Routine maintenance of outdoor drainage systems
In order for your gutter system to be able to serve the entire stipulated warranty period and even longer, it needs periodic preventive inspection and cleaning from external contaminants and debris. It is pollution and debris that most often cause stagnation of water in gutters and storm pipes, disrupting the functionality of the entire system and often leading to violations and damage to its elements. As a result of the accumulation of debris, water stagnation, metal corrosion or the appearance of hardened dirt occur.
First of all, when inspecting, it is necessary to pay attention to such places that are most often subject to obstruction of the passage of debris: this usually occurs at the junctions of system components. In such cases, it is necessary to clean the drains from debris.
Debris and leaves from gutter systems must be removed periodically.
During operation, damage to the elements of gutters occurs due to mechanical influences. Particularly frequent consequences are the appearance of cracks after hail, ruptures and deformations after freezing of water at low temperatures.
Calculation of the number of pipes
Also, engineering calculation determines the number of pipes required for a particular building, and the method of their fastening. Usually the criteria for calculation are as follows. For every 10 meters of gutter installed along the perimeter of the roof, one downpipe with a diameter of 100 mm is required. Sometimes the roof area, or rather its projection, is taken as a reference point.
The point is the following. A roof slope with an area of, say, 100 square meters, set at an angle of 30 degrees (to the horizontal) will take on more rainwater than a slope with the same area, but set at an angle of 45 degrees. It turns out that the greater the angle of inclination of the roof, the less water will fall on the slope. This means that it is advisable to calculate the amount of “received” water not according to the area of \u200b\u200bthe roof itself, but according to the area of its projection onto a horizontal plane.
Experts believe that for every 100 square meters of roof projection, one gutter riser is needed. In addition, the often complex structure of the building necessitates the installation of additional drainpipes. In particular, when calculating the drainage system, experts take into account the presence of gables, bay windows, ledges, and other design features of the roof and facade.
The cheapest gutter system is made of galvanized steel. This budget option is most often used by the housing and communal services system. The fact is that in the cities of central Russia, and even more so in the northern regions, public utilities have to clear the roof of snow, ice, icicles. Any gutter system does not withstand scrap blows.
If we talk about private buildings, then they often use heating of the edges of the roof with the help of a heat-conducting cord. The same approach is possible in elite buildings, but there is no need to talk about the mass use of an electric anti-icing system yet. Therefore, experts consider the use of galvanized pipes in the drainage systems of mass housing blocks to be the best approach. A crowbar destroys metal and plastic gutters approximately equally, and therefore it is advisable to use the cheapest material so that every few years, during repairs, replace old gutters with new ones.
In private buildings, galvanized steel is rarely used, mainly gutter systems are made of painted metal, plastic, or metal with a polymer coating. Special charm - copper drains. This luxury is used, as a rule, in elite buildings covered with copper roofs. However, the compatibility of the gutter system in color and texture with the interior of the building is a very common approach when choosing a material.Gutters and pipes made of PVC or metal, as a rule, are chosen to match the roof, but sometimes the colors are combined, taking into account the color of the facade. So, the gutters can be red or green to match the color of the roof, and the pipes can be yellow or gray to match the color of the facade.
Repair of drainage systems
The need for repair of gutters arises in such situations:
- rust began to show clearly on the metal gutters;
- plastic drains have cracks due to temperature changes;
- in the wind, the drainage system rattles and sways;
- leaks occur at the joints of gutters or storm pipes;
- water overflows through the gutters and leaves at insufficient speed through the storm pipes.
Wind rattles are usually caused by weakening in the fastening of gutters to a wall or roof. The normal passage of water and its overflow through the gutters is facilitated by the presence of pollution or violation of the plane of the joints with their silting.
Sometimes, in order to restore the normal functionality of the drain, you just need to tighten the clamps of the clamps and fasteners (eliminates rattling) and fix the broken joints. When leaks occur at the joints of structural elements, it is enough to ensure the tightness of the connection. In some cases, this problem is eliminated by the use of special sealants. In cases where a structural element has too significant defects that the repair of gutters does not eliminate, it is necessary to replace its damaged sections. This may require the purchase of individual components of the structure.
Replaceable elements of the construction of gutters
The advantage of metal over plastic
Experts believe that the advantage of a metal gutter system over a plastic one is that metal is not afraid of severe frost. But plastic can crack, especially if it freezes suddenly, and water freezes in the drain. It is all the more expedient to equip a metal drain in a building with a metal roof. True, it should be borne in mind that the metal drainage system rings, so lovers of silence may not like this material.
Experts recommend the use of PVC gutter systems in those buildings where the roof is lined with shingles. The fact is that a flexible roof is often sprinkled with mineral chips, and during operation the crumb peels off: it is washed off the roof along with rainwater. The crumb, which has abrasive properties, scratches gutters and pipes. Small scratches do not affect the functional properties of the plastic drain, but the abrasive can tear off the paint from metal pipes and gutters. After that, the structure begins to rust. Rust not only spoils the appearance, but in especially advanced cases it eats through a pipe or gutter, and a leak appears in the drain. Problems of installing an external drain
According to experts, the "secondary" attitude to the installation of the drain creates additional problems. Non-standard approaches became especially characteristic during the crisis years. When building a house, they invest “the last money” in it, and therefore they decide to save on the arrangement of the drainage system. However, during the operation of the building, it turns out that this approach was erroneous: water from the roof whips over the heads of passers-by (owners), and slanting rain floods the facade. Then specialists are called in and asked to attach a drainage system to an already finished building.
