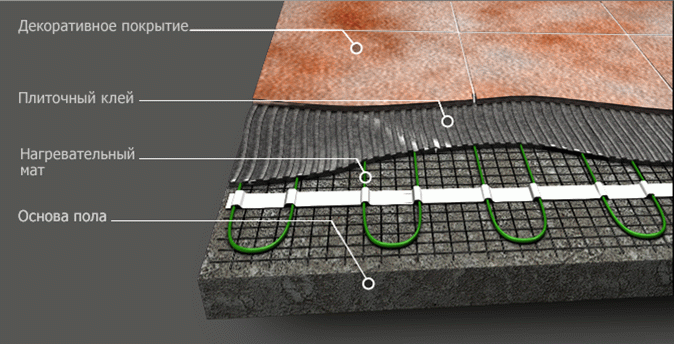
Industrial systems
As mentioned above, a feature of a two-core heating cable is the minimum electromagnetic field created, which is the main criterion for applicability in places of permanent residence of people.
In cases where the resistive cable is used in systems for anti-icing of roofs of industrial enterprises, snowmelt of access roads, as well as in systems for thermal storage heating of state institutions, children's schools and preschool institutions, i.e. in those cases when during its operation there are no people in the immediate vicinity, a single-core heating cable is used. Its advantage is a symmetrical temperature field on the shell surface and low cost.
An additional factor is the harsh operating conditions of anti-icing systems: in summer the temperature on the roof surface can reach +80 °C, and in winter it can drop to -50 °C. Snowmelt systems can be laid under asphalt at temperatures of up to 165°C, and asphalt pavers generate enormous compressive force on the still wet pavement.
For operation at low ambient temperatures as part of snow melting and anti-icing systems, for example, a single-core reinforced Woks-Arm with a power of 30 W / m is intended (Fig. 7). The sheath material of this cable is designed to operate at a temperature of 125⁰С, withstand exposure to 150 °С for 240 hours and 165 °С for 180 minutes without loss of mechanical and dielectric properties. Steel-copper braid 4 (Fig. 8) performs the function of "light armor", preventing the cable from breaking under its own weight, which makes it self-supporting in anti-icing systems. It prevents breakage of a product laid directly in asphalt, since high shear forces are created during its installation. A cable without armor, regardless of the thermal resistance of its sheath, cannot be placed immediately in asphalt. In addition to all of the above, such a braid performs the functions of a ground conductor and an electromagnetic field screen.

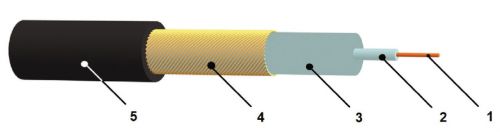
Rice. 8. Design of a single-core NK: 1 - heating core; 2 - primary layer of insulation; 3 - secondary insulation layer; 4 - reinforced steel-copper braid; 5 - heat-resistant shell, resistant to UV
The single-core design is also used for heating the soil, where it is recommended to use NK with a polyethylene sheath. This material has a low maximum operating temperature - only 90 ° C, but this is enough to heat the soil. Working in a wet environment, polyethylene does not absorb moisture like PVC. Any shell, except for silicone and polyethylene, absorbs moisture from the soil and the insulation resistance drops over time, which causes the residual current device (RCD) to trip. In addition, the shell must effectively withstand the constant impact of all kinds of organic substances - mainly acids and alkalis, which are part of fertilizers.
The recommended specific power of NK for soil heating systems is 18 W/m, which does not cause its overdrying.
conclusions
There are 8 factors that have a decisive influence on the design:
- The need to move the NK during operation;
- laying conditions;
- Humidity;
- Acidity of the environment;
- Temperature;
- Exposure to UV rays;
- The time spent by people near the switched on;
- The magnitude of mechanical loads during laying and during operation.
The main conclusion that can be drawn is that it is impossible to make a universal heating cable. One can only try to embody in each individual design the maximum number of technical characteristics that do not exclude each other.
