How to paint galvanized pipes with your own hands
Having decided to paint a galvanized pipe with your own hands, first carefully read all the stages of the process. The result will please for many years, provided that all requirements for pipe preparation and painting are met.
Pipe surface preparation
Previously, experts recommended to withstand a year of contact with the weather and only then paint. This requirement is due to the natural process of zinc oxidation and the formation of the so-called "white rust". With the advent of modern coloring compositions, the need for aging the pipe has disappeared.
Usually, finished products made of galvanized steel leave the factory conveyor in a special protective lubricant. This layer protects the zinc coating from rapid contact with the environment, but before painting, so that the paint does not peel off, it must be removed with any alkaline solution. The solution must be thoroughly rinsed with water and allowed to dry completely.
Painting process
Before painting, to improve the adhesion of the zinc layer to the paint, it is recommended to treat the surface of the pipe with a special primer. Some craftsmen recommend cleaning the zinc layer with any abrasive, such as sandpaper. But it should be remembered that in this way the product will lose the protective properties of zinc.
Having chosen the paint in accordance with the recommendations and future operating conditions of the pipe, after the primer has completely dried, you need to proceed to the painting itself. It is most convenient to apply with a spray gun, but you can also use a brush or a small roller. After applying the first coat, allow the paint to dry for the time specified by the manufacturer. Then apply a second coat and let dry again. After that, the galvanized pipe is ready for installation and use.
Coloring video
For a more visual representation of the painting of galvanized pipes, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the painting video (corrugated board is painted in the video, but there is no difference in technology). It presents the process in detail with step-by-step instructions, gives recommendations that will help you do the job as well as possible, and considers typical mistakes made by beginners.
In conclusion, I would like to note that galvanized steel metal pipes are popular among private sector builders due to their reliability and low cost. After reviewing the article on how to choose a paint and paint a pipe, you can extend its service life for many years.
What is galvanized steel
In the production of building products, it is widely practiced to coat the steel sheet with a thin layer of zinc. This increases the service life of the product due to resistance to corrosion and aggressive environments. Galvanized steel coil is used for the manufacture of roofing and fence material, water supply systems and many other areas.
How to distinguish stainless steel from galvanized
Unlike galvanizing, stainless steel is an alloy with the addition of chromium. Stainless steel sheet is not coated, its surface and cut color is uniform, usually dull. Galvanized steel, during the coating process, is covered with characteristic crystallization patterns, or has a mirror surface with a blue tint.
If the stainless steel is processed to a mirror finish, it will be possible to find out exactly what is in front of you using a chemical reaction. Hydrochloric acid should be dripped onto the edge of the steel sheet. Interacting with zinc, hydrogen chloride provokes bubbling spots on the surface.In addition, chromium alloys are not magnetic, if the magnet is attached to a sheet of steel, it is probably galvanized.
Types and differences of colors
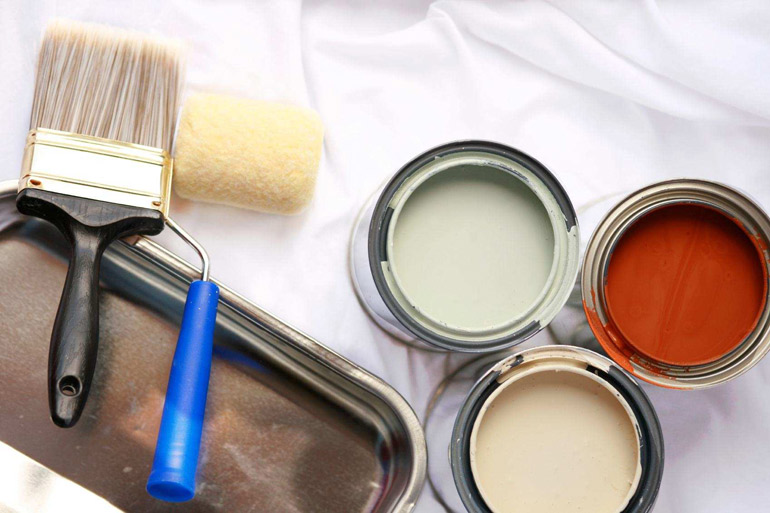
Among the whole variety of types of paints, it must be remembered that not every one is suitable for metal work, such surfaces are considered the most capricious in painting. According to their advantages, polymer powder dyes could be called ideal. They are perfectly combined with metals, durable, wear-resistant. But they have a big drawback - the coloring process is possible only with the help of special equipment.
