Advantages and disadvantages of protective coating
The advantages of galvanized casings include:
- light weight (galvanized steel sheets have a large area, and at the same time weigh little);
- simplicity and ease of installation on already assembled structures;
- complete readiness for installation;
- possessing high strength;
- durability;
- compliance with all fire safety rules and building codes;
- compactness and ease of transportation;
- aesthetic appearance;
- possibility of application both outside and inside the premises.
The disadvantage is the need for periodic inspections during the period of operation to detect damage, followed by replacement of the defective part with a new product of the same dimensions.
transcript
1 NEW CLAD - THERMAL INSULATION COVER
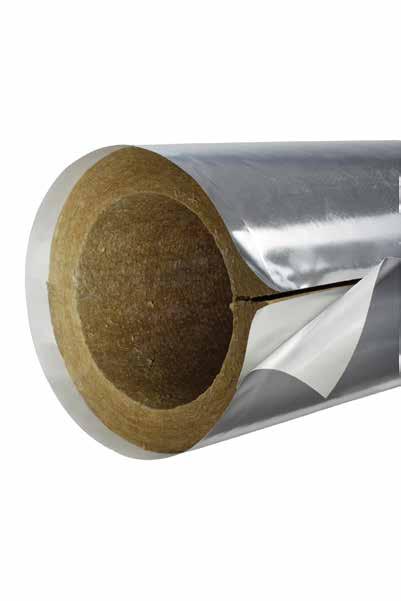
2 PAROC INSULATION WITH CLAD FINISHED COVER Clad products are an excellent solution for a variety of industrial applications, both indoors and outdoors. Clad coated materials can be used over a wide temperature range: PAROC Pro Lamella Mat Clad up to C, PAROC Pro Section 140 Clad cylinders up to C. Using Clad coated Paroc products is a cost effective solution and saves a significant amount of installation labor. You get an insulating structure and a cover layer at the same time. An additional benefit of Clad, unlike galvanized steel and aluminium, is that it is of no value to vandals. Thanks to the reinforced fiberglass fabric with aluminized coating, resistant to UV radiation. Clad coated products are excellent for insulating outdoor pipelines. These materials can also be used to insulate HVAC systems.
3 MOISTURE PROTECTION Clad has excellent moisture protection properties. The cover layer is a vapor barrier coating that prevents the ingress of atmospheric precipitation into the insulation, and also prevents the condensation of moisture from the surrounding air in the thickness of the material when insulating cold surfaces. Protection against moisture guarantees the preservation of excellent thermal insulation properties of the material, as well as reduces the risk of corrosion on the insulated surface. Clad coated insulation performs as designed because stays dry, which makes Paroc's solution stable, durable and energy efficient. ELASTICITY The elasticity of the Clad cover layer allows the use of Paroc mineral wool in knots where physical stability is required. When using traditional cover materials, the structure can be easily damaged. Mechanical damage leads to leakage, moisture penetration into the insulation, pollution, heat loss and corrosion. Paroc with Clad is the solution to all of these problems, as it is more elastic.
4 UV PROTECTION When using the material outdoors, not only mechanical strength is important, but also UV protection. Paroc cylinders and lamella mats with a Clad top coat are UV protected, meaning they retain their performance and tidy appearance. ASSEMBLY Paroc Clad products are very easy and quick to install. You receive at the same time both isolation and an integumentary layer. This means that you save money on the cost of installation and significantly reduce the time of work. For gluing the joints, it is necessary to use adhesive tape based on butyl rubber.
5 PAROC PRODUCTS WITH CLAD COVER The Clad cover on Paroc products is featured on PAROC Pro Section 140 Clad cylinders and PAROC Pro Lamella Mat Clad. PAROC Pro Section 140 Clad Specifications Specific density Length Inner diameter Insulation thickness Fire classification according to GOST 30244, NPB Maximum operating temperature В2, Д1, Т1) Insulation of pipelines and heating networks С 50 0 С С С С С 0.042 0.047 0.065 0.087 0.115 PAROC Pro Lamella Mat Clad Specifications Specific density Width x length Insulation thickness Compressive strength Fire classification according to GOST 30244, NPB temperature Thermal conductivity, W / mK, at different average temperatures: Indicators 50 kg / m 3 width 500 or 1000 mm x length mm (varies depending on the thickness) mm 6 kN/m 2 (with a deformation of 10%) KM2 (G1, V2, D1, T1) The base is non-combustible C. The temperature of the surface of the coating should not exceed C (temperature limitation is determined by the thermal stability of the coating adhesive) 10 0 S 50 0 S M S S 0.039 0.045 0.055 0.081 0.120 SAVE YOUR MONEY WITH PAROC'S ADVANCED INSULATION SOLUTIONS!
