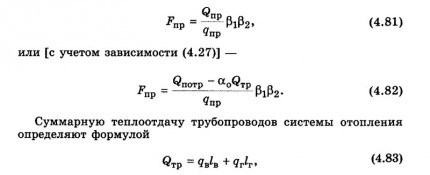How to regulate heating batteries
To understand how the temperature is adjusted, let's remember how a heating radiator works. It is a labyrinth of pipes with different types of fins to increase heat transfer. Hot water enters the radiator inlet, passing through the labyrinth, it heats the metal. This, in turn, heats up the surrounding air. Due to the fact that on modern radiators the fins have a special shape that improves air movement (convection), hot air spreads very quickly. With active heating, a noticeable flow of heat comes from the radiators.
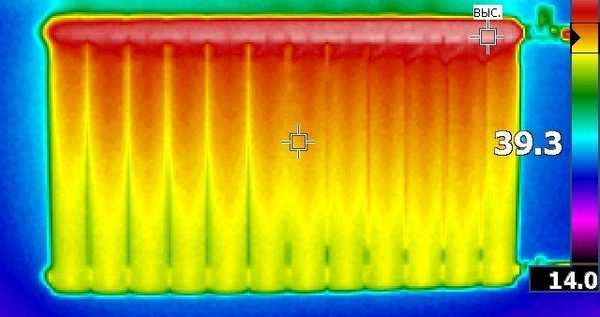
This battery is very hot. In this case, the regulator must be installed
From all this it follows that by changing the amount of coolant passing through the battery, it is possible to change the temperature in the room (within certain limits). This is what the corresponding fittings do - control valves and thermostats.
We must say right away that no regulators can increase heat transfer. They just lower it. If the room is hot - put it on, if it's cold - this is not your option.
How effectively the temperature of the batteries changes depends, firstly, on how the system is designed, whether there is a power reserve for heating devices, and secondly, on how correctly the regulators themselves are selected and installed. A significant role is played by the inertia of the system as a whole, and the heating devices themselves. For example, aluminum heats up and cools down quickly, while cast iron, which has a large mass, changes temperature very slowly. So with cast iron there is no point in changing something: it is too long to wait for the result.
Options for connecting and installing control valves. But in order to be able to repair the radiator without stopping the system, you need to install a ball valve before the regulator (click on the picture to enlarge it)
Ways to increase heat transfer
From the point of view of the return to space of the maximum amount of heat, it is less efficient than a pipe, except perhaps a ball. It has an even worse surface to volume ratio.
What did the ancestors do to heat these monstrous heating devices?
How to increase the heat transfer of the pipe?
Increased the infrared radiation of the heater
. A simple painting of the register with black matte paint gave a noticeable warming in the room.
By the way, the current chrome plating of modern bathroom coils looks spectacular, but from the point of view of the heat transfer of the device, it is idiocy of the purest water.
The heat transfer of steel pipes can also be increased due to fins welded or otherwise mounted outside the pipe
.
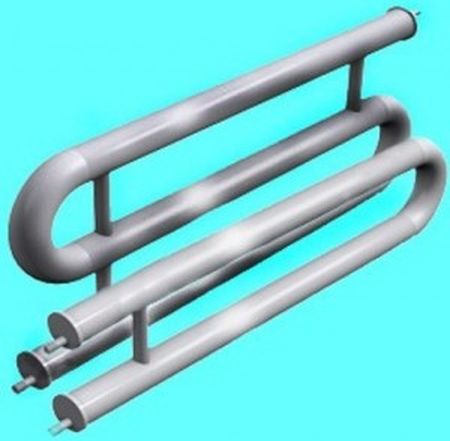
The final stage of the implementation of this method is a convector, a pipe coil with transverse plates. Of course, in this case, all methods for calculating the heat transfer of a pipe are not applicable - the pipe gives off a smaller part of the heat in this device.
Install a reflective screen behind the battery
The battery spreads heat in all directions, that is, it also heats the wall facing the street. A reflective screen attached to the wall behind the radiator will help direct all the heat into the room. The most affordable option from foilizolon is a foamed synthetic material (polyethylene) covered with foil on one side. You can use regular baking foil.