However, as mentioned above, gutter holders are attached to the rafters and battens during the construction of the roof - even before the waterproofing (if any) and the coating are laid. It is not so easy to “attach” the gutters to the finished roof, especially if the roof is not “edged” with a frontal board. In this case, you have to get to the rafters to drive hooks into them.But sometimes craftsmen find more affordable and reliable roofing elements (you have to be creative) in order to install gutter fasteners on them. As mentioned above, PVC and painted metal gutters are the most common. According to experts, the average cost of one meter of a plastic drain is from 150 to 200 rubles, and a metal (painted) one is from 200 to 300 rubles.
Storm sewer
Lack of well-maintained and cleaned storm drains many of us have repeatedly had to "sip" our own shoes on rain-drenched streets. It is not the heavy rain that is to blame, but the lack of an established rainwater drainage system. It cannot be ruled out that on the flooded streets, the storm drain was covered with asphalt during the next road repair, or this is a flaw in the staff, who does not clean it in a timely manner. In the construction project of a building, street, microdistrict, storm sewers must be provided. As mentioned above, water should flow directly into the storm drain from the internal drain of the building.
The water, "lowered" to the ground through the pipes of the external drainage system, must also eventually be removed from the streets through stormwater. Sanitary regulations categorically prohibit draining rainwater into the general sewer system, since the water washing the streets is contaminated with engine oils, fuel, and cleaning these components requires reagents that are not provided for in a conventional sewer system.
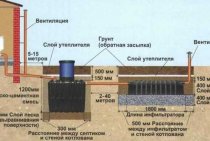
From the surface drainage systems of the stormwater drainage system, water enters the storm sewer system, and then to the treatment plant, designed specifically to clean the rainwater that washed the city streets “along the way”. This is how the city storm sewer system is arranged. In a private house, the owner, who has sufficient funds, also provides for storm sewers during the construction of the building and the arrangement of the plot. As a rule, the drainage system of a land plot, a storm drain laid along the paths, and other engineering infrastructure facilities are thought out and designed as part of a single system.
Experts recommend taking into account that sanitary services require that storm water be treated also in a private courtyard, and separately from the main sewer. However, in practice, there are few people who want to “clean the rain”. More often, storm water, as well as other excess moisture that excessively waters the area, is diverted to the nearest ravine or filtration fields.
surface drainage
Surface drainage is a network of drainage channels and tanks - sand traps. Through a system of vertical and horizontal drainage systems, rainwater flows from the surface storm drain into the storm sewer collectors, and then enters the treatment plant. Drainage channels are most often constructed from prefabricated trays, which are covered with drainage grates. But sometimes drainage channels are concreted on the spot using formwork. Trays are manufactured industrially from concrete, plastic, polymer concrete and other materials. Noteworthy are products made from composite materials, including trays containing mineral components (crumb) “poured” into a polymer form.
According to experts, the main advantage of composite trays is that they are strong enough, despite their relatively low weight. Often, in areas lined with paving slabs (on streets, in gardens, squares, in private estates), drainage gutters made of the same material are used. Experts believe that the main criterion when choosing trays (when it comes to building a private house) is often the distance. That is, the shoulder of transportation from the place of purchase of building materials to the building under construction.
If a house is being built nearby, the owners often prefer to pave the surface drainage with concrete trays. But from afar it is easier to bring relatively light and well-packed products. Although, of course, the material from which the trays are made must be provided for by the project. As well as the cross section of the drainage system, the number and volume of sand traps, the type of drainage grate and a number of other elements of the system. In urban planning, other approaches are usually used. On the roadway, and even more so on major highways, high-strength trays made of concrete or reinforced concrete are installed. From above they are covered with cast-iron gratings with a special fastening.
Accordingly, the more durable materials are used to lay the drainage channel, the more powerful the grate should be. For a drainage system that does not experience significant external load, plastic, steel (galvanized or stainless steel), bimetallic or copper gratings can be used. The latter, however, are quite expensive. Lattices come in various shapes, including cellular. They not only protect pedestrians and vehicle wheels from accidentally falling into the drainage tray, but also prevent debris from entering the storm sewer.
Thus, it is advisable to choose the "step width" of the grating and the size of the cells based on the size of potential "weeds". Among them are fallen leaves of trees, which easily fall into trays covered with large bars. Sand traps are shaped like heavily recessed trays. They are also made of concrete, plastic or other "tray" materials. As a rule, the last channel at the end of the drainage line is connected to the sand trap. Due to the special deep shape of the sand trap, the speed of rainwater flow is reduced. Substances in rainwater (mainly sand and small pebbles, which are abundantly sprinkled on sidewalks in winter on ice) settle to the bottom of the sand trap, and rainwater flows into the storm sewer.
According to experts, for the stable operation of the storm drain, the sand trap must be cleaned several times per season. Silt, sand, dirt, can be scooped out "manually" by removing the protective grate. At the same time, it is advisable to use plastic sand traps equipped with removable waste baskets in areas “not loaded” with heavy transport. Emptying such containers is much more convenient.
Views: 3439
Back to section "Storm water treatment plant"12 August 2013