Do it yourself with acrylic, alkyd and vinyl dyes. When choosing a paint for home coating, it is recommended not to save on the cost of a paint product, choosing it in accordance with the recommendations of specialists.
Acrylic
Acrylic-based paints for metal appeared not so long ago, but quickly gained recognition. Such a coating is durable, does not fade and resists corrosion well due to the base on an organic solvent and special additives in the composition. Does not crack over time, does not support combustion, tolerates heating to high values.
The cost of acrylic paints is also very attractive. In addition, it is convenient to work with it - if it gets on the skin until completely dry, the paint is washed off with water. Environmentally friendly and the absence of a characteristic chemical smell allows you to use it in a house with small children.
Alkyd
Alkyd paints are well combined with galvanized surfaces. Unlike oil, they protect against rust and cracks. They have good drying speed and adhesion. They give a dense glossy color. They are relatively inexpensive.
Disadvantages include flammability and poor heat endurance in direct sunlight
It is important to work with them in a well-ventilated area, as their fumes are toxic. In addition, over time, alkyd compounds react with the zinc layer, and reduce its protective properties.
Vinyl enamels
The only significant disadvantage of vinyl enamels is their high cost. They have excellent covering properties, are easy to apply, resistant to corrosion and chemical attack. They form a water and weather resistant coating that withstands temperature changes from -60℃ to +100/+130℃.
Connection of galvanized pipes by solder welding
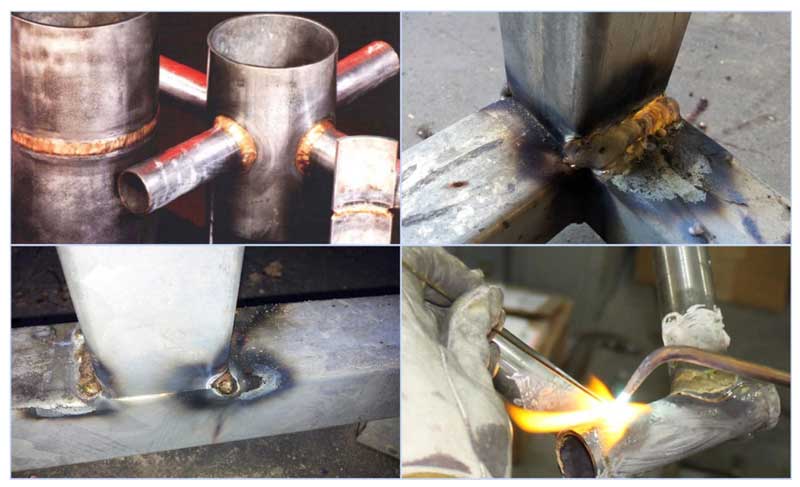
From the above examples, it can be seen that welding with electrodes and a gas torch leads to the destruction of the zinc protective layer, and if it can be restored from the outside in several effective ways, then the inner surface is left unprotected.
Based on the shortcomings of the two methods of connecting products with galvanization, an intermediate option was developed that combines their positive qualities - soldering. Its essence lies in the fact that when welding, a gas burner is used with a lower combustion temperature than an electric arc, a stainless additive and fluxes protecting the zinc surface at the point of contact with the flame and around the seam.
We will consider the technology of performing welding and soldering works using the materials of the French supplier of their products to the domestic market Castolin as an example.