From sheet material, you need to cut a screen wider and 10-20 cm higher than the radiator, place it behind the battery with the foil side into the room. To fix the screen, any glue, liquid nails or double-sided tape will do.
The foam material will trap air, thereby creating additional thermal insulation, and the foil will reflect heat, directing it into the room.
Definition of heat transfer
For correct sizing registers for heating rooms in accordance with heat losses, it is necessary to know the value of heat transfer from a pipe 1 meter long. This value depends on the diameter used and the temperature difference between the coolant and the environment. The temperature difference is determined by the formula:
∆t= 0.5 (t1 + t2) – tk,
where t1 and t2 are the temperatures at the boiler inlet and outlet, respectively;
tk is the temperature in the heated room.
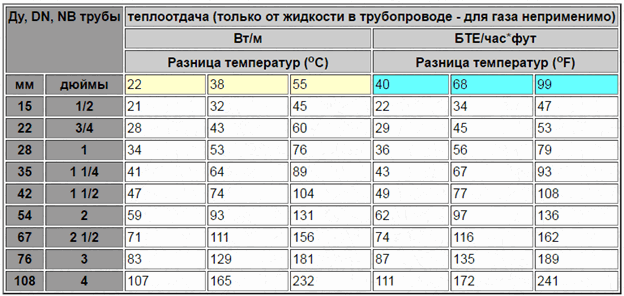
To quickly determine the approximate value of the amount of heat received from the register, the heat transfer table of 1 m of steel pipe will help. Despite the fact that the result is very approximate, this method is the most convenient and does not require complex calculations.
For reference: 1 BTU/hr ft2 oF = 5.678 W/m2K = 4.882 kcal/hr m2 oC.
The table shows what will be the heat transfer of steel pipes in the air at certain temperature differences. Interpolation calculations are made for intermediate temperature differences.
To more accurately determine the amount of heat that a steel pipe gives, you should use the classic formula:
Q=K F ∆t,
where: Q – heat transfer, W;
K is the heat transfer coefficient, W/(m2 0С);
F—surface area, m2;
∆t – temperature difference, 0С.
The principle of determining ∆t was described above, and the value of F is found by a simple geometric formula for the surface of a cylinder: F = π d l,
where π = 3.14, and d and l are the diameter and length of the pipe, respectively, m.
When calculating a section with a length of 1 m, the formula takes the form Q = 3.14 K d ∆t.
Note: when determining the heat transfer of a single pipe, it is enough to substitute the reference value of the heat transfer coefficient for steel when transferring heat from water to air, which is 11.3 W / (m2 0С). For a heater, the value of K depends not only on the material from which the pipes are made, but also on their diameter and the number of threads, since they influence each other.
The average values of heat transfer coefficients for the most popular types of heating devices are shown in the table.
Important! When substituting values into formulas, you must carefully monitor the units of measurement. All quantities must have dimensions that are consistent with each other.
Thus, the heat transfer coefficient found in kcal / (h m2 0С) must be converted to W / (m2 0С), given that 1 kcal / h \u003d 1.163 W.
Of course, the heat transfer table of steel pipes allows you to get a result faster than calculating by formulas, but if accuracy is important, you will have to tinker a little.
To determine the required register size, the required heat output must be divided by the heat output of 1 meter, rounded up to the nearest whole number. As a guide, you can take the average data for an insulated room up to 3 m high: 1 m of a register with a diameter of 60 mm can heat 1 m2 of a room.
Note: As can be seen from the table, the K coefficient for steel pipes can vary from 8 to 12.5 kcal / (hour m2 0C). An increase in the diameters and number of threads leads to a decrease in the efficiency of heat transfer. In this regard, to increase the heat transfer of the register, preference should be given to increasing the length of the elements.
It must also be taken into account that large pipes require an increased volume of water in the system, which creates an additional load on the boiler. The recommended distance between the threads is equal to the diameter of the pipes plus another 50 mm.
If the system is filled not with water, but with a non-freezing liquid, then this significantly affects the heat transfer of the register and requires an increase in its size after additional calculations. This is especially true when using devices with heating elements and oil as a coolant.
The steel pipeline is a fairly strong, durable product with good heat dissipation. Smooth pipe registers can have various configurations, are very easy to maintain and do not require periodic flushing.This allows them to successfully compete with light bimetallic and aluminum heaters, as well as with traditional "indestructible" cast-iron radiators.