All manufacturers have differences in the range of resistances, the characteristics of the insulating materials used, the number and material of the heating conductors, and the screen design. Each of these designs was created to solve a certain range of tasks, and copes well with them.
Problems arise when trying to use the heating cable for other purposes.
Viewed: 7 726
Installation and connection
In order for the heating wire to perform its functions during its service life, it is necessary to carry out the correct installation. With a certain experience, it will not take much time and effort, but before you start it is necessary to stock up on the following materials and tools:
- cable of the required length;
- scissors;
- gland;
- tee;
- hair dryer;
- electrical wire.
Having prepared all the necessary equipment, you can proceed with the installation. It is performed in two ways: external and internal.
To provide the first method of laying, you need to clean the surface used from dirt and dust. Next, the wire is laid along the entire required area. Then, with an interval of 30 cm, it is attached to the clamps on the surface that needs to be protected from deformation.
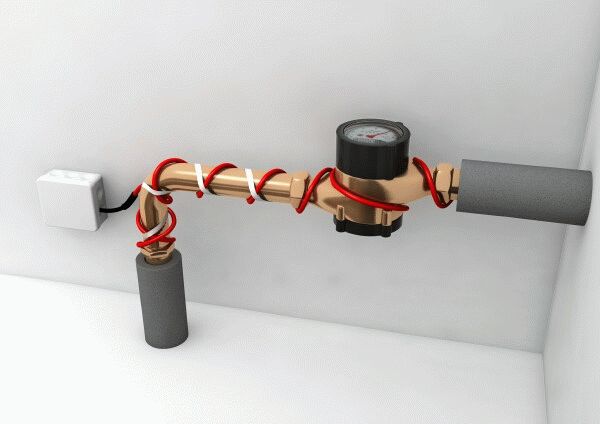
The second method is more often used to protect water pipes and drains from freezing. To do this, a tee is built into the pipe. Further, a wire is inserted through the upper hole, and a water pipe is connected to the consumer through a side outlet.
More detailed information on laying the heating element can be found in the attached instructions.
Regardless of the choice of installation, the self-regulating wire is connected to the power supply using crimp sleeves, thanks to which the connection is strong and reliable.
Having considered the characteristics and principle of operation of a self-regulating heating cable, one can be convinced that this is indeed an innovative development, with the use of which many problems can be prevented in the winter.
When choosing it, it is only important to take into account the combination of power and temperature with the heating object
How to choose a heating cable
Heating cable is a heat-generating cable intended for heating structures and equipment. It has gained particular popularity in industry, where there is a need for heating or protection against freezing of pipelines and process facilities. It is often used in everyday life: floor heating, pipe freezing protection, roof anti-icing systems in private houses.
The choice of heating cable depends on the area of application. For use in residential premises, two-core shielded products of both resistive and self-regulating types with polymer insulation and a seamless polyethylene sheath are used. And for heating, for example, an underground sewer or a drainage system, a screen is not required. Here the main selection criterion is reliability and resistance to external influences. These criteria are met by a self-regulating heating cable, the characteristics of which are as follows: it does not overheat, its partial damage does not lead to failure of the entire system.
Armored cables are used for laying in especially difficult conditions, for example, in open areas, for underground heating or in hazardous areas. Such cables are covered on the outside with a one-piece stainless steel sheath, which protects against corrosion and rodents.
The calculation of the power of the heating cable is made individually for a specific situation.
- a heating cable with a power of 35-60 W / m is used to heat plastic gutters,
- power 50-70 W / m is needed for metal hanging gutters,
- metal gutters on the roof are heated with a cable with a power of 50-100 W / m.
You can more accurately calculate the power of the cable, knowing the data on thermal insulation and roof structure.
- on pipes of small diameters, 16-24 W is sufficient for external cable installation, and only 13 W when laid inside the pipe,
- on pipes of large diameters, 30-40 W are required for installation outside and only 13 W for internal installation.