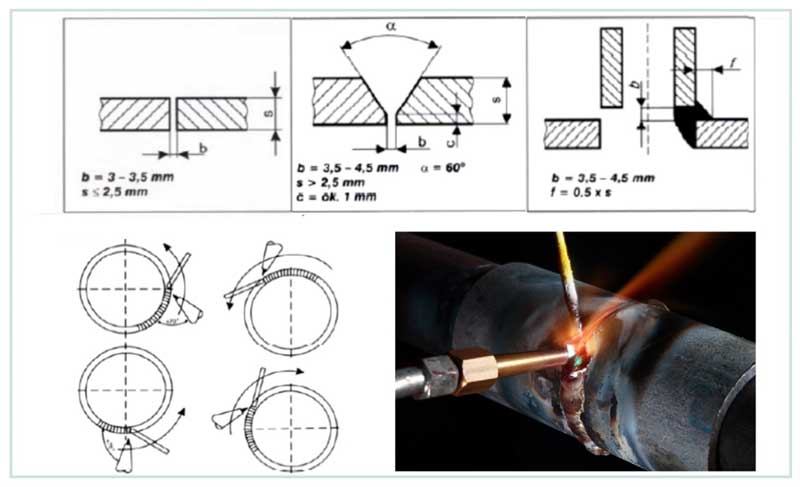
Rice. 15 Brazing tolerances and torch position
Preparation and soldering
For joining galvanized parts, various Castolin solders (18, 18F, 18MF, 18 XFC) are used, the most expensive of them is Castolin 18XFC 2.0 mm on a copper-zinc base (57% copper and 42% zinc) with the addition of silver (1%) has a melting temperature of 870 - 895º C. Such solders are used for high-strength soldering of alloyed and non-alloyed steels, galvanized materials, soldering of copper and nickel parts, the domestic analogue of Castolin 18XFC is L-57. The main stages of preparatory work before soldering and its implementation:
- Preparing pipes for connection. If the wall thickness is less than 2.5 mm, a butt joint is used, for values greater than 2.5 mm, V-machining is used. The angle of inclination of the processed ends of 60 degrees is obtained by mechanical removal of the layer by grinding, milling or manually with a grinder, sandpaper or a file.
- Flame selection. For domestic use, a burner nozzle diameter of 1 - 2 mm is quite enough, with which flame it is possible to weld pipes with a diameter of up to 250 mm with a wall thickness of 2 - 6 mm. To accurately determine the size of the nozzle for soldering, take its diameter one size smaller than in conventional standard welding.
- Flame adjustment. An acetylene-oxygen composition with an excess of oxygen is used - in this case, silicon oxides are formed that prevent the evaporation of zinc. An intermittent flame contributes to overheating and evaporation of zinc in areas adjacent to the seam, so its correct adjustment is important - the burner flame must be uniform.
- soldering technique. To join the two edges, the “left hand” soldering technique is used, in which the solder is in front of the flame, the burner should have an inclination angle of 15 to 30 degrees when filling the seam, if a remelting seam is performed, the angle is set to 70 to 75 degrees. The width of the gap between the parts, the thickness or height of the reinforcement is selected in accordance with Fig.15.
Rice. 16 Soldering galvanized
Flux application
Before applying surfacing, galvanized products must be treated with Castolin 18 flux, they cover the outer and inner surfaces of the attached parts with a strip at least 20 mm wide from the end. In addition to protecting zinc, melting at 416º C, from evaporation that occurs at 906º C, the color of the flux signals the start of soldering.
With a wall thickness of up to 4 mm, a single-pass seam is used; at the end of the work, the outer surface is cleaned with a stainless brush, and the inner surface is washed with water after 24 hours.
Is welding of galvanized pipes allowed and its features
The main problem in welding galvanized steel pipelines is the presence of a coating that prevents fusion. Since the boiling point of zinc is 906º C, and the weld is heated to 1200º C, the zinc burns out during welding and only after that the steel is joined. Carrying out welding work with galvanized steel has the following features:
- Welders with little experience are not always able to evenly weld the zinc sheath and get a good even seam - in order not to create additional problems, before welding it is easier to remove the protective layer of the coating with a grinder with a metal disc, file or sandpaper. Chemicals are also used for this - galvanizing can be removed using solutions of hydrochloric, nitric and sulfuric acids.
- Zinc fumes cause significant harm to human health, have a sweetish taste, therefore, the following requirements of safety regulations (TB) should be observed before performing welding work. It is necessary to provide the workplace with flow ventilation, without which, according to safety regulations, the welder is prohibited from working, and use means to protect the respiratory tract from the ingress of zinc fumes.
- Standard welding methods lead to damage to the zinc layer, while the seam remains unprotected and the overall corrosion resistance of the entire welded structure is significantly reduced. For subsequent protection of the seam, it is better to use similar zinc-containing cold galvanizing compounds, the technology and materials for which are described above.
- Sometimes, due to intense evaporation of zinc, the surface of the pipe is covered with small cracks, to prevent this effect, it is useful to use fluxes. The main purpose of welding fluxes is to isolate the seam surface from oxygen access, to stabilize the burning of the arc, to form a weld and to dope to enrich the seam joint with metal.
