Varieties
Depending on the production technology, several varieties of polyethylene are distinguished.
HDPE, PSD and LDPE
The abbreviations mean low, medium and high pressure polyethylene.
The difference between them is in the conditions and technology of ethylene gas polymerization:
- HDPE is formed at a pressure of 0.1-2 MPa and a temperature of 120-150C in the presence of catalysts;
- PSD is produced at approximately the same temperature (100-120C), but already at a pressure of 3-4 MPa. Catalysts are still needed to run the reaction;
- LDPE requires a pressure of up to 300 MPa at a temperature of 200-260 degrees, but its production does without exotic additives: only oxygen initiating the reaction is needed to start polymerization.
PEX
Unlike a HDPE or LDPE pipe, a PEX pipe does not have the main disadvantage of a polymer - its low heat resistance. By what means is this achieved?
With certain types of processing, polyethylene molecules, stretched into parallel chains, begin to be cross-linked. At this increases the mechanical strength of the product and its resistance to temperature
: PEX can withstand heat up to 180 degrees or more without destruction.

Four technologies are used to process the polymer:
- Heating with peroxides (this is how PE-Xa is obtained)
- Chemical treatment with silane and catalyst (PE-Xb);
- High energy electron beam irradiation (PE-Xc);
- Nitrogen treatment (PE-Xd).
For different technologies, domestic GOSTs allow different degrees of crosslinking (the percentage of cross-linked molecules that determines the physical characteristics of the polymer):

Polyethylene PE-Xa is the leader in the degree of crosslinking.
It would seem that PE-Xa should have maximum strength. However, the actual characteristics of a real pipe are affected not only by the number of bonds, but also by their strength, and it differs for bonds obtained in different ways.
PERT
The only distinguishing feature of this type of polyethylene is its higher heat resistance due to the introduction of active copolymers into it (more precisely, actene, C8H16). Plastic surpasses PEX in this parameter and is able to remain solid at temperatures up to 200-220C.
A distinctive feature of the PERT pipe is its high temperature resistance. Otherwise, it differs little from ordinary polyethylene.
Installation
How are polyethylene pipes installed?
Bells
The tightness of the connection of the socket sewer pipes is ensured by rubber seals in the sockets. The pipe or fitting is pressed into the socket with your own hands or with the help of a simple device from a clamp and a lever. The outer chamfer must be removed from the edge of the pipe.
Sliding couplings
Corrugated pipes are connected differently:
- Between the corrugation rings, a rubber sealing ring is put on the pipe;
- A coupling is pushed onto it with the help of a lever and a clamp or with the involvement of loading equipment. Its inner surface is pre-lubricated with silicone grease for better glide.