Water and gas pipes are widely used in outdoor heating networks with open laying due to their high rigidity and wear resistance. The expediency of using steel pipes for space heating is determined by the operating conditions, financial capabilities and aesthetic taste of the owners. The use of registers is most justified in industrial and technical premises, but in other cases they also have their advantages.
Author (Site Expert): Irina Chernetskaya
Registers
The simplest design is registers. These are pipes welded from the ends of medium or large diameter, single or connected in sections with jumper tubes. They can be seen at the entrances, at industrial facilities or in private houses with individual heating.
To increase their thermal power, the method of increasing the area is used - thin metal plates are welded. This improves the heat transfer of the battery by almost one and a half times. Compact radiators, the closest relatives of cast-iron accordion batteries, have approximately the same heat transfer. Although, of course, they are far from panel bimetallic devices.
In order to maximize the heat transfer of heating radiators, a simple and inexpensive convection method is used. This method consists in the correct hanging of the device. It is installed as close as possible to the floor, where cold air accumulates, but leave the gaps necessary for circulation, including at the wall itself.
With this installation, the battery sections come into contact with a medium that has the lowest temperature possible under these conditions, that is, the thermal head increases. And the air heated by the registers, thanks to the gaps left, rises unhindered, and the room is heated faster.
An excellent method is to increase the heat transfer surface area. They do it in different ways:
- By increasing the total length of the heating pipes by forming U-shaped registers from them.
- Finning - strictly speaking, this method increases not specifically the thermal conductivity of the steel pipe, but the entire radiator, but the power increases by 50%.
- Increasing the number of sections.
Black surfaces have the best heat dissipation, but not every interior will fit such a gloomy battery, which is why this method has not found application. Registers traditionally continue to be painted white.
Towel dryers
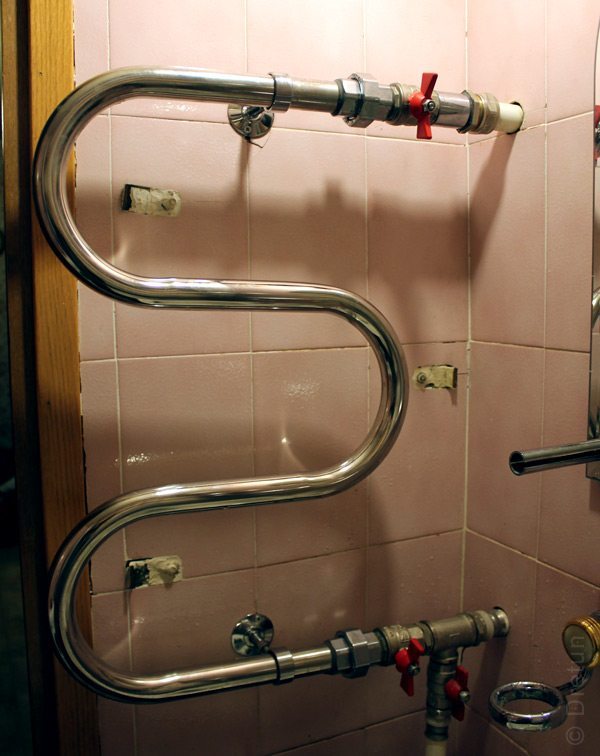
The bathroom towel warmer itself is a clear example of how you can improve the heat transfer of a pipe. The “serpentine” of the device is nothing more than an artificially increased area of thermal radiation. Since earlier they were only part of a common heating branch, it was possible to change the diameter. Therefore, the heat transfer area was increased by simply increasing the length.
By the way, just a stainless steel water heated towel rail will look good in black. Shiny and chrome products, although they look beautiful, prevent heat transfer between the pipe and the environment.
For vertically oriented systems such as radiators, the way in which the inlet and outlet pipes are connected matters. The heat output of one device with different installations can change significantly:
- 100% efficiency - diagonal connection (hot water inlet from above, outlet from the reverse side below);
- 97% - one-way top entry;
- 88% - lower;
- 80% - diagonal reverse (with a lower entry);
- 78% - one-sided with a bottom inlet and waste water outlet.