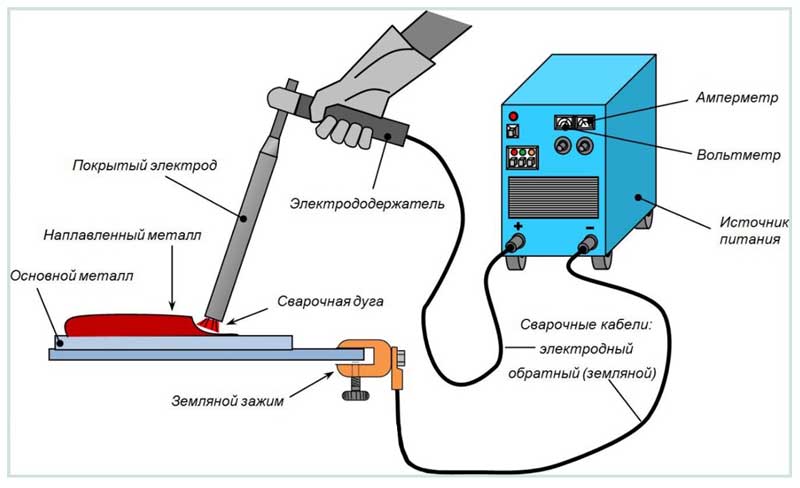
Rice. 7 Electric arc welding
Choice of electrodes
The process of welding galvanized pipes differs little from the welding of ferrous metal. The technological feature of the work is to reduce the welding time while increasing the current strength of the process. Rutile coated electrodes allow this to be achieved.
Rutile electrodes
Rutile electrodes are electrodes whose coating consists of titanium oxide with impurities of aluminosilicates and carbonates.
Advantages of rutile coated electrodes:
- the presence of titanium oxide facilitates the process of ignition of the electrode at the beginning of work or when it is attenuated during work;
- characteristics of the welding arc make it possible to obtain a high-quality seam, without lack of fusion, cracks, with high resistance to wear;
- minimum spatter of metal reduces the loss of molten metal.
The presence of iron powder in the rutile coating reduces the level of steel alloying, which increases the strength of the resulting joint.
Interpretation and designation of electrodes
Basic electrodes
Basic coated electrodes are used for welding thick-walled low-alloy steel pipes. Powder coating here has a complex composition of ferroalloys, calcium fluoride, magnesium compounds.
The cooking process is accompanied by the release of carbon oxides, which protect the molten metal from the damaging effects of atmospheric oxygen and hydrogen.
What is the difference between galvanized pipes and ordinary pipes
About 60% of the zinc extracted from the bowels of the earth by the mining industry is used in the production of galvanized rolled products, another 20% is used for galvanizing metal structures (cases of automotive and industrial equipment, building materials), machine parts and mechanisms.
The difference between structural steel and non-corrosive metals (tin, aluminum, lead, zinc) is that the latter, when oxidized in air, form an oxide, which, in the form of a protective film, becomes a barrier to the access of oxygen to the metal. Thus, the film prevents further oxidation and preserves the metal from corrosion damage. Iron, unlike non-ferrous metals and alloys, during corrosion forms a loose hydroxide of a large volume, as a result of which oxygen freely penetrates to its surface and the oxidation process continues.
The essence of the technology lies in the fact that from an electrochemical point of view, iron forms a galvanic pair with zinc, in which the more active zinc enters into a corrosive interaction with oxygen first, leaving the iron in a chemically passive state. Similarly, the corrosion of iron can be significantly accelerated if tin, which is a more passive element in a galvanic couple with iron, is applied to its surface and its shell is damaged.
Metal pipes of any steel grade are subjected to galvanizing, covering not only their outer, but also their inner surface, while the highest quality and uniform layer is obtained in seamless rolled products. Various technologies are used to apply zinc, which can be used not only on an industrial scale, but also in small private production - many commercial firms are engaged in custom-made galvanizing of steel parts.