6 NEW CLAD COVERING LAYER FOR INDUSTRIAL HEAT INSULATION Parok LLC 1011TIRU0515 Russia Savushkina, 126, lit. A Moscow branch: , Moscow, st. Krasnoproletarskaya, 30, building 1 Tel.:
Installation of grounding and zero protective conductors.
Grounding conductors are laid horizontally and vertically or parallel to the inclined structures of buildings.
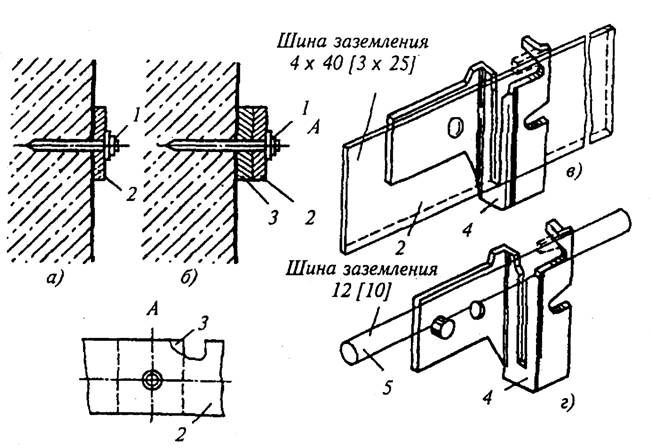
In dry rooms, grounding conductors are laid directly on concrete and brick bases with fastening strips with dowel-nails (Fig. 3.3, a), and in damp, especially damp rooms and rooms with caustic vapors - on linings (Fig. 3.3, b) or supports (holders) at a distance of at least 10 mm from the base (Fig. 3.3, c, d). Conductors are fixed at distances of 600-1000 mm on straight sections, 100 mm at turns from the tops of corners, 100 mm from branch points, 400-600 mm from the floor level of the premises and at least 50 mm from the lower surface of the removable ceilings of the channels. The connection of grounding conductors and their connection to the metal structures of buildings is carried out by overlap welding, with the exception of detachable places intended for measurements. When connecting conductors, the length of the overlap for welding is taken equal to the width of the strip with a rectangular section and six diameters - with a round section.
Grounding conductors to the bodies of machines and apparatuses are connected under the grounding bolt on their bodies. If the machines are skid-mounted, they are earthed by connecting the skid to an earth conductor. Openly laid grounding and zero protective conductors have a distinctive color - a yellow strip along the conductor is painted over a green background.
Types of fastening of grounding conductors: a - to the wall; b - on linings; c, d - on holders for strip and round steel; U - dowel; 2 - strip; 3 - lining; 4 - holder; 5 - round steel
Places intended for connecting inventory portable grounding conductors are not painted.
Technology of installation of lightning protection devices for buildings and structures.
Lightning protection devices (lightning rods) consist of lightning receivers that directly perceive a lightning strike, down conductors and ground electrodes. For the installation of lightning rods, rods made of round, strip, angular, tubular steel with a cross section of at least 100 mm2, a length of at least 200 mm are installed vertically, fixing them on a support or directly on the protected building or structure itself;
cable - from a steel multi-wire galvanized cable of at least 35 mm2 (diameter about 7 mm), strengthened on supports above the protected buildings or structures;
lightning protection mesh - made of steel wire with a diameter of 6 mm is laid directly on the non-metallic roof of the building or under fireproof insulation. Depending on the category of the building, according to the lightning protection device, meshes are used with cells measuring 6 x 6; 3 x 12; 12 x 12; 6 x 24 m.Metal roofing and other metal parts rising above the building (structure) can also serve as a lightning rod. Designs of down conductors and ground electrodes in devices
lightning protection devices are similar to the designs of grounding conductors and grounding conductors in protective earthing devices of electrical installations, therefore the requirements for their device and laying, as well as installation work methods, are similar to those described above.
To protect underground metal structures from corrosion caused by stray currents, polarized drainage is used. The protection ensures the removal of stray currents from underground metal structures through a drainage device into the rail network or the negative bus of the traction substation. Polarized electrical drainage UEDZ-2 is used if the potential of the underground metal structure in relation to the rail network or to the ground is positive or alternating and when the potential difference "underground rail structure" is greater than the potential difference "underground structure - earth".
UEDZ-2 is installed on the wall of the building, on a pole, on metal supports or a special stand at a height of 1-1.5 m from the ground. Drainage must be accessible at any time of the year. Drainage cables lead through the holes on the bottom of the housing.
The cable going to the protected metal structure is connected to the terminal with the (-) sign. The drainage cable is laid in the ground to a depth of 0.5-0.7 m, in accordance with the standard documentation, series 5.905-6 "Assemblies and details of electrical protection of underground engineering networks against corrosion."
What materials are used
This type of insulation is made of thin-sheet galvanized steel in the form of cylinders or shells of different diameters, from which you can choose the right option for any external pipeline.