Heat loss
No less often, the high coefficient of thermal conductivity of a steel pipe has to be considered as a negative factor.When heat needs to be delivered with minimal losses to the end point to the consumer, the conductivity of steel should be reduced. Such a need arises on the main pipelines and heating mains laid on the surface.
To lower into an insulating shell made of mineral wool or expanded polystyrene, foil thermal insulation is used that shields the infrared radiation spectrum. You can also take steel pipes, insulated with several layers of polyethylene foam while still in production.
To determine the effectiveness of the insulation used, a standard calculation of a steel pipe is made through the heat transfer coefficient. But the result is multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. The difference between the two intermediate results will show how effectively the temperature of the coolant inside the pipe is maintained. If the figure turns out to be unsatisfactory, the thickness of the insulating shell should be increased or a material with a lower thermal conductivity should be selected.
WATCH VIDEO
In everyday life, the use of decorative screens or hanging appliances, as is the case with a heated towel rail, leads to heat loss and a decrease in the efficiency of steel heating pipes. The installation of such equipment in wall niches is also undesirable. The pipes themselves are not to blame for these losses, since they regularly heat the surrounding air and objects, but what this heat is spent on is a question for the owners.
The calculation of the heat transfer of the pipe is required when designing heating, and is needed to understand how much heat is required to warm the premises and how long it will take. If the installation is not carried out according to standard projects, then such a calculation is necessary.
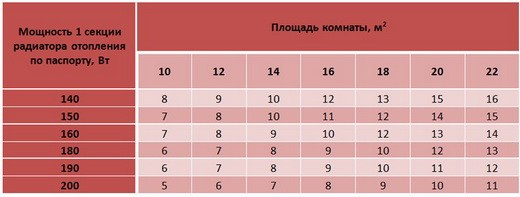
Heat dissipation of heating radiators table - Climate in the house
The main criteria for choosing devices for heating housing is its heat transfer.
This is a coefficient that determines the amount of heat generated by the device.
In other words, the higher the heat transfer, the faster and better the house will be heated.
How much heat is needed for heating?
To accurately calculate the required amount of heat for a room, many factors should be taken into account: the climatic features of the area, the cubic capacity of the building, the possible heat loss of housing (the number of windows and doors, building material, the presence of insulation, etc.). This calculation system is quite laborious and is used in rare cases.
Basically, the calculation of heat is determined on the basis of the established approximate coefficients: for a room with ceilings not higher than 3 meters, 1 kW of thermal energy is required per 10 m2. For the northern regions, the figure increases to 1.3 kW.
For example, a room with an area of 80 m2 requires 8 kW of power for optimal heating. For the northern regions, the amount of thermal energy will increase to 10.4 kW
Heat dissipation is a key performance indicator
The heat transfer coefficient of radiators is an indicator of its power. It determines the amount of heat released over a certain period of time. The power of the convector is affected by: the physical properties of the device, its type of connection, temperature and speed of the coolant.
The power of the convector, indicated in its data sheet, is due to the physical properties of the material from which the device is made, and depends on its center distance. To calculate the required number of radiator sections for a room, you will need the area of \u200b\u200bhousing and the heat flux coefficient of the device.
Calculations are made according to the formula:
Number of sections = S/ 10 * energy factor (K) / heat flow rate (Q)
Calculation: 50 / 10 * 1 / 0.18 = 27.7. That is, 28 sections will be needed to heat the room. For monolithic devices, for place Q, we set the heat transfer coefficient of the radiator and as a result we get the required number of batteries.
If convectors are installed next to sources that affect heat loss (windows, doors), then the energy coefficient is taken from the calculation - 1.3.
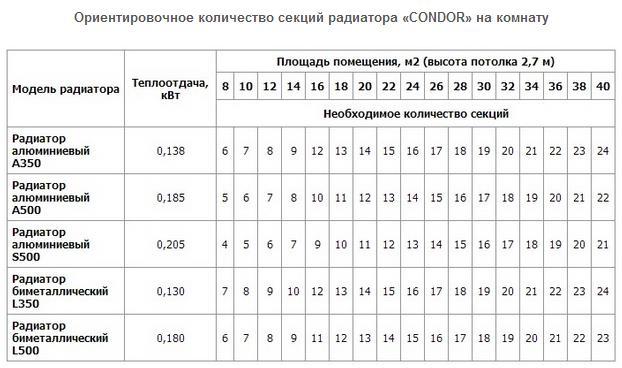
For heating, radiators are used: steel, aluminum, copper, cast iron, bimetallic (steel + aluminum), and they all have a different amount of heat flow due to the properties of the metal.
