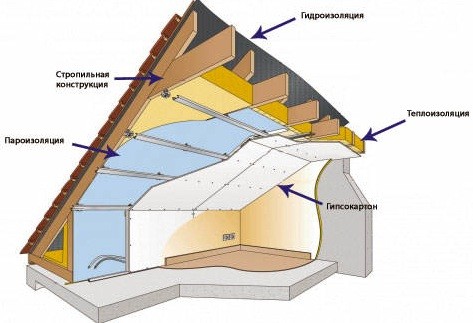
Work order:
- The main frame is mounted from boards 50x150 (200). They must be fixed between the base of the wall and the joists parallel along the wide side at a distance of 590-600 mm from each other so that the gap between them is 10-15 mm less than the width of the insulation used.
- On the outside of the frame, a sheet of moisture-proof chipboard or a cut board treated with protective compounds is stuffed. Next, a vapor-permeable membrane is attached and along the crate with a bar 25x30 or 30x40 wind protection. The last layer is siding.
- From the inside, mineral wool is laid between the elements of the frame. Channels are laid or gaps are formed, combining the ventilation of the under-roof space with the ventilation of the gable insulation layer.
- A vapor barrier membrane is fixed along the entire plane of the pediment with entry to the roof slopes and merging with the vapor barrier screen of the roofing pie. On the crate with a bar 30x40, fixed perpendicular to the frame, the interior trim is attached.
Interior decoration can be drywall, lining or PVC panels. This ends the warming of the gables. With the right choice of insulation thickness, the outer surface of the pediment under the skin is 1-2 degrees higher than the external temperature, due to which active ventilation and removal of excess moisture and condensate are maintained.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=binqf7X84yI%3F
The pediment is the side part of the roof facade. Translated from Latin, "pediment" means "the front of the wall." It is not only a decorative decoration of the roof, but also serves as a support for the beams that hold the roof.
The shape of the pediment depends on the design of the roof and can be triangular (in gable roofs) and multifaceted (in roofs with an attic). As a material, the material from which the walls of the house are erected is usually used.
There are two effective ways to insulate the attic gable: from the outside or from the inside of the building.
- Warming of the pediment in a house with frame walls is carried out from the inside of the room using steam and waterproofing, to prevent the formation of condensate between the insulation and the wall.
- In houses made of block materials, the pediment is insulated from the outside. The technology of the ventilated facade allows you to keep warm, prevent freezing of the walls and the appearance of moisture that evaporates naturally.

Insulation thickness
The attic implies the presence of insulation and heating to the same extent as the rest of the premises in the house. Therefore, the total heat resistance of the roof and gables, of course, should not be less than that of the walls. Given that warm air will still rise from the whole house to the attic, the thickness of the insulation can be 10-15% more.
The second determining factor is vapor and waterproofing.Moisture and water vapor, also under the influence of convection currents, will rise under the roof, and it is imperative to provide for the separation of the internal air in the room from the thermal insulation layer and separate ventilation.
Materials for insulation of the attic outside
Various materials can be used to insulate the attic from the outside, but whatever material is chosen, it must have the following performance characteristics:
- resistance to mold and moss germination;
- durability;
- maximum thermal insulation;
- environmental friendliness;
- fire safety;
- maintaining performance over time.
As relevant for this type of work, the following types of heaters can be distinguished, since they have all the properties mentioned:
- Glass wool. Known to all material has a long history. High resistance to fire, low thermal conductivity and affordable price make this material a fairly acceptable material, but the inconvenience of work significantly increases the time of insulation measures, and in some people it causes allergic reactions associated with the content of glass fibers in the composition.
- Minvata. It is a safer and more environmentally friendly option for glass wool. In addition, it is not prone to moisture absorption and has excellent sound insulation. Therefore, attics insulated with mineral wool are suitable for creating living rooms or libraries (if the house has a high roof).
Such heat-insulating material as polystyrene foam requires special attention. This material comes in two versions, consider them:
- Styrofoam. The classic modification of expanded polystyrene, which consists of 98% of weightless granules with an impermeable shell. They are subjected to short-term high-temperature sintering, which gives the foam all the necessary qualities. As a result, the granules are pressed together and form a plate of the required size.
- Penoplex (extruded foam). The foamed mass of polystyrene is passed through the head of a special extruder, which leads to the formation of foam. In all respects, this material is superior to polystyrene, therefore, insulation of the attic gable from the outside with penoplex can be said to be the most acceptable option.