About the characteristics of the heating cable
The operation of the cable is based on the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy, and its main characteristic is power (the higher the power, the greater the heat transfer).
The cable consists of:
- Internal conductive core (metal alloy with high electrical resistance).
- Polymer braid and copper or aluminum wire braid.
- Sheath made of PVC from external influences.
Manufacturers produce an assortment line of several types of cables with different technical characteristics and design features, including cables with one or two cores, with or without a screen. The price of the cable itself also depends on this. The cheapest is a single-core unshielded cable (has a minus - susceptibility to mechanical stress).
What is the best heating cable? About the principle of action
Heating cables are divided into several types and are used in accordance with the tasks at hand. Resistive cables are used for underfloor heating systems at home and outdoors, as well as for heating pipes with a diameter of not more than 4 cm. Following the manufacturer's recommendations, it can be laid on any surface. With the correct installation of a flexible resistive cable, you will receive uniform heating of the room. In other cases: roof heating, large-diameter pipes, ramps, industrial heating, it is recommended to use a self-regulating cable using special thermostats and sensors to measure the outside temperature and turn on the heating in a timely manner.
Resistive cable:
The most simple and inexpensive cable to manufacture, which is distinguished by a high specific heat release, from the pluses - the preservation of technical characteristics throughout the entire service life. Since the cable has a constant power, it is sold in ready-made sections of a fixed length. This imposes its own limitations: it is impossible to shorten the finished section, this leads to a doubling of heat generation, burnout of the insulation and failure of the entire system.
Specifications of heating cables
To select a heating cable, you need to understand what technical characteristics you need to pay attention to, as well as understand what the heating needs are. This article will discuss the main characteristics of heating cables for the needs of heating water pipes.
Heating cable power
The first characteristic that you need to pay attention to is the power of the heating cable. It is measured in watts per linear meter and, depending on the models, can be from 5 to 150 W / m
The greater the power, the greater the consumption of electricity and the greater the heat output.
To heat the water supply, low-power cables are used - from 5 to 25 W / m, depending on how the heating cable is installed and where the water supply passes, you can focus on the following power:
- the water supply is laid in the ground, the cable inside the pipe is enough 5 W / m
- the water supply is laid in the ground, the cable is outside the pipe - power from 10 W / m
- water supply is laid through the air - from 20 W / m
The pipe and the heating cable in all cases must be insulated with a layer of insulation of at least 3-5 mm.
In the case of a resistive heating cable, the power remains constant throughout its entire length and regardless of the temperature of the pipe, but the self-regulating cable reduces the power consumption and its temperature if the pipe is already heated. This saves a significant amount of electricity, and the greater the working power of the self-regulating cable, the greater the savings.
The dependence of heating power on temperature is shown in the graph.
The graph shows power versus temperature for five different self-regulating cables with different power ratings from 15 W/m to 45 W/m.The greatest efficiency from the use of such cables is obtained when used in conditions of an extended water supply system, which runs in very different temperature conditions. The greater the temperature difference, the greater the savings.
However, when heating a small section of the water supply, it is not so noticeable. If water is supplied from a well, then its temperature, regardless of the time of year, ranges from 2 to 6 degrees, and the task of the heating cable is simply to prevent it from freezing, that is, to maintain it at a level of about +5 degrees Celsius. This means that the heating cable will operate in the temperature range from 0 to 5 degrees, while the difference in power is only a few watts (from 2 W for a low-power cable, up to 5 W for a 45-watt cable).
Heating cable temperature
The second important characteristic is the operating temperature. According to this indicator, all heating cables are divided into three categories:
- Low temperature with operating temperature up to 65 degrees
- Medium temperature - 120 degrees
- High temperature - up to 240 degrees
Only low-temperature cables are used for heating the water supply, moreover, they never work at temperatures even close to their maximum 65 degrees.