Comparison of indicators: analysis and table
In addition to the material from which the device is made, the center distance affects the power factor - the height between the axes of the upper and lower outlets. The value of thermal conductivity also has a significant effect on the efficiency.
Production material
Copper and aluminum convectors have the highest heat transfer. The lowest power factor is observed in cast iron batteries, but it is compensated by their ability to retain heat for a long time.
The efficiency of the efficiency is affected by the correct installation of heat appliances:
- The optimal distance between the floor and the battery is 70-120 mm, between the window sill - at least 80 mm.
- It is mandatory to install an air vent (Maevsky crane).
- The horizontal position of the heater.
Radiators with the best heat dissipation:
Warm floor
Not so long ago, from a heated towel rail or a room radiator, it became a continuation of the general heating system in the apartment, significantly increasing the area of \u200b\u200bthe heating surface. But water as a heat carrier in this situation can create many problems.
No matter how reliable steel pipes are, they are not eternal, and the joints, especially threaded ones, can leak over time. Just imagine that this happened inside a concrete screed, which is not so easy to remove. For this reason, a warm floor in a water version is practically not used.
If you do decide to implement this system, you will have to think about how to make it as efficient as possible. Power must be calculated with the utmost precision. But if the numbers show that the heat transfer is insufficient, it is necessary first of all to take care of increasing the efficiency of steel pipes.
Since this design does not come into contact with the air in the room, but heats the floor materials, you can play only by increasing the length of the pipes. Therefore, they are laid in a compact, but long "snake". Due to its large surface area, it transfers a lot of heat.
Nuance: with dense laying of several linear meters of the pipe, the heat transfer of the warm floor as a whole will increase, and each individual segment will not be critical, but will decrease.
The reason is that too closely located pipes partially establish heat exchange with each other. A heated zone is created around each, which leads to some decrease in the thermal head.
Heat loss through pipes
In a city apartment, everything is simple: both the risers, and the supply to the heating devices, and the devices themselves are located in a heated room. What's the point in worrying about how much heat the riser dissipates if it serves the same purpose - heating?
However, already in the entrances of apartment buildings, in the basements and in some warehouses, the situation is radically different. You need to heat one room, and bring the coolant to it through another. Hence - attempts to minimize the heat transfer of the pipes through which hot water enters the batteries.
thermal insulation
The most obvious way how the heat transfer of a steel pipe can be reduced is the thermal insulation of this pipe. Twenty years ago, there were two ways to do this: recommended by regulatory documents (insulation with glass wool wrapped with non-combustible fabric; even earlier, external insulation was generally made solid using gypsum or cement mortar) and realistic: pipes were simply wrapped with rags.
Now there are a lot of quite adequate ways to limit heat loss: here are foam linings for pipes, and split shells made of foamed polyethylene, and mineral wool.
In the construction of new houses, these materials are actively used; however, in the housing and communal system, the limited, politely speaking, budget leads to the fact that the pipes in the basements are still just wrapping ss ... um, torn rags.
Changing the connection method of the radiator
Do you know the situation when half of the battery is hot and half is cold? Most often in this case, the connection method is to blame. Take a look at how the device works with a one-sided connection of a radiator with a coolant supply from above.
Pay attention to how much worse the far sections work
Now let's take a look at the one-way connection diagram with the coolant supply from below.
We see the same effect.
And here is a two-way connection with a top and bottom feed.
Seeing the same effect Seeing the same effect
If you find yourself in one of the schemes presented above, then you are out of luck. The most rational in terms of work efficiency is a diagonal connection with a feed from above.
The entire heat exchange area of the radiator is heated evenly, the radiator operates at full capacity
And what to do in the case when you don’t want to change the pipe layout or it’s impossible? In this case, we can advise you to purchase radiators that have some trick in their design. This is a special partition between the first and second sections, which changes the direction of movement of the coolant.
A special plug turns the bottom two-way connection into the diagonal one we need with the top connection. This option is suitable for the top two-way connection
In the case of a one-way connection, special flow extensions have shown their effectiveness.