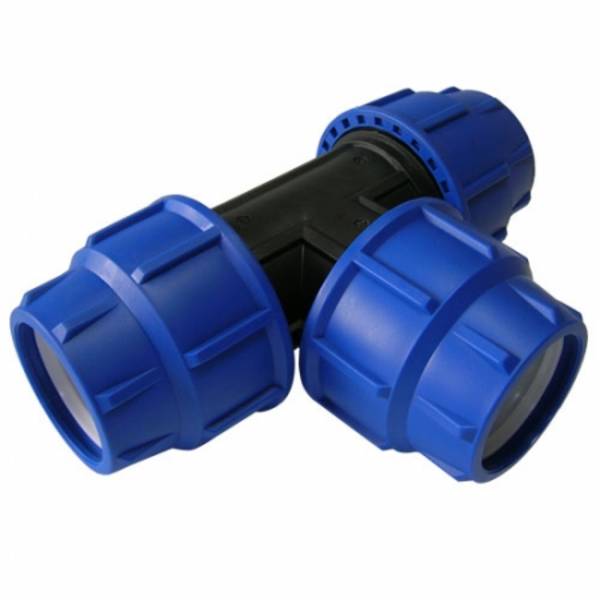
Compression fittings
This type of connection is used on cold water. The fitting is a union nut that compresses the pipe with a ring (rubber or polyethylene) of conical section.
The assembly of the connection is extremely simple:
- Loosen fitting nut;
- Without distortions, insert the pipe into it with a translational movement;
- Tighten the nut by hand, without the use of tools.
Electrofusion fittings
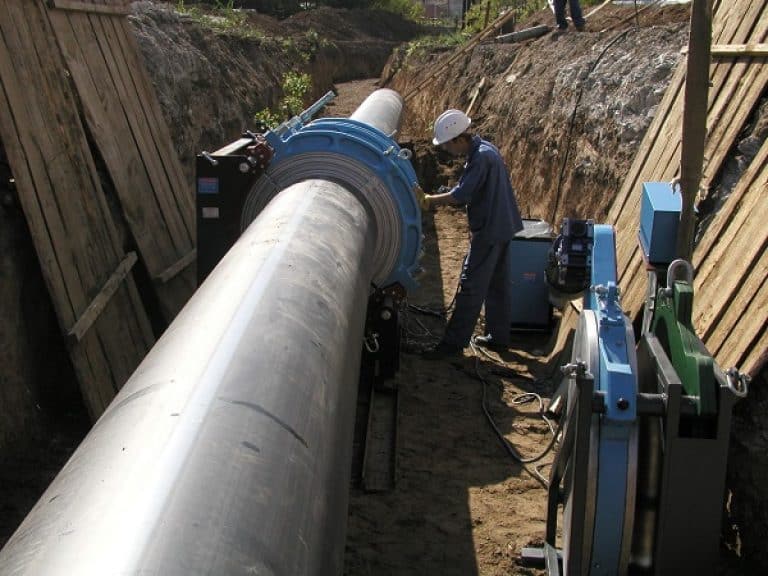
This is a typical solution for underground gas pipelines. It attracts by the fact that welding is performed in a fully automatic mode, eliminating any errors.
The essence of the method is a short-term power supply to the contact terminals in a socket fitting with a built-in heating coil. When the coil is heated, the coupling is reliably welded to the pipe.The welding machine reads data on the temperature and duration of heating from a bar code on the surface of the fitting.

In the photo - the connection of the gas pipeline with an electrofusion fitting.
Socket Weld Fittings
PERT polyethylene, unlike PEX, retains thermoplastic properties: it is able to melt when heated and solidify when cooled. This feature allows you to use extremely cheap coupling fittings for connecting pipes. The inner surface of the fitting and the outer side of the end of the pipe are melted on the heating element of the soldering iron and combined; after cooling, they form a single whole.

Union fittings
Cross-linked polyethylene has another interesting feature - shape memory. If you stretch the pipe, it will quickly return to its previous size.
That is why fittings with herringbone fittings and compression sleeves are used to connect PEX pipes. The end of the pipe is stretched by the expander and put on the fitting; the slipped sleeve eliminates accidental undocking during a jerk.

Butt welding
Butt welding is used for the installation of pipelines made of HDPE and LDPE with a wall thickness of more than 4 mm. The ends are faceted and centered relative to each other, after which they are pressed against a flat heating element for a short time.
After removing the heating mirror, the ends are pressed against each other with a force of 1.5 kg/cm2 and fixed until the polymer hardens.