Application area
According to the field of application, cables are divided into two types:
- Food - only it can be used for installation inside a pipe when heating a water supply system, which is used for domestic needs, supplying drinking water.
- Technical - used for mounting outside the pipe in any case, it can be mounted inside the pipe only when water is not consumed (for example, in irrigation, washing or heating systems).
Heating cables are used for heating plumbing, roofing, cornices and other elements where water freezing in winter is undesirable. The simplest option is resistive heating cables, they are single-core and two-core.
Self-regulating heating cables are used to heat water pipes in places where they are laid above the freezing level of the soil - for example, at the points where the pipeline enters the house. A self-regulating cable has the ability to independently change the intensity of heating in different areas depending on the need: the lower the temperature of the heated object, the more the cable heats up.
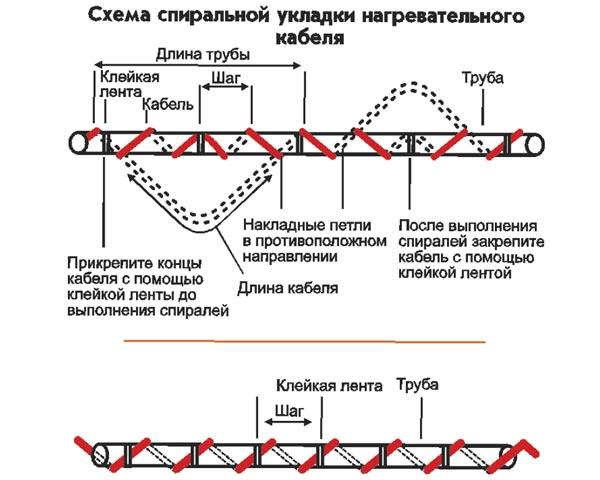
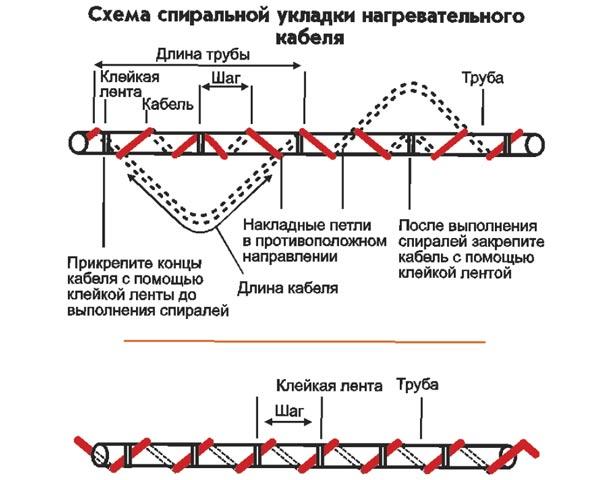
The self-regulating heating cable can be installed in different ways: inside the pipe and outside, placed along the pipe or in a spiral.
The thermostat is an electrical circuit switching device that is used to turn on and off heating devices such as radiators, heating cables in a floor heating system or in anti-icing systems. In principle, the connection diagram is the same for all thermostats.
Features and Benefits of Constant Wattage Cable Products

- high flexibility of the design, providing the possibility of bending in any direction;
- the presence of PTFE insulation, which guarantees the protection of fragile elements from mechanical damage;
- high heating power;
- the ability to withstand the negative effects of extreme temperatures (200-260 degrees).
In the manufacture of heating cables, experts use zonal parallel elements with current-carrying conductors wound around them. The gap between their contact points is decisive when measuring the heating zone. Thanks to the parallel design, the product can be cut and banded for maximum ease of installation. On the website https://elix.ru/greyushhij-kabel/raychem/fmt-and-fht/20fmt2-ct-(1244-006058) constant power cable products can be purchased in different versions. They are distinguished by their ability to withstand steaming, the influence of temperatures reaching 260 degrees.