The principle of operation of the flow extension
There are also devices for optimizing a one-way bottom connection, but we think the general principle has now become clear to you.
Comment Sergey Kharitonov Leading Engineer for Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning LLC "GK Spetsstroy" For obvious reasons, such things are best provided for at the design stage of the heating system, so as not to rack your brains later. After all, any alteration will require disconnecting the riser, the skills of a locksmith or monetary costs, and in some cases, coordination with the Housing Office.
Conclusion: 100% effective.
Types of heating systems and the principle of adjusting radiators
Handle with valve
In order to properly adjust the temperature of the radiators, you need to know the general structure of the heating system and the layout of the coolant pipes.
In the case of individual heating, adjustment is easier when:
- The system is powered by a powerful boiler.
- Each battery is equipped with a three-way valve.
- Forced pumping of the coolant has been installed.
At the stage of installation work for individual heating, it is necessary to take into account the minimum number of bends in the system. This is necessary in order to reduce heat loss and not reduce the pressure of the coolant supplied to the radiators.
For uniform heating and rational use of heat, a valve is mounted on each battery. With it, you can reduce the water supply or disconnect it from the general heating system in an unused room.
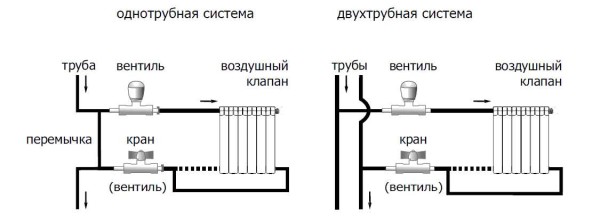
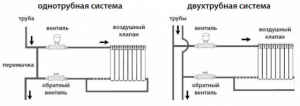
- In the central heating system of multi-storey buildings, equipped with a supply of coolant through a pipeline from top to bottom vertically, it is impossible to adjust the radiators. In this situation, the upper floors open windows due to the heat, and it is cold in the rooms of the lower floors, since the radiators there are barely warm.
- More perfect one-pipe network. Here, the coolant is supplied to each battery with its subsequent return to the central riser. Therefore, there is no noticeable temperature difference in the apartments of the upper and lower floors of these houses.In this case, the supply pipe of each radiator is equipped with a control valve.
- A two-pipe system, where two risers are mounted, provides the supply of coolant to the heating radiator and vice versa. To increase or decrease the coolant flow, each battery is equipped with a separate valve with a manual or automatic thermostat.
We make a calculation
The formula for calculating heat transfer is as follows:
Q = K*F*dT, where
- K - coefficient of thermal conductivity of steel;
- Q is the heat transfer coefficient, W;
- F is the area of the pipe section for which the calculation is made, m 2 dT is the temperature pressure (the sum of the primary and final temperatures, taking into account room temperature), ° C.
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is selected taking into account the area of the product. Its size also depends on the number of threads laid in the premises. On average, the value of the coefficient lies in the range of 8-12.5.
dT is also called temperature difference. To calculate the parameter, you need to add the temperature that was at the outlet of the boiler with the temperature that was recorded at the inlet to the boiler. The resulting value is multiplied by 0.5 (or divided by 2). The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
dT \u003d (0.5 * (T 1 + T 2)) - T to
If the steel pipe is insulated, then the value obtained is multiplied by the efficiency of the thermal insulation material. It reflects the percentage of heat that was given away during the passage of the coolant.
Increase in heat transfer.
To effectively increase the radiated heat, there are many ways:
- convector installation;
- painting pipes with black paint;
- register setting;
- additional battery sections.
The convector is a curved pipe with metal plates. You can make it yourself or buy a more modern analogue in the store.
The use of matte black paint for painting the surface of the coolant also gives a good result. Aesthetically, it does not look very attractive, but when it comes to comfort, you have to choose.
Another inexpensive and fairly popular design is the register. These are several interconnected wide pipes with welded sections. They also include heated towel rails, radiators, trunk lines, and even an ordinary steel pipe fixed around the entire perimeter of the room.
Step-by-step instructions for adjusting the temperature
To ensure a comfortable stay in the room, you need to perform some basic actions.