Types of pressure pipes made of polyethylene
HDPE pipes are classified according to the maximum pressure of the transported working medium and the so-called weight category, since the resistance to pressure depends on the density of the material, which is directly proportional to the mass of the product.
| Class (kind) | Limit pressure, kgf/cm² | Ultimate pressure, bar |
|---|---|---|
| lungs | 2,5 | 2,45 |
| medium-light | 4 | 3,92 |
| medium | 6 | 5,88 |
| heavy | 10 | 9,80 |
When installing a pipeline from HDPE components, it is especially important to correctly make nodal connections. Experts recommend adhering to the following rules for connecting pressure pipes:
Experts recommend adhering to the following rules for connecting pressure pipes:
- Pipes with a diameter of more than 110 mm are best connected by welding. Welds are the strongest, tightest and most stable, but cannot be dismantled.
- If you need to make a detachable assembly on a pipeline with a large diameter, flange fittings are used.
- When laying household communications, pipes with a diameter of up to 110 mm are usually used - it is permissible to connect them using fittings, it is even possible to make collapsible connections. When making a weld, a burr will appear along it - an influx of polyethylene, which will reduce the throughput of the pipes.
- Pipes of any diameter can be connected using thermistor fittings - a hybrid assembly is obtained, one-piece, reliable, but without a burr inside.
- Cut low-pressure polyethylene with a fine-toothed saw or pipe cutter. The cut is performed strictly across the pipe, avoiding distortions.
- Before connecting polymer products by any method, it is necessary to level the pipe cut, clean, degrease and dry the mating surfaces.
Executing nodes in various ways also has its own characteristics:
- For a welded joint, you need to heat the ends of the pipes and gently squeeze them, accurately matching the edges. It is difficult to perform this operation without a special tool, but if a small number of nodes is needed, it is quite possible. If you need to perform a large number of operations, you need a set for welding polymer pipes: a mirror heater and a centralizer. The pipes are fixed in the centralizer, a mirror is inserted between the ends, the sections are heated and, having removed the heater, the pipe edges are pressed against each other by the centralizer. When using such a set, heating occurs evenly, and pairing is without distortion.
- The thermistor, or electrofusion, connection is simpler, but it cannot be done without heated electric welding equipment and a special fitting.Fittings for this method are made of polyethylene, and a heating coil is located inside the housing. The fitting is installed on the pipes, an electric welding machine is connected to its external terminals, after which the spiral heats up, melting the fitting body and the edges of the pipes. The heated plastic of the connected elements and the electrical fitting is welded.
- Flange connection also requires a welding machine - for attaching flanges to pipes. Flange fittings for pressure polyethylene pipes consist of the flange itself - a plate with holes for bolts, and a flange - a smooth-walled fitting with an end plate. The flange is put on the pipe and shifted along it from the edge. Then a shoulder is welded to the pipe, after the seam cools down, the flange is shifted to the edge of the pipe, where it abuts against the end plate of the shoulder. Having prepared the pipes in this way, they are connected to each other. To do this, the flange holes are combined, bolts are installed in them and tightened in pairs: first, two diametrically opposite bolts, then the next pair.
Normative documents
In the Russian Federation, polyethylene pipes are produced according to several regulatory documents, depending on the pipe material and its area of application.
Pressure
The interstate GOST 18599-2001 is responsible for the production of pressure pipes.
Here are its key points:
- The working temperature of the pipes is from 0 to +40C. Standard - 20C. The nominal operating pressure is limited to 2.5 MPa (25 kgf/cm2);
- The polyethylene pipe is designed to transport both water and other liquids and gases;
- The diameters of polyethylene pipes are from 10 to 2000 millimeters. The table given in the text of the standard includes not only the nominal diameter, but also the wall thickness: it varies from 2 to 118.5 mm;


