The most versatile and reliable wall covering in bathrooms is tile. That is why the ability to independently calculate the tiles for the bathroom is a necessary skill for anyone who is engaged in or is just planning to do repairs.
There are two types of independent calculations of the number of tiles needed. Both are simple - even a beginner can handle it, although it will take a little time.
- Primary calculation - based only on the area of the surface to be lined. It must be carried out in order to determine the approximate budget for materials. If the desired amount is known, he will help you find out if it is enough to buy the selected tile.
- Detailed - based on a sketch, taking into account the layout, seams, etc.
Primary calculation (handy calculators)
The methodology for this calculation is simple: you need to calculate the total area of \u200b\u200bthe walls.
All you need is a tape measure and a calculator.
- First, we measure the height of the ceiling.
- Now you need to find the perimeter of the room - the sum of the lengths of all the walls. Let's measure them and add up the indicators.
- We calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe walls of the bathroom, for this we multiply the perimeter by the height.
- The resulting area is divided by the area of one tile (length times width) and we get the number of elements needed for facing the surfaces.
Primary calculation example:
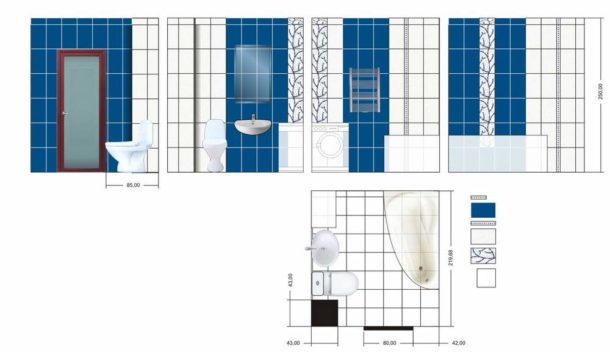
The bathroom has 4 walls, the length of the short one is 2.43 m, the long one is 3.7 m.
The height of the room is 2.66 m.
We consider the perimeter of the bathroom by adding the lengths of all the walls:
Perimeter = (2.43 + 3.7) × 2 = 12.26 m
We consider the area of \u200b\u200bthe walls:
Area \u003d 2.66 × 12.26 \u003d 32.61 square meters m.
Rounding up to a higher whole value, we get 33 square meters. m.
Our handy calculator will help you easily calculate the required area, taking into account the doorway.
Therefore, to clad the walls in this bathroom, you need 33 square meters. m tiles.
Let's count the number of tiles in pieces for this area.
Let the product size be 20 × 30 cm or 0.2 × 0.3 m.
The area of one cladding element is 0.2 m × 0.3 m = 0.06 sq. m.
Then the number of tiles for pasting the entire room in this example will be:
33 sq. m: 0.06 sq. m = 550 pieces.
For a quick calculation, just enter the data in the form below.
Now you know how many tiles you need, you can choose and order!
You can calculate the number of packs of tiles, if it is more convenient in a particular case. For packaging, the manufacturer and seller usually immediately give the total area of the material in it. Therefore, we simply divide the calculated area of \u200b\u200bthe walls by the area of \u200b\u200bthe tiles in the pack and get the number of packages needed to clad the bathroom.
The calculation is approximate and does not take into account trimming in the corners of the room, gaps in pasting and decor.
Choose and buy tiles online
I prefer to buy tiles online - it's very easy, convenient and safe. You can buy tiles without leaving your home. Most often I order delivery directly to the object, so as not to waste time and not “hit” the car.
In the online store you can see the exact characteristics and real customer reviews. There is a photo of how the tile looks already finished.
Moreover, paying for tiles with your card, I get cashback up to 33% of the purchase amount!
It turns out a double benefit! I don’t risk my health, I don’t waste time on the road, I get paid tiles at the time I specified, and I save up to 33% on this.
Detailed calculation: sketching
For a detailed calculation, you need a sketch of the bathroom. To compile it, you need to consider:
- what kind of tile pattern will be on the surfaces;
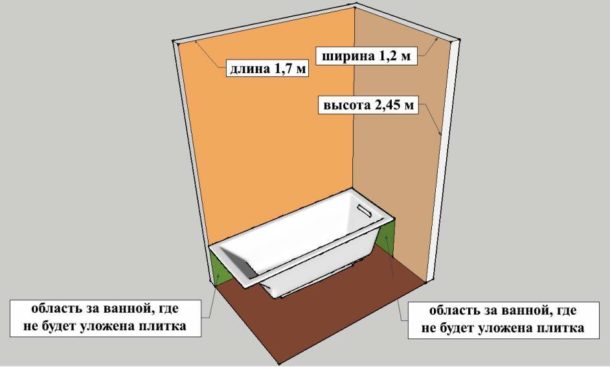
- places without tiles (for example, behind the bathroom);
- layout option.