Top Heating Cord Manufacturers
If you look at the market, there are products from such manufacturers:
- INTERM.
- HEMSTETD.
- FENIX.
- GRAY HOT.
- EXON.
- NEXANS.
IN-TERM is a Czech brand that produces cables of various power (from 172 W). The workpiece is at least 8 m long. If you look at the product range, 550 W products are considered the most common. The length of the workpiece is 27 m, that is, the optimal heating area is 3.8 square meters.
 Brand IN-TERM
Brand IN-TERM
The information is indicated if a step of 14 cm is taken. If we consider a step of 12 cm, then the figure decreases to 3.2 square meters.
Also on the market there are products of the trading company HEMSTETD. It produces cables with a length of 8.9 m. If we consider models for heaters, the longest wire has a length of 197 m. With such a wire, an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 24 square meters can be heated (this is if the step is 12.5 cm).
For each square meter, according to the manufacturer, 140 watts of power is consumed. When choosing a cable of 197 m in increments of 10 cm, it is allowed to heat an area of 119.7 square meters. The total power of the workpiece for the water supply is 3350 watts. The Czechs offer to consider FENIX products. ADSV series wires are considered common.
 ADSV Series Wires
ADSV Series Wires
The minimum length of blanks is 8.5 m at a power of 162 W. If you lay the wire in 14 cm increments, it will warm up a room area of 12 square meters in frost. The 2-core shielded communication cable can have a maximum length of 149m with a total power of 2600W. If you lay it in increments of 10 cm, the material will be able to warm up a room with a total area of 15 square meters when freezing.
Interesting! Consumers also do not exclude GRAY-HOT products from the list, which are produced in Ukraine. The company produces two-core heating cables.
The minimum power of the workpiece for the pipe is 92 watts. We are talking about a wire 6 m long, and if it is laid in 10 cm increments, an area of 0.6 square meters can be heated. The manufacturer suggests considering a product with a rated power of 1929 watts. The workpiece has a length of 128 m, if it is laid in 10 cm increments, it is easy to warm up a room with a total area of up to 13 square meters.
For a change, it is worth considering the products of the strong NEXANS brand. It comes from Norway, blanks of various capacities are produced. If you look at small products, their power starts at 300 watts. A cable with a length of 17.6 linear meters is capable of heating an area of 2.2 square meters. The manufacturer provides wiring with a maximum power of 3100 watts.
The wires of this series have a length of 185 m, designed for a square of 23.2 square meters. Separately, it is proposed to consider a two-core shielded wire of higher power.
If we talk about German quality, it is worth mentioning the SHTOLLER brand. The manufacturer decided to produce only two-core shielded wires with a power of 200 kW or more. The maximum indicator of this series is 3000 watts. The blank has a length of 150 m. The product is designed for a square of 18.7 square meters.
The concept and properties of a heating cable are described above. When choosing a material, it is worth considering the advantages and disadvantages of the wire. Varieties of models are also provided, plus a variety of manufacturers is taken into account.
What is pipe heating cable
The heating cable for heating pipes is heated by the action of a passing electric current and is the main component of the system designed to prevent defrosting of pipes of external communication systems.
The operation of the cable is based on the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy. A characteristic feature of these products is that they do not transfer energy, but only receive it, converting electricity into heat without the use of an oxidizer or fuel.
The main characteristic of a heating cable - specific heat output, measured in W / m - shows the power that is released per unit of its length.
Heating cable sections have different lengths. It can be a segment of several centimeters, or quite long - several hundred meters. It all depends on the needs of the consumers.
Heating cable design
Components of the heating cable:
- The inner core is the main element. It is made from an alloy with good electrical resistance.
- The protective sheath of the main conductor is a polymeric insulating material equipped with a continuous screen of aluminum or a screening copper wire mesh.
- The overall sheath is made of polyvinyl chloride, designed to provide reliable protection of all components of the cable from environmental influences.