Pipe marking is applied to its outer surface and includes:
- The word "pipe" or the designation of the manufacturer;
- Abbreviated designation of the type of polyethylene by density (PE 32 - PE 100);
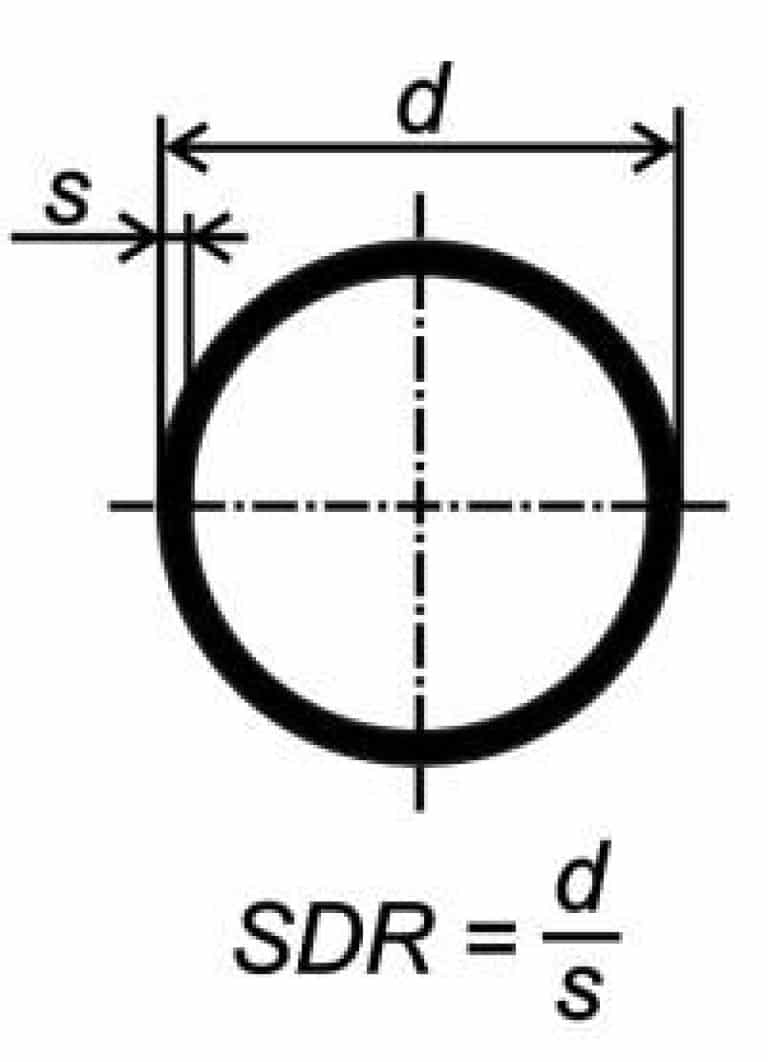
- SDR is a dimensional ratio equal to the result of dividing the diameter by the wall thickness. The smaller the SDR, the stronger the pipe;
- Dash;
- Diameter;
- Wall thickness in millimeters;
- Purpose ("drinking" or "technical");
- Standard designation.
Gas
Polyethylene gas pipes are produced according to the national standard GOST 50838 - 2009.
Here is its summary.
The standard applies to all pipes for underground gas pipelines.

The laying of plastic gas pipes on the surface is strictly prohibited: the polymer is combustible and does not differ in anti-vandal properties;

- The range of sizes is from 16 to 630 mm. The wall thickness is also regulated in this case. It ranges from 2.3 to 57.2 mm;
- With a diameter of 200 mm or more, delivery is possible only in straight sections, with a smaller section - in coils or coils.
The designation includes:
- The word "pipe";
- Material designations (PE 80, PE 100);
- Indication of the purpose of the pipe for transporting gas (the word "gas");
- Outside diameter;
- wall thickness;
- The name of the standard.
Sewer
Polyethylene sewer pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 22689.2-89. Unfortunately, I have not seen them for sale for a long time. Why "Unfortunately?
Judge for yourself:
- Unlike PVC and cast iron, polyethylene sewerage perfectly tolerates minor deformations and bends during installation;
- As we have already found out above, she is not afraid of defrosting;
- Thanks to thick and elastic walls, it slightly inferior to the cast-iron pipe in terms of sound insulation
while maintaining the low weight and ease of installation characteristic of plastic.

GOST provides for only four sizes:
To connect the pipes to each other and to the fitting, sockets with rubber seals are used.
A special case
Corrugated sewer pipes (for example, the domestic Corsis line from Polyplastic) are produced according to technical conditions, and not according to GOST, and the structure of such a pipe differs markedly from conventional polyethylene sewage.
Corsis are made two-layered: the corrugated outer layer provides maximum ring rigidity, and the smooth inner layer provides minimum hydraulic resistance.

Technologies of the Polyplastic company allow manufacturing products with a diameter of up to 3000 mm (Korsis Eco line) and a length of up to 12 meters. Pipes of this size are massively used in the installation of sewers.
Multilayer for water supply and heating
The latest standard for today is GOST R 53630-2009.
The list of products regulated by him includes PEX and PERT pipes, but not all, but only multilayer ones:
Including a layer of perceiving hydrostatic load (M-pipes). Example - PEX / AL / PEX (cross-linked polyethylene with a layer of aluminum);