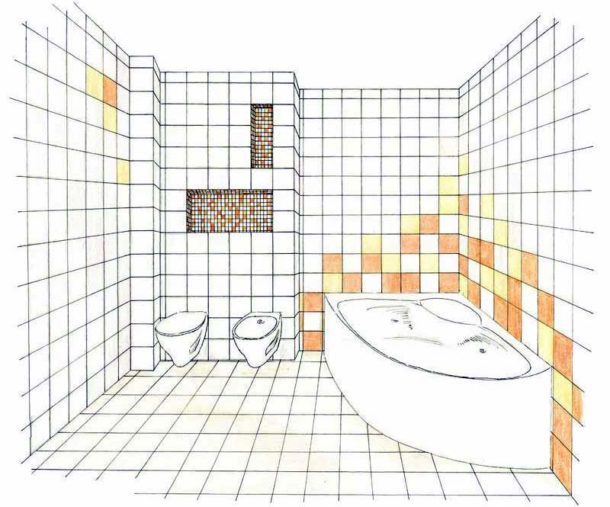
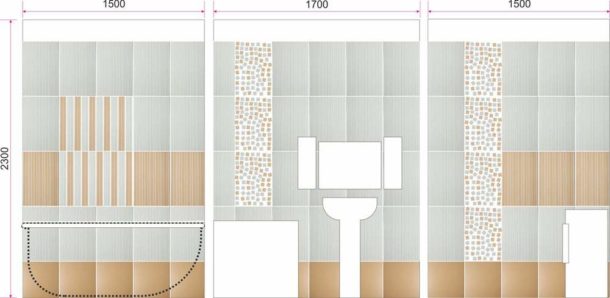
The most popular tile patterns:
- One type of tile, without decor.
- Vertical and horizontal stripes.
- Chaotic inserts of piece decor on a tiled background.
- Using the finished panel.
- Breaking down walls into color blocks (for example, the top of one shade, the bottom of another).
Places to skip when laying tiles:
- behind the bathroom;
- for furniture;
- behind the mirrors. Especially if only a mirror sheet is planned, which is usually glued to an unlined surface.
Economic option
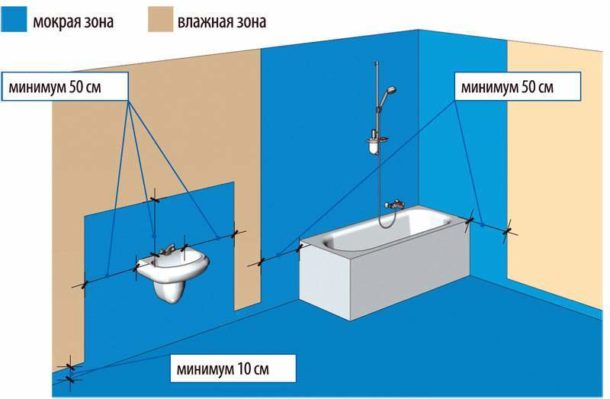
Only a wet area can be tiled with tiles, that is, the place of direct contact of surfaces with water - near the bathroom or shower. The remaining walls are painted with specialized resistant paints.
Plus in selective lining is obvious - financial savings. Each square meter is not only the price of the tile itself, but also the cost of work and consumables. The downside is that it will no longer be possible to make a rearrangement, only during the next repair. The decision is always individual and depends on the budget and features of a particular room.
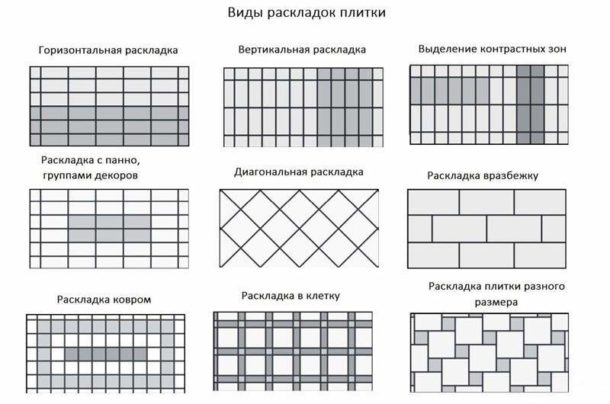
Layout types
When drawing up a sketch, you need to choose one of the tile layout options, which may be as follows:
- Seam to seam, or straight layout. This is the traditional, most economical way. The tile is arranged in even rows, each next joining the previous one at an angle of 90 degrees both vertically and horizontally.
- Diagonal. Finishing elements are not placed at a right angle, but at an inclination of 45 degrees. The most costly layout for tile consumption, since it turns out a lot of scraps.
- Laying with an offset or "spread out". It looks like a straight line, but each row is offset from the previous one, usually by half the size of the trim element.
Other types of layouts (herringbone, modular and others) are much less common than the three presented.