Selection Tips
When choosing one or another paint, first of all, you should pay attention to the functions that the pipe will perform. If it is intended for a cold drain, it is more important to take into account the anti-corrosion properties
For pipes of hot water heat resistance. The shelf life should be normal, since after their expiration the composition of the paints begins to collapse.
approximate price
The exact cost of paint depends on many parameters, such as the manufacturer, the volume of packaging, the place of purchase and other nuances. The table below shows approximate paint prices:
| Type of paint | Price per kg, rub |
| Acrylic | 250-650 |
| Alkyd | 150-450 |
| Vinyl | 350-1000 |
When buying, pay attention to the mention of the compatibility of this type of material with zinc surfaces on the package with paint. Not all paints are suitable for working with galvanizing
Purpose and scope
Profile pipes are used in various fields.When only such products appeared, the main direction of application was the laying of communications for the transportation of gaseous, liquid media. Today, the area of use of such products has expanded significantly. They are used in the construction of various structures: buildings, fences, etc.
Profile pipes are used in the construction of bridges, objects that require the use of durable reinforcement. Pre-perforated products are used in furniture production. With the help of profile pipes with different characteristics, metal structures of any complexity are created. Due to such advantages as strength, ease of processing, such products are used in shipbuilding and other heavy industries.
The final stage and subsequent processing of the joint
Welded galvanized pipes have a seam that is not protected from corrosion; when welding with gas burners, a significant area of galvanizing around the joint burns out - all this leads to poor corrosion resistance of the joint. Before and after welding, processing and smoothing the seam with abrasive materials, the following methods are used to combat corrosion:
- When welding using gas burners, rods made of corrosion-resistant stainless materials (zinc-cadmium, brass) are used.
- To protect the outer surface, thermal spraying of zinc or a coating of zinc-containing materials in the form of paint is used.
It should be noted that these methods are effective in the case of using a galvanized pipeline for gas supply, if a welded coated pipe is installed in a heating system, then the zinc layer that has burned out from the inside no longer protects its surface, and corrosion will occur quite quickly. Therefore, when using zinc pipes for heating, it uses other modern methods of connecting them using fitting fittings.
Rice. 14 Braze-weld parts with zinc metal surface - appearance
Benefits of a galvanized chimney
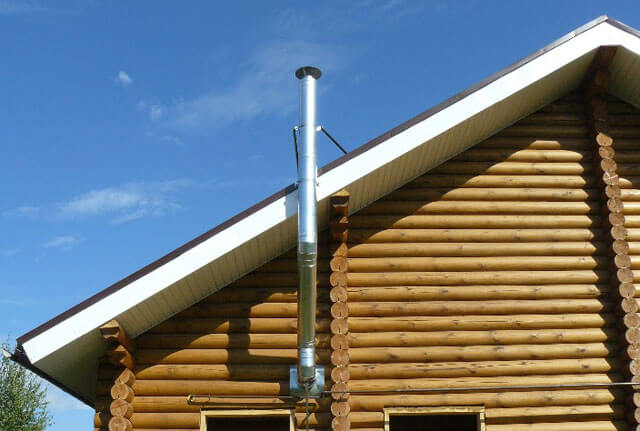
Zinc protection automatically turns an ordinary metal pipe into a reliable and high-quality material that can resist corrosion for a very long time. Chimneys made of galvanized pipes are used in a variety of operating conditions - autonomous heating systems and fireplaces, small country houses, baths and saunas.
The raw material that is used as the starting material in the production of galvanized pipes is ordinary steel sheet, which has suitable flexibility. At first glance, it may seem that this is a tin product, but this impression is deceptive - properly processed metal has completely different characteristics.
Galvanized chimney pipe has many advantages:
- Reliable protection of the pipe against corrosion and various acids;
- Fast system warm-up and stable traction;
- Simple and quick installation of a modular chimney, achieved through a special pipe connection scheme;
- Simplicity of design, allowing you to assemble the chimney yourself;
- Versatility, thanks to which you can connect the chimney to a variety of heat sources;
- Ease of repair - a damaged part can be easily replaced with a new one without complete disassembly of the chimney;
- Fire safety (however, to achieve it, it is necessary during installation to ensure that there is no direct contact of the chimney with combustible materials).