There are various types of heating cables on the market. Their price depends on the number of internal cores. The cheapest - single-core cables - have the simplest design. Their disadvantage is that they do not have protection against electromagnetic radiation, which is provided in two- and three-core cables with an additional conductive core.
Resistive heating cable for plumbing.
The resistive heating cable system works according to the following principle: a cable is laid along the entire length of the pipe (on the surface or inside), the temperature sensors installed on the pipe determine the ambient temperature, and the control thermostat is sensitive to any change in relation to the specified parameters. If the temperature drops below, the heating system automatically turns on: current flows, the conductor begins to generate heat, heat the pipe and the water in it. When the required temperature level is reached, the system automatically turns off.
The cable consists of a metal core enclosed in insulation. Its heating occurs evenly along the entire length and, if you do not monitor the temperature regime, it may burn out. In order for the operation of such a heating system to be most efficient, it is necessary to provide the pipeline with very good thermal insulation - this will significantly reduce energy costs and reduce heat loss. Any materials with a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, such as mineral wool, can be used for thermal insulation.
Depending on the power, the heating cable can be laid on the pipe in one or more parallel lines, in a spiral or in waves. Laying is easy, without tension, attached to the surface with adhesive tape made of aluminum. To increase the contact of the cable with the pipe and ensure better heat distribution over the surface, you can wrap the pipe with the cable with several layers of aluminum foil.
Primary requirements
The heating element of the NK, like any electric heater, is a conductive core. Depending on the required power, its resistance is determined based on the Ohm formula:
I=U/R (1)
By substitution - P=U×I (2), we get the final form: R=U2/P (3)
The length of the conductor (m) with resistivity ρ can be determined by the formula: l=R×S/ρ, (4) where: ρ – resistivity, Ohm∙m; S is the cross section of the conductor, m2; R is the electrical resistance of the conductor, Ohm.
From formula (4) it follows that, other things being equal, namely the given power P, which is determined by the total resistance to direct current R and the cross section of the conductor S, its length is inversely proportional to the resistivity ρ.
Using the given dependence, it is possible to calculate heating elements of any length and power. The main task is the ability of the material surrounding the heating element to take this amount of thermal energy.
The main advantage of resistive cable is its flexibility, which is also its main limitation. The sheath material cannot have such a high thermal conductivity as the metal sheath of an electric heating element, and usually does not exceed 30 W/m.
The current DBN V.2.5-24-2012 “Electric cable heating system” severely limits the maximum specific (linear) power of the heating cable laid on wooden logs and the air gap of a wooden floor to 10 W / m. For a heating cable that is completely covered with a cement-sand mortar, the maximum power input is regulated at a level not exceeding 25 W/m.
The value of the specific surface power depends on its size. So, for example, if a cable with a diameter of 4.0 mm with a specific power input of 10 W / m is characterized by an indicator of 0.080 W / cm2; then ø6.5 mm with a specific power input of 16.5 W / m - 0.081 W / cm2. A flat cable with a size of 6x10 mm and a specific power of 23 W/m has a specific surface power of 0.083 W/cm2. As can be seen from the given values, the difference is less than ±2% of the average value, which guarantees absolutely identical thermal conditions on the surface of the shell of these products.
In addition to thermal power, the heating cable, and especially its sheath, must have high mechanical strength, because installation in a screed is carried out under "hard" conditions:
- special metal tape used during installation must not damage the shell;
- tile adhesive is applied with a metal spatula (this is necessary to ensure uniform heat removal from the cable surface), which should also not damage the sheath;
- electricians and tilers walking on the cable, accidental drop of the tool on the cable, should not affect its performance.
All this puts forward increased requirements for the mechanical strength of the heating cable, namely, the ability to resist for 30 seconds without insulation breakdown: crushing by a metal plate 100 × 100 × 10 mm, with a load of 600 N; stretching with a force of 120 N; a single shock load of 2 J at a temperature of minus 5°C (which is equivalent to the fall of a steel object weighing 500 g from a height of 0.4 m).
