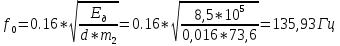6.1.1. Adding Noise from Multiple Sources
At
hitting the calculated point of noise from
multiple sources add up them
intensity. Intensity level
with the simultaneous operation of these sources
defined as
(4.12)
where
Li– intensity level (or sound
pressure)i-th source;n- number
sources.
If
All noise sources have the same
intensity level, then
(4.13)
For
summation of noise from two sources
dependency can be applied
(4.14)
where
–max(L1,L2) –
maximum intensity level value
from two sources; ΔL- additive determined according to table 4.2
depending on the modulus of the difference
intensitiesL1andL2.
table
4.2
Definition
additives ΔL
|
|L1-L2| |
1 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
|
ΔL |
3 |
2,5 |
2 |
1,5 |
1 |
0,6 |
0,4 |
0,2 |
At
If necessary, this method can
spread to any number
noise sources.
Reviewed
features of level summation
allow us to draw a practical conclusion
about what to reduce indoor noise
you must first reduce the noise from more
powerful sources.
Determination of the airborne sound insulation index between the bearing floor slab
Index
insulation of airborne noise enclosing
solid section structures with
surface density over 100 kg/m3
determined
according to the formula:
,
where
m
- surface density,
K—
coefficient taking into account the relative
increasing the flexural stiffness of their concretes
on light aggregates in relation to
heavy concrete structures with
same surface density, is determined
according to table No. 10 SNiP 23-103 2003. For solid
enclosing structures with a density
1800 kg/m3
and more K=1
We define
surface density of the carrier plate
overlap according to the formula:
,
where
ρ - the density of the reinforced concrete slab is equal to
,
h
– plate thickness equal to 140 mm
,
where
m1
is the surface density of the carrier
floor slabs.
We define
TO:
K=1,
because ρ≥1800 kg/m3
We count
carrier plate airborne noise index
overlap according to the formula:
,
because m1≥100
kg/m2
We define
surface density of the structure
floors above the soundproofing layer.
At
the presence of a soundproof layer
determine surface density m
floor structures above soundproofing
layer as the sum of surface densities
structural elements:
,
where
m2
– surface density of the structure
floor above the soundproofing layer kg/m2
ptie
=1600 kg/m3
htie=
40 mm
pthe park=
800 kg/m3
hthe park=
12 mm
We define
load on the soundproofing layer
overlap.
where
R
– floor payload varies
from 2000 to 3000 Pa
g
- acceleration of gravity,
taken equal to 10 m/s2
P=
2000, Pa
=>
5000Pa
table
No. 16 SP 23-103 2003
|
materials |
Density, |
Dynamic |
|||||
|
2000 |
5000 |
10000 |
|||||
|
Ed |
e |
Ed |
e |
Ed |
e |
||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
7. |
|||||||
|
Penotherm (NPP-LE) |
6,6×105 |
0,1 |
8,5×105 |
0,2 |
9,2×105 |
0,25 |
|
Ed=8,5*105
Pa
ε=0.2
We define
soundproofing layer thickness
crimped state:
,where
d
\u003d 0.02 - thickness of the soundproof layer
uncompressed
We find
structure resonance frequency:
(accept
by geometric mean values
frequencies
)
Definition
airborne sound insulation index
By
table find the isolation index
airborne noise (Rw)
given interfloor overlap.
Rw0
= 51.13 dB
table
No. 15 SP 23-103 2003
|
floor construction |
fp, |
Air insulation index |
|||||
|
43 |
46 |
49 |
52 |
55 |
57 |
||
|
2. Floor covering on a monolithic |
160 |
50 |
51 |
53 |
54 |
55 |
57 |
Rw
= 54 dB
Conclusion:
room
under floor
can be used as premises
common areas (corridors, lobbies,
halls) because
normative value of the insulation index
airborne noise
for floors
Rw(norms)
= 47 dB,
what satisfiesRw(norms)
≤ Rw(calc)
(47≤54),
hence
cover meets requirements
SP 23-103 2003
Definition
index of the reduced level of shock
noise under the interfloor ceiling with
floor on a soundproof layer.