- Initially, on each battery, it is necessary to bleed the air until water flows in a trickle from the tap.
- Then you need to adjust the pressure in the batteries.
- To do this, in the first battery from the boiler, you need to open the valve by two turns, in the second - by three, and then in the same way, increasing the number of turns of the opened valve on each radiator. Thus, the coolant pressure is evenly distributed over all radiators. This will ensure its normal passage through the pipes and better heating of the batteries.
- In a forced heating system, control valves will help to pump the coolant, control the rational consumption of heat.
- In the flow system, the temperature is well regulated by the thermostats built into each battery.
- In a two-pipe heating system, it is possible to control not only the temperature of the coolant, but also its amount in the batteries using both manual and automatic control systems.
Simple Ways to Improve Battery Efficiency
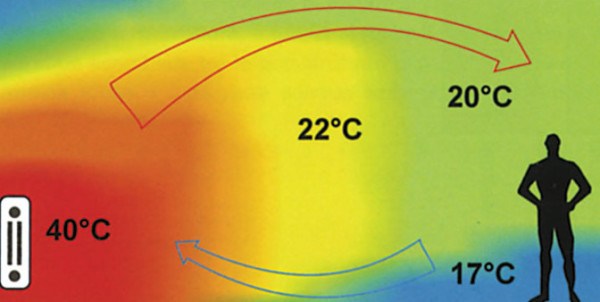
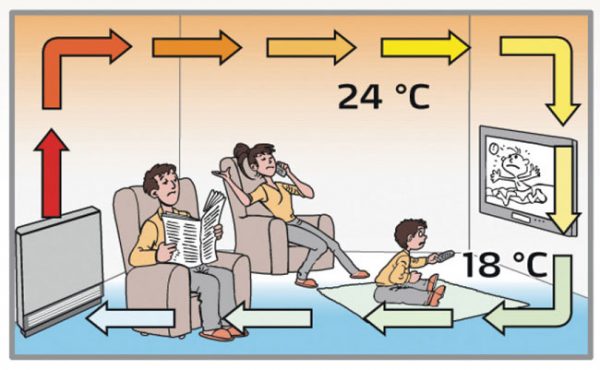
To increase the heat transfer of radiators, it is recommended to improve the air circulation in the heated room.
To do this, you need to free the heating batteries as much as possible, that is, remove the nearby furniture, remove the protective screens, and curtains.
This will increase air circulation, which in turn will increase the temperature inside the room.
If the above method did not bring the desired results, then you can speed up the air circulation with the help of fans.
In this case, it should be said that the faster the air moves, the more heat it takes from the radiator and spreads throughout the room.
It turns out that in order to increase the heat transfer of radiators, it is necessary to install a fan opposite them. This method is efficient but noisy.
In order to silence such a system and give it greater autonomy, it is recommended to install computer fans. In this case, fans must be installed directly under the batteries.
Using this method, it turns out to increase the temperature in the room from 5 to 10 degrees. It is also worth noting that the use of computer fans to increase the heat transfer of radiators is considered a fairly cheap way.
Another simple way to increase the heat dissipation of the batteries is to install a heat-reflecting shield behind the heatsink. Such a screen allows you to direct thermal energy directly into the room.
In this case, the ideal option is foil isolon, which is a foam base with foil. It is worth saying that the use of foil isolone will not only direct the heat in the right direction, but also insulate the wall.
Almost any adhesive can be used to install the heat-reflecting screen. It is worth knowing that the screen area should be slightly larger than the size of the radiator.
Results and conclusions.
- I managed to increase the air temperature in the room by as much as 6ºС, and even by 9ºС in the extreme mode of operation of the fans, which confirmed the assumption that it is possible to increase the heat transfer of the central heating battery, even at such a low coolant temperature.
- When using a conventional household fan without a speed controller, the room becomes too noisy. However, if you use the heat accumulated in the room, then, for example, you can turn off the fan in the bedroom at night, and, on the contrary, turn it on in the dining room. Then, you can use the fan at full power.
- If you are in that part of the room where the movement of air generated by the fan is most noticeable, then a false sensation of a decrease in temperature is created.
- Those who are afraid that the fan will wind up a lot can calculate the monthly energy consumption.
35(Watt) * 24(hours) * 30(days) ≈ 25(kWh)