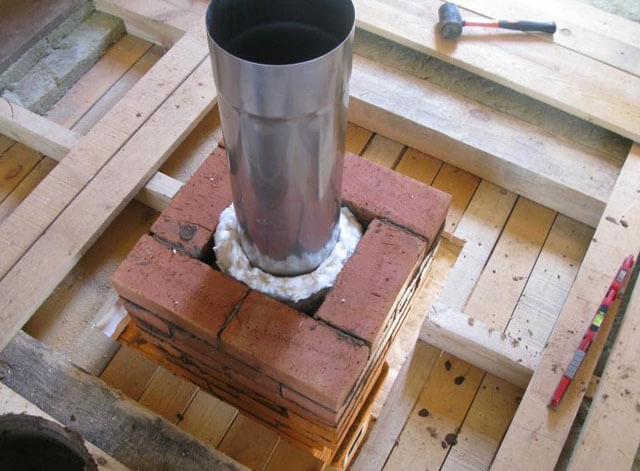
The chimney is usually led to the roof or wall of the building. In the latter case, the chimney must be insulated so as not to run into trouble during operation.
Choice of electrodes

And this will lead to the formation of pores and cracks at the level of crystallization of steel, and, as a result, to a decrease in the quality of the joint of the joined products. Therefore, the main requirement for welding galvanized pipes is the removal of the zinc layer in the joint area.
If it is not possible to remove the protective coating, then special electrodes are used to connect galvanized pipes. In principle, welding a galvanized product is practically no different from the same process of joining ordinary steel. But there are some nuances.
Firstly, the welding electrode itself is a metal rod coated with powder. It is the type of powder layer that affects which metals can be welded.
In the case of welding galvanized pipes, electrodes are used either with a rutile coating or with a basic one. The first is used if the pipes are made of carbon steels (for example, steel 20), the second if they are made of low alloy steel (C345).
Rutile coating

The slag obtained during welding has a high alkalinity, so the metal of the joint has such indicators as high impact strength and increased protection against hot cracking.
The only requirement for rutile electrodes for welding galvanized pipes is to dry them for an hour at a temperature of +200 °C before starting the process. But you can use consumables only after a day.
Basic coating

When burned inside the welding zone, the powder releases carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, which protect the molten metal from the effects of oxygen and hydrogen. The last two reduce the quality of welding. Typically, these electrodes are used for welding pipelines from pipes with a thick wall.
Advantages and disadvantages
Positive qualities of profile products:
- high strength;
- ease of processing;
- the possibility of finalizing the design by bending;
- relatively low weight due to the cavity inside;
- universality;
- a wide range of varieties;
- long service life (30-50 years);
- low thermal conductivity;
- higher resistance to increased pressure inside the product, as well as water hammer;
- when using galvanized products as reinforcement during the construction of buildings, there is a decrease in pressure on the foundation, this is due to the fact that metal pipes take on a significant part of the load;
- the ability to operate in harsh conditions.
Another advantage of galvanizing is that there is no need for additional processing. To extend the service life, the existing protective coating is sufficient. There are some drawbacks to this product as well. So, they note a higher price compared to analogues made of ferrous metal. In addition, zinc-coated products are highly susceptible to mechanical damage. If the integrity of the protective layer is violated, the service life of the structure of such pipes will be significantly reduced.
Types of galvanized chimneys and accessories
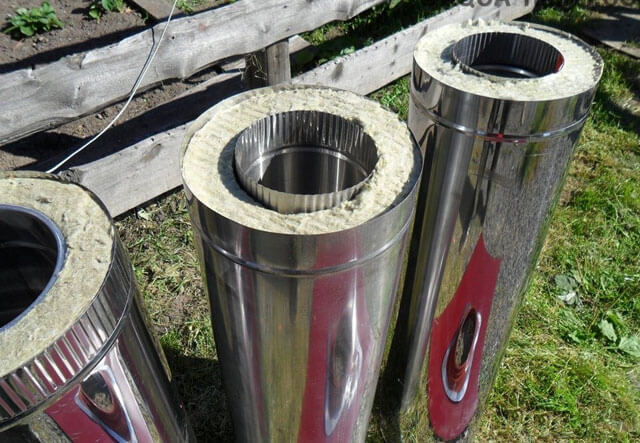
There are two types of pipes used to equip the chimney:
- Single-circuit;
- Double-circuit.
The following items should be included with such a chimney:
- Tees;
- adapters;
- Couplings;
- revision hatches;
- Valve to eliminate moisture;
- Supports for mounting the structure near vertical surfaces.
Simple systems are successfully used in buildings that are operated only in summer (country baths or small houses).The assembly of a single-circuit chimney is quite simple and quite within the power of a good owner, but the finished design has a serious drawback - too high a level of condensate.