The requirements for resistive cables that are intended for the manufacture of heating surfaces of floors, walls and other surfaces are completely different than those that apply to products for anti-icing systems for buildings, snowmelt or soil heating.
In each of these cases, the properties of the cable must be different. This forces manufacturers to increase the range, which places a financial burden on them, or to produce a universal cable for all occasions, which places a burden on the consumer.
The task of the manufacturer is to create a flexible, mechanically strong design with dimensions that are determined by the desired specific power input. In Ukraine, there are heating systems of both foreign - DEVI, Nexans - and domestic production. Their design varies depending on the specific application.
Features of installation of cables of constant power
The process of installation of cable products intended for heating is not particularly laborious in execution, but requires the use of complex systems for monitoring and control. At the first stage, the cable is fixed on the surface to be heated. To do this, you can use heat-resistant aluminum tape or other material that can withstand high temperatures. The next steps include removing the external silicone protection, removing the resistive film from exposed areas, mounting the electrical insulating cap, separating and insulating the contacts.
It is possible to ensure a long service life of cable products by using high-quality products that have an ideal technical condition. Therefore, before carrying out any work, it is necessary to check each meter section by connecting it to the power supply.
- Modern cable ducts
- Olmi-Connect: metal cable trays
- Constant wattage heating cable
- AEG hobs
- Electrical goods are the basis of life support at home.
- How to choose a voltage stabilizer for a heating boiler?
- How to choose an uninterruptible power supply for home and office
- Wireless Internet in a private house or country house
- How to save energy in the house Life hacks for the homeowner
- Voltage stabilizer "Saturn": operational advantages of the device
- Werkel switches that "think" for the owners of the house
- How to properly transport the cable
- Residual current devices - safety of people and equipment.
- Features of choosing a quality cable
- New Products of the Kursk Electrical Apparatus Plant
- Calling a Master Electrician
- Pros and cons of LED lighting in offices
- Power line support
- Rules for laying electrical wiring in a wooden house
- Czech crystal chandeliers from Elite Bohemia
- BR cable channels from HAGER - full speed ahead!
- How to choose lamps for the street and at home
- Functionality and design - skirting cable ducts from HAGER
- Designer lamps: room lighting design
- The quality of electrical energy at the enterprise - fight or accept?
- To help a specialist: a modern approach to building AVR systems
- Contactor: today and tomorrow
- Floodlights for street lighting
- Cottage electrical project
- Overview and characteristics of LED strips
- Energy saving at facilities. Condensing plants
- Accuracy in the details
- Energy saving in industry
- Small Wiring Recipes: Elium Legrand Plugs.
- Legrand's rule: a modern office means efficient lighting of every square meter.
- Safe and economical lighting from Impulse Sveta
- Art in every detail - chandeliers from the best manufacturers.
- Advantages of LED lighting and its scope
- Quintela cable systems
- "Vessels" of the energy supply system
- Merten and Gira - German sockets and switches
- DPX3 - a new generation of Legrand circuit breakers
- A fast and reliable way to connect up to 40 MW from SpetsEnergoDevelopment LLC
- Application of LED spotlights
- Recessed luminaires
- Measures to encourage energy-saving technologies
- Modern architectural lighting of urban objects
- Reconstruction of electrical networks and drains
- Variety of choices: table lamps and floor lamps Globo
- Luminaires for suspended ceilings
- Circuit breakers Legrand
- NEPTUN XP on the radio is a next generation leak protection system.
- Diesel power plants for country houses and construction sites
- How to install electrical wiring
- Features of choosing a UPS for home electronics
- Teleco systems are modern light control technology.
- Automation without conditions.
- Accounting and protection under the control of Energomera.
- Single-phase electric meter TsE6807B "Energomera": new look - new advantages.
- Energomera metering devices are safe, reliable, aesthetically pleasing.