Installation of galvanized protective shells is carried out on a previously fixed heat-insulating material:
- polyurethane foam. This insulator has a low thermal conductivity, hygroscopicity, durability, good adhesion to steel and sheath material, applied by spraying. By agreement with the customer, pipes in polyurethane foam insulation (PPU) are equipped with a system of ODK (operational remote control). It allows real-time information about damage to the steel pipe and casing, the appearance of places of moisture in the heat-insulating layer, violations of the signal wire;
- PPU shells - products made of foamed polyurethane, made in the form of split cylinders, semi-cylinders, prefabricated elements. Are fixed on a pipe on a coupler;
- foam polymer mineral. The material has a low water absorption coefficient, retains heat well in the line. The cost of foam polymer-mineral insulation (PPM) is lower than other options for heat insulators;
- extruded polyethylene. Pipe insulation using extruded polyethylene is considered reinforced (RH). It is applied in the factory, forms a completely waterproof layer, resistant to temperature extremes and the effects of various chemical compounds and aggressive environments;
- rubber-bituminous mastic. Performs the function of waterproofing metal pipes without affecting the reduction of their thermal conductivity. The technology of insulation with rubber-bitumen mastic involves the application of several layers: a primer that increases the adhesion of metal surfaces, polymer-bitumen mastic and a non-woven fabric for reinforcement. To wrap the insulated surface of pipes, a polymer film or galvanization is used.
Designs and types of fittings
Engineering communications networks have a complex spatial configuration, they include shut-off and control and control and measuring fittings.Therefore, to isolate such structures, not only straight sections are necessary, but also various shaped elements: tees, bends, transitions, plugs, etc.
straight section
This is a ready-to-mount product in the form of an open cylinder. It is mounted with an overlap with other segments, fastened with locks - latches, self-tapping screws or rivets.
The main standard sizes of straight sections of shells:
- length - from 470 mm to 1000 mm;
- outer diameter - from 60 mm to 500 mm (in 10 mm increments), from 90 mm to 1000 mm (in 10 mm increments);
- holes for fasteners - 4-6 pcs. with a diameter of 2.7 mm for self-tapping screws or in the amount of 3-6 pcs. with a diameter of 3.2 mm for installing rivets or snaps.
Withdrawal
Elbows - parts made of galvanized steel with a thickness of 0.55; 0.7; 1.0 mm with a bend radius of 90 or 45 degrees. They are used in places where the pipeline changes direction, to protect the thermal insulation of shaped elements.
Tee
Tees protect the branching of pipeline networks. Available in several versions:
- round T-shaped 90 degrees;
- straight with the same length of pipes;
- with a shortened shoulder length at 30 and 45 degrees.
They are installed in the same way as rectilinear products with an overlap, fastened to metal screws (such as bedbugs) or riveting.
Plug/transition
End caps are designed to protect the heat-insulating layer at the end of pipelines. They consist of two parts with ridges, mounting holes and self-tapping screws.
A transition is a straight section of a concentric or eccentric shell that is ready for installation. It has one longitudinal and two transverse ridges, holes for fasteners and the required number of self-tapping screws. It protects a fitting installed at the junction of pipes of different diameters or made of different materials.
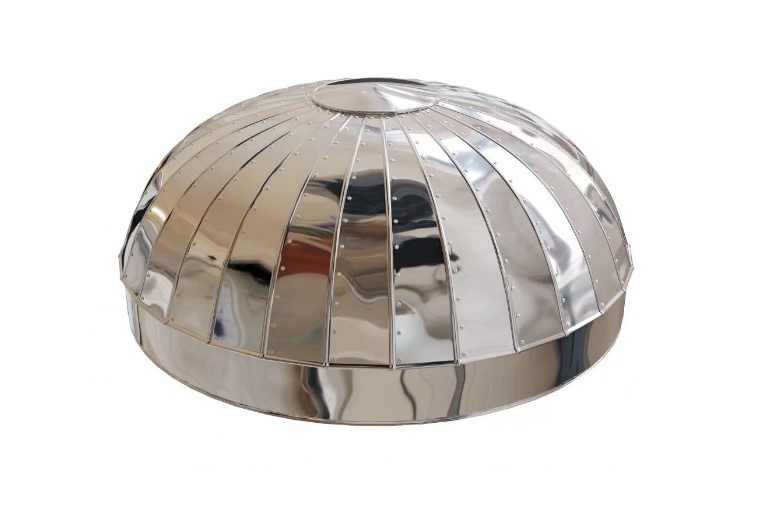
Zeppelins
Zeppelins are round shaped products made up of segments (petals).
Ridges and holes for rivets (self-tapping screws) are provided along the edge of each segment. Zeppelins are used to insulate the ends of containers and reservoirs.