Including more than one layer of polymer (P - pipes). An example is PEX/PERT (two-layer construction made of cross-linked and thermo-modified polyethylene).
There are few requirements in the GOST text:
- The surface of the inner and outer shells should not have pronounced irregularities and defects;
- Pipes must withstand a constant hydrostatic pressure equal to that declared by the manufacturer, without destruction and deformation;
- The adhesive bond between the metal and polymer shells should not delaminate under load and without it.
Where is HDPE pipe 32 mm used
Polyethylene products made of HDPE are designed for use in systems:
- drinking water supply;
- transportation of combustible gases;
- non-pressure drains;
- irrigation and drainage of groundwater;
- protection of power and low-current cables.
Polyethylene products are available in 2 versions:
- Smooth. Single-layer product with even outer and inner walls. It can be used in irrigation systems and pumping chemically inactive liquids.
- Corrugated. One- or two-layer product with a smooth inner surface. This design provides greater strength and rigidity of the product. Corrugated pipes are used in the arrangement of drainage and dirty water drainage systems, as well as a water conveyor in a personal plot, where high strength is required when laying at great depths.
What are HDPE pipes
Watch this video on YouTube
According to sanitary and technical standards, a non-pressure HDPE product is not used in hot water supply systems, as well as in water supply systems that transport fluid under high pressure.
In dirty water drainage systems, a plastic pipe with a diameter of 32 mm is used to create new and repair or replace old pipelines. High-quality assembled design will be strong, reliable and will last a long time.
Products of this diameter are often used to protect various types of power and low-current cables. In such HDPE products, it can be laid in the ground, concrete and places with a high level of groundwater. The cable can be in a waterproof and durable sheath for a long time, because the service life of the pipes is about 50 years.
SDR polymer pipes
SDR is another important indicator of polymer products. This is a non-linear characteristic that determines the ratio of the outer diameter of the nozzle to the thickness of the plastic walls. Naturally, the SDR of gas pipes can be much larger than that of water supply conductors.
Depending on the needs, this indicator can have a ratio from 41 to 6. For example, a pipe with a diameter of 1000 mm and a minimum allowable wall thickness of 25 will have a ratio of 40. For high density polyethylene, the ratio is maintained in the range of 15–20. According to SDR, experts calculate the maximum pressure that is permissible in the water supply system at a temperature of 20 degrees (for cold water) and 40 degrees (for hot).
Why is this matching of parameters so important? A high SDR indicates good patency, but the thinness of the walls. Whereas low SDR is a sign of low permeability, but high strength and density of bends
Here S is the series coefficient.It is a standard indicator, which is determined by the table of standard sizes. The parametric series R10 is used for the calculation.
Areas of use
Are there any restrictions on the use of polyethylene pipes?
Cold water supply
No limits. If the strength of the pipe corresponds to the design pressure in the water supply, it can be safely used for the installation of risers and cold water distribution: the operating temperature all year round does not exceed the maximum 40 degrees for HDPE and LDPE.

Hot water supply
Theoretically, the parameters of hot water supply (70C at pressures up to 6-7 kgf / cm2) fit into the values recommended for PEX and PERT. Can these pipes be used for DHW distribution in an apartment or cottage?
The answer depends on the source of hot water. If you are connected to your own boiler - everything is in order. But with the DHW system, powered from the elevator unit and further from the heating main, everything is much more complicated.

The mode of its operation is completely determined by the so-called human factor:
- If at the peak of cold weather the DHW is not transferred to the return pipeline in the elevator unit, the water temperature may noticeably exceed 100 degrees. PEX and PERT degrade rapidly at temperatures above 90C: at 100C, the service life of a PEX pipe is reduced from 25-50 years to ... ta-dam ... 100-200 hours;
- If during the spring temperature tests of the heating main the locksmith responsible for your house does not turn off the hot water supply, the result will be the same: water superheated to 100 - 130 degrees will go into the hot water supply system;
The conclusions are obvious. In houses with centralized hot water supply, it is better to use metal pipes - copper, steel (including galvanized) and corrugated stainless steel.