A single-circuit galvanized gas pipe is not suitable for those system options that go out into the atmosphere without insulation - this is fraught with rapid destruction of the pipe due to the active appearance of moisture and long warming up in winter. Such a design can only be used temporarily - for example, when building a new house that needs to be heated at least somehow, and serious solutions cannot yet be implemented.
Chimneys made of double-circuit galvanized pipes, in addition to high performance, have good visual qualities, which are achieved through a special coating used to process most metal parts.
Double-circuit chimneys have several advantages:
- High reliability;
- Improving the efficiency of heating equipment;
- Protection against the appearance of condensate;
- Ability to work at temperatures up to 450 degrees;
- aesthetic appeal.
Conclusion
When choosing a chimney or the elements necessary for its installation, it is necessary to take into account the diameter of the pipes so that the structure can be easily assembled. In addition, when choosing a design, it is necessary to consider all its characteristics and take them into account during installation. A properly installed galvanized chimney will perform the functions assigned to it with high quality.
What it is
Galvanized profile pipes are produced by different methods. What unites them is the need to form metal blanks. In this case, the method of cold or hot deformation is used. They differ in material temperature. With hot forming, the procedure is facilitated, since a well-heated metal is characterized by plasticity. When another method is used, the risk of breaking the integrity of the product at the folds increases.
In production, different types of material are used. High carbon steel is popular. This type of metal is the most plastic, due to which the high quality of profile products is ensured. After the end of the production process, the blanks must be coated with a zinc-containing composition. In this case, the surface is saturated with zinc.
To protect pipes from corrosion in the future, different methods are used:
- After molding, the products are cleaned, which allows you to remove the slightest defects. Then they are immersed in a container with a liquid zinc-containing solution. The thickness of the protective layer can be changed depending on the intended purpose of the products. This parameter is determined by the number of immersions in the molten zinc bath.
- In the manufacture of metal profile pipes, galvanized sheets are used. During the production process, the protective coating can be deformed, for example, during welding. If these areas are not treated with a zinc-containing solution, the pipe will quickly rust, and its service life will be reduced.
There is an alternative option - the method of cold galvanizing. In this case, special equipment is used, with the help of which a protective coating is applied to metal blanks. Galvanizing using this technology can also be done manually. This method is based on the principle of interaction of molecules of 2 metals under the influence of an electric current. As a result, the protective coating firmly adheres to the metal surface.
Do I need to paint galvanized metal
The zinc layer on the surface of the steel reacts slowly, but with the external environment. The steel sheet in the process of manufacturing the pipe is subjected to pressure rolling, cutting, welded joints are possible. These parts of the part become more vulnerable, reducing the life of the entire pipe. Applying a layer of paint adds durability, gives aesthetic appearance
But there are some nuances that are important to consider in order to avoid annoying mistakes that reduce all efforts to zero.
What requirements must be met by paint compositions
In middle and northern latitudes, weather conditions affect the coating especially aggressively, so it is important to secure building components by all available means. When choosing paint for a galvanized pipe for a drain, it is important to take into account some requirements for it.
The paint must provide:
- Reliable protection from environmental factors.
- Sun fade resistance.
- Good adhesion with zinc layer.
- Resistant to moisture and temperature extremes.
- Fast drying and easy to apply.
These requirements are especially relevant for pipes intended for outdoor installation. Painting compositions for steel will provide protection and an attractive appearance.
Docking methods
It is important to properly connect galvanized steel pipes to each other. If the fastening technology is not observed, the integrity of the protective coating is violated
Docking methods during installation of the pipeline system, metal structures:
- Special connecting elements: fittings, crab systems. This option is suitable for lightweight structures. Connecting elements allow you to maintain the integrity of the galvanization. At the same time, they wrap around the product from all sides, are fixed with fasteners.
- Collars, branch pipes with a flange. These fasteners are used when installing round pipes, designed for different loads. The clamp is used during the installation of products in any area. A flanged pipe is installed when connecting a corrugated pipe to a flat surface, such as a ceiling, floor, etc.
When choosing connecting elements, the characteristics of communications are taken into account. The most important are the shape and size of the section. Fittings should be selected so that in the future it would be possible to provide a minimum gap between the outer surface of the corrugated pipe and the inner wall of the connecting element.