Sheaths for valves and flanges
They are made in the form of a detachable box with the necessary ridges and special locks - latches, for rigid and reliable fixation of parts of the product. They serve to protect the heat-insulating layer from the negative effects of the environment at the locations of locking devices, various instrumentation, flange connections of the pipeline system.
Cones
Cone shells are a type of cone-shaped galvanized coating with longitudinal and transverse ridges. They perform the function of protecting the thermal insulation layer on the end surfaces of the tanks, on the chimney pipes and ventilation ducts from the side of the street.
Sidebars
The tie-in shell is a straight segment having a longitudinal and transverse ridge and a curvilinear junction for mating with the main insulation element, holes for fasteners and the required number of self-tapping screws. It is used to protect the insulation layer at the junction (branch) of lines from the main pipeline.
Integumentary protective layer and Equipment
When insulating equipment, pipelines, tanks and air ducts located on the street - all heat-insulating materials require the use of a cover layer of insulation. The only exceptions are those materials - which are already duplicated (usually glued with the cover layer).
You can watch an overview of galvanized shells in our video:
The need to use a cover layer is also indicated in legislative documents - in particular, the main guiding document for the design of pipeline insulation at the moment is SP 61.13330.2012 “Thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines”. This set of rules should be observed when designing thermal insulation of the outer surface of equipment, pipelines, gas ducts and air ducts located in buildings, structures and in the open air with a temperature of the substances contained in them from minus 180 to +600 ° C, including pipelines of heating networks at all laying methods.
Here are some terms and definitions:
- Cover layer: Structural element installed on the outer surface of thermal insulation to protect against mechanical damage and environmental influences;
- Vapor barrier layer: An element of the thermal insulation structure of equipment and pipelines with a temperature below the ambient temperature, which protects the thermal insulation layer from the penetration of water vapor into it due to the difference in partial vapor pressures at the cold surface and in the environment;
According to SP 61.13330.2012 p4.4., the composition of the design of thermal insulation for surfaces with a positive temperature should include as mandatory elements:
- thermal insulation layer
- cover layer
- fastening elements.
Now there are many materials that can also combine these two qualities at the same time.
Despite the fact that the standards were released back in the 70-80s, and often in the market you can hear “the regulatory framework is outdated” - we can proudly say that great engineering potential was incorporated into these recommendations! The realities of those years were such that technologies did not allow making high-quality products and the engineering thought of real experienced scientists came into force. Even with poor quality materials, with the help of suspensions, wires, support brackets, support rings and other “little things”, it was possible to create a heat-insulating coating that could stand for ten years.
TECHNOLOGY OF INSTALLATION.
ATTENTION! When performing work with "NPSA", it is necessary to be guided by the Rules for labor protection when working with open fire. NPO "Stroypolimer" together with the design institute LLC "Gorkapstroy" developed an Album of technical solutions for the use of "NPSA" for heat pipelines manufactured in accordance with GOST 30732-2006
The album contains a description of "NPSA", the technology of its application on the elements of the heat pipeline. Positive feedback from the institutes of JSC VNIPIEnergoprom, JSC Mosinzhproekt, fire certificate, test reports for determining the flammability and toxicity group
NPO "Stroypolimer" together with the design institute OOO "Gorkapstroy" developed an Album of technical solutions for the use of "NPSA" for heat pipelines manufactured in accordance with GOST 30732-2006. The album contains a description of "NPSA", the technology of its application on the elements of the heat pipeline. Positive feedback from the institutes of JSC VNIPIEnergoprom, JSC Mosinzhproekt, fire certificate, test reports for determining the combustibility and toxicity group.
Cutting sheets "NPSA" is carried out using cutting shears.
Sheets-blanks "NPSA" due to the constant stickiness of the adhesive film are attached to the elements of the heat pipe, which greatly simplifies the installation of "NPSA" on the surface of the heat pipe.
Sheet and tape "NPSA" is joined into a "lock". The developed design of the “lock” joint guarantees a reliable fastening of the LPSA on the PE pipe-sheath. Sheets "NPSA" are additionally connected with a stapler using stainless steel clips.
With the help of external heating with a hair dryer or a gas burner, the “NPSA” surface is heated to a temperature of 200ºС, after which it is evenly rolled over the entire surface of the heat pipe element using a roller or other tool. The heating temperature is controlled by a contact thermometer.
Sheets "NPSA" are joined together with an overlap, the size of the overlap is not less than 50 mm.
When joining "NPSA" sheets on the corner elements of the heat pipeline or when pairing elements of different diameters, the "NPSA" sheets are joined end-to-end, followed by applying a tape of "NPSA" 100 mm wide to the junction. Prior to fixing the "NPSA", the surface of the heat pipe must be cleaned of dirt and dust and degreased if there are traces of oil or other organic compounds on the surface of the pipe-shell.