Heating
Can polyethylene be used for heating?
And here a simple and unambiguous instruction will not please the reader's attention. First, let's separate the flies from the cutlets
There are two types of heating, which differ markedly in the characteristics of the coolant:
- Convection. Heating appliances (convectors, radiators, registers) are heated up to 75C in an autonomous circuit and up to 95C in the central heating system;
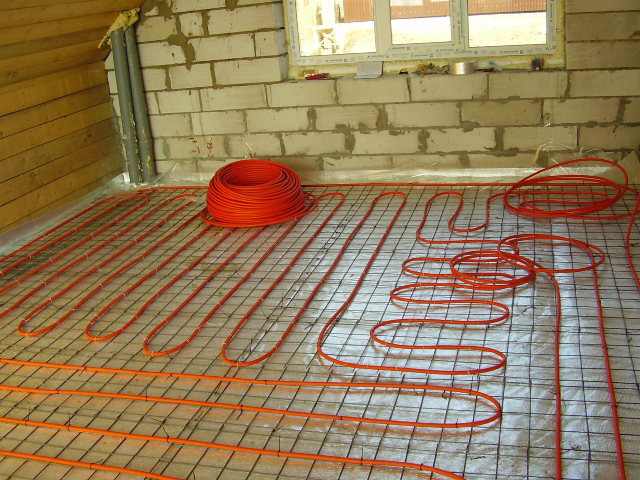
- Low-temperature intra-floor (warm floor). Here the temperature of the coolant does not exceed 40 degrees.

The use of polyethylene in the central heating system, I think, can not be commented on: the same factors operate here as in centralized hot water supply systems. Will PERT or PEX serve happily ever after on autonomous convection heating?
At a constant temperature of 70 degrees, the estimated service life of PEX will be ... only 2.5 years. Obviously, here polymer pipes will not be the best choice.
But as a water-heated floor, they are ideal. At +40, the expected service life will be at least a quarter of a century.
Sewerage
Are there any restrictions on the use of a polyethylene pipe for waste disposal?
Only one thing - their operating temperature. Hot drains over time lead to deformation of the polyethylene walls. If the constant operating temperature of the sewer does not exceed 50 degrees, pipes can be used without restrictions.
When laying above ground (along the wall, basement ceiling, etc.), the pipe must be fastened in increments of no more than 8 diameters. Polyethylene, even more than PVC, is prone to deformation under its own weight. This is clearly seen in the condition of polyethylene combs (internal sewerage) in houses built in the 70s - 80s of the last century.

PVC sewerage is fastened in increments of no more than 10 diameters, from polyethylene - no more than 8.
Benefits of using PE pipes
The wide range of applications of these products is explained by many advantages over their metal counterparts, such as:
- products made of polyethylene have a warranty period of about 50 years;
- they are not exposed to moisture, aggressive environment, corrosion, stray currents, do not need cathodic protection;
- have a small weight;
- installation is simple, while achieving maximum tightness, and there is no need for professional equipment;
- pipes are frost-resistant, do not burst even when water freezes in them;
- due to the ideal inner surface of the pipe, deposits do not form on the walls;
- prices for the purchase and installation of pipes are acceptable.
The main parameter for choosing plastic outlets for the house is their size. All diameters of polyethylene pipes are standardized. Depending on the type of manufacture and the impurities used, the allowable overall dimensions can vary significantly.
The main requirements for the dimensions of polyethylene pipes for cold and hot water are given in the document GOST 18599-2001 for Russia and DSTU B V.2.7–151:2008 for Ukraine. Both of these standards are fully compliant with international ISO 4427-1:2007. Its requirements apply to any plastic pressure pipe plastic products.
Main settings:
Diameter table and its explanation
Diameter of polymer pipes
The diameters of polyethylene pipes are also strictly standardized. Unlike gas pipes, water supply systems are manufactured in the range from 10 to 300 mm. In some cases, it is also possible to use a 600 mm pipe, but only as an external non-pressure sewer system.
The most common are low pressure polyethylene pipes 20 mm, 25 mm, 50 mm, 100 mm and 160 mm. To calculate their inner diameter, which, by the way, is not indicated in the standard marking, you need to subtract the wall thickness from the outer diameter. Fittings are calculated in a similar way.
The resulting difference will be the inner diameter. Naturally, having all this data, you can also easily calculate the SDR for nozzles. For diameter 20, the minimum ratio between diameter and wall should be 2.8.