Where is galvanized pipe insulation used?
The scope of galvanized PPU pipes for the transportation of liquid, gaseous and bulk materials is regulated by GOST 30732-2006, which establishes the following parameters of the transported medium:
- Working pressure in water and steam supply systems - no more than 16 bar. (atm.).
- The nominal temperature of the carrier is up to +140º C, the temperature of the passing liquid can be increased to +150º C if the heating system operates in the +70 - +150º C mode, set for outdoor temperatures below -35º C in the European part of Russia, in Siberia and the Far East .
The PPU pipeline with galvanized insulation is a product intended for surface laying of thermal communications; when placed underground, it is pulled in the passages of channels and tunnels, its main areas of application:
Oil and gas industry. Pipelines with polyurethane foam coating in the shell are used for ground laying of oil and gas pipelines; in the climate of the Far North, insulation prevents excessive cooling of oil products and gas, which reduces their mobility.
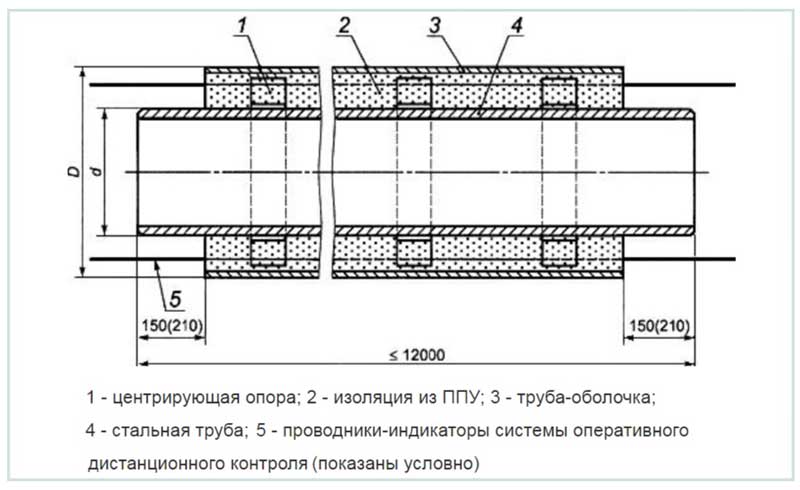
Rice. 3 PPU coated shell - pipe design according to GOST 30732-2006
- Chemical and food industry. In the process of chemical and food production, through the insulated pipeline, components heated to high temperatures, which are part of the technological process, are fed into containers and reservoirs, while reducing heat losses reduces the cost of production.
- Communal sphere. PPU pipes are the main type of pipes for hot water supply and building heating systems, their use allows you to protect the pipeline from cooling and, accordingly, save significant heat resources for heating water.
- Household economy.In everyday life, factory pipes with ready-made PPU insulation and a galvanized sheath for hot water supply are very rarely used - they must be located outside on the surface, which is unacceptable on individual land plots. One of the options for use is installation as a finished chimney insulation.
Also, sliding and prefabricated insulating casings of various types with locking elements, installed according to the shell principle, are made of galvanized steel, their areas of application:
- Intra-house engineering systems - pipelines for hot and cold water supply, heating, ventilation shafts.
- Isolation of chimneys of stoves and fireplaces from the environment and in places of passage through ceiling and wall partitions, the roof.
- Laying of thermal routes in closed underground tunnels and collectors.
- Isolation of open parts of machines and mechanisms with high temperature from contact to prevent burns.

Rice. 4 Dimensional parameters of PPU pipes and insulating steel shells
Problems of joining zinc pipes by welding
There are three sides to the problem of welding galvanized metal. The first is that zinc, if inhaled by a worker, can cause respiratory arrest. The welding temperature of steel fluctuates around 1200 degrees. In this case, the zinc coating begins to evaporate already at a temperature slightly above 900 degrees.
If welding work is carried out indoors, then it is necessary to ensure effective ventilation.
The second problem is that the presence of molten zinc degrades the quality of the joint. Zinc is mixed with the base alloy, embedding in the crystal lattice and weakening it. Intensive evaporation of the zinc coating causes the formation of bubbles, cavities, and inhomogeneity of the weld.
It would seem that by removing the galvanizing at the junction, it is possible to safely and efficiently connect pipes. However, here lies the third problem - local removal of galvanizing leads to rapid wear of communications at the junction.