Draw a diagram for each wall
After drawing up a sketch, you can proceed to the final calculation. To do this, you need to draw up a diagram of each wall, which is planned to be tiled.
The scheme should include:
- the length of the wall and its height;
- places where there will be no tiles, indicating the size of these areas;
- decorative inserts.
You will also need values such as:
- length and width of elements;
- seam width.
Calculation for direct nesting
We count how many tiles will line up.
To simplify the calculations, we immediately increase the size of the elements by the width of the seam. For example, a tile has dimensions of 35 × 25 cm, and taking into account the joint width of 3 mm, the parameters are 35.3 cm × 25.3 cm.
Let's look at an example:
Let the length of the wall (DS) be 235 cm. We will lay out the tiles vertically, its width (SHP) - 25.3 cm.
DS : SHP = 235 cm : 25.3 cm = 9.28 pcs.
We round up to a larger integer value - for laying one row you will need 10 pieces.
Similar calculation for height:
The height of the wall (BC) is 260 cm, the length of the cladding element (DL) is 35.3 cm.
BC : VP = 260 cm : 35.3 cm = 7.4 pcs.
Rounding up, we get 8 pcs.
Thus, for facing a surface of 260 × 235 cm with a tile of 25 × 35 cm, you will need:
The number of tiles in a row × the number of elements in height = 10 × 8 = 80 pieces.
Similar calculations are performed for each wall.
After counting the number of tiles, taking into account the layout, a grid of rows and columns is applied to the sketch directly on top of all available designations.
How to take into account areas without tiles in calculations?
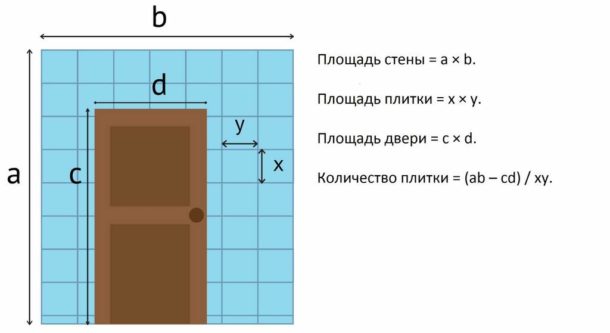
Let's take a door as an example. Let's turn to the scheme of the wall with the applied grid.
Thanks to the real calculation of the location of the elements, immediately after the grid is applied, you can see how many tiles cross the door. We count the number of integer elements that fell on the opening, and subtract them from the total number. Tiles that partially intersect the area of the door are not subtracted.
We do the same with any area that remains unlined.
How to adjust the result taking into account the decor?
The easiest and most economical option is if the decor has the size of a background tile. Then we replace the main elements in the calculations with decor (in rows, columns or individually), subtracting this amount from the total.
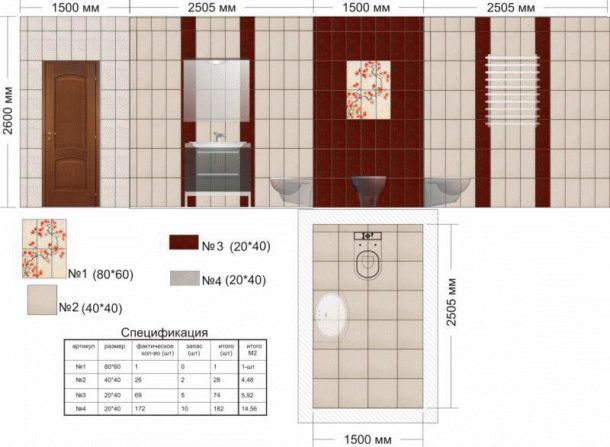
Example:
On the already calculated surface there should be a decor located vertically.Its size coincides with the parameters of the main elements.
The size of the wall in tiles is 8 rows × 10 columns.
So, taking into account the decor, which will take one column, the main tile will have 9 columns by 8 rows, i.e. 72 elements. The decor will be represented by 8 tiles.
We do the same with the decor located horizontally. Piece decor is simply subtracted from the total.
If the decorative elements do not match the main ones in size, we use the calculation principle for areas without cladding (example with a door). We apply decor and a grid of the main tile to the wall scheme. Then we determine how many whole products are at the intersection, and subtract them from the total number.
Calculation for the layout "Razbezhku"
For this method, every second row will require one more element than with a direct layout. We make the calculation according to the method described above, and add the missing elements by the number of rows.
Calculation for the "Diagonal" layout
Accurate calculations for this option, taking into account decor and gaps, are possible only according to a diagram drawn on an exact scale.
It will be correct after all the calculations to additionally multiply the result by 1.1. This sets an error of 10%. This will save you from searching for similar ceramic tiles in case of errors in cutting, color variation and other troubles.
All these rules apply to tile calculations on any surface, including in the toilet and for tiles on the floor.