Index
reduced impact noise Lnw
under floor slab
on the soundproof layer
determine according to table No. 17 SP 23-103 2003 in
depending on the value of the index
reduced impact noise for carrier
floor slabs Lnw,
determined according to table No. 18 SP 23-103
2003, and natural frequencies
floor lying on soundproof
layer f,
determined by the formula:
Where
Ed
– dynamic modulus of elasticity
soundproofing layer, Pa
ε
– relative compression of the material
soundproofing layer under load
on the soundproof layer, Pa
By
table No. 16 SP 23-103 2003 we find:
Ed=8,5*105
Pa
ε=0.2
By
Table No. 18 SP 23-103 2003 we find:
Lnw
= 76 dB
Notes:
-
At
sheet suspended ceiling
(GKL, GVL, etc.) from the values Lnwsubtracted
1 dB -
At
filling the space above the hanging
sound-absorbing ceiling
from values Lnw
subtracted 2 dB
Calculate
the frequency of floor oscillations according to the formula for
Ed=8,5*105
pa,
ε=0.2, reduced thickness
(accept
by geometric mean values
frequencies
)
By
table No. 17 SP 23-103 2003 we find the index
reduced impact noise level Lnw
= 58 dB
Conclusionroom
located under an intermediate floor
can be used as a room
music classes of secondary educational
establishments because of the normative value
index of the reduced level of shock
floor noiseLnw(norms)
=58
db that satisfiesLnw(norms)
≥ Lnw(calc)
(58≥58),
hence
cover meets requirements
SP 23-103 2003
Carrying out SHVI from A to Z

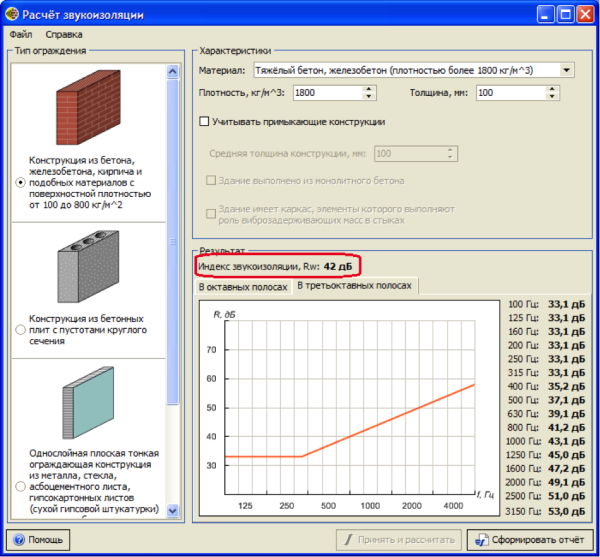
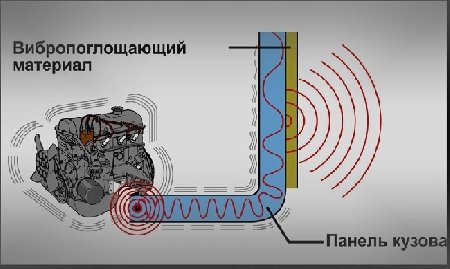
How to use the formula to calculate sound insulation
Carrying out Shvi or rather, protection from external / internal noise was originally provided for by the design of most cars. Only the standard SHVI is not effective enough in most cases. As a result, the following unpleasant moments arise.
- The level of comfort in the car interior is significantly reduced, which is especially important during long trips.
- There is a rapid fatigue of the driver of the vehicle, which causes inattention and errors.
- As a result, various extreme situations begin to arise on the road, including minor and even major accidents as a result of a decrease in attentiveness, and as a result, traffic safety.
Noises that are known to have a negative effect on the driver and passengers are created from:
- A functioning power plant;
- Transmission working components;
- tires;
- exhaust systems;
- Body and its details.
Formulas for calculating sound insulation
To date, numerous technologies and materials are known that can effectively neutralize noise and reduce vibration. They are most often used in car services. There are also instructions that allow you to conduct SHVI on your own. Initially, it is necessary to be able to make a competent choice of appropriate materials for the SHVI.
In particular, you should know that materials differ in the following characteristics:
- Absorption. It is customary to distinguish shvi materials that absorb noise and sound waves. One of the most effective materials of this type is considered to be acoustic felt lined with a bituminous layer.On the other hand, such a material has long been considered obsolete after the release of modern porous materials with similar characteristics.
- Insulators. These materials are capable of reflecting sound waves. For the most part, they are used to isolate the engine compartment or hood, and are also used as a second layer in the car interior.
SHVI Rockwool
- Vibration isolators. These are materials that effectively reduce the vibration frequency of interior panels made of metal or plastic material. It is customary to refer Bimast, Vizomat, etc. to such Shvi.
- Seals. Materials that easily eliminate squeaks and tapping of cladding panels, as well as other interior elements. The best sealants are Madeleine, Bitoplast, etc.
For the best effect, it is customary to combine materials.
As mentioned above, to calculate the required amount of materials, certain measurements are required:
- Using a ruler, measure the body element.
- Then, by simple calculations, determine the area.
- Enter the data into the calculator or roughly calculate how much material will be needed.
Shvi sheets
The table below shows the approximate amount of certain materials used for shvi different areas of the car body.
| materials | Hood | Roof | Door | Floor |
| Bimast | 2 sheets | 1 sheet | 5 sheets | |
| Visamat | 2 sheets | 2 sheets | ||
| Vibroplast | 0.3 sheets | 1 sheet | ||
| Accent | 1 sheet | 0.25 sheets | 2 sheets | |
| splenitis | 0.75 sheets | |||
| Bitoplast | 0.5 sheet |
Decided on the materials. Now you need to properly prepare all the surfaces that will have to be processed.
- First of all, it is recommended to dismantle the upholstery of body parts - the hood, roof, luggage compartment and other elements scheduled for processing. It is recommended to carefully monitor the corrosion spots on the metal surfaces of the parts. If they are, then everything must be cleaned, treated with rust converters, primed and coated with paint.
- Secondly, if the standard Shvi has lost its strength, that is, elasticity, all sheets must be dismantled. To remove bitumen residues from the base, it is recommended to use white spirit.
- Next, it will be necessary to remove all contaminants, thoroughly degrease the body elements with a solvent. The surfaces must be perfectly clean so that the materials of the SHVI adhere to the body parts as tightly as possible.
Shvi in packages
Shvi materials, such as Bimast or Vibroplast, are rarely glued in whole and large pieces. They are applied in strips and pieces cut with their own hands. This allows you to save material, conduct shvi competently and practically.
Here's how cutting is done:
- First, rectangles are marked on the material (on some models there are molded squares with an area of \u200b\u200b1 cm2) and cut along the lines.
- Be sure to take into account the size of the drainage holes.
On the contrary, materials such as Accent, Splenium or Isoton are glued in large pieces.
This is important to consider when cutting with your own hands.
The best formula for calculating shvi materials