— —
CAUTION 1
СиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ñ Ð¼Ð¾Ð³ÑÑÑÑбÑÑÑ Ð¼ÐµÑÑнÑми и ÑенÑÑалÑнÑми.
a
СиÑÑема Ð¼Ð¾Ð¶ÐµÑ Ð±ÑÑÑ Ð¼ÐµÑÑной и ÑенÑÑалÑной.
a
|
Ð · Ð ¼ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ' a |
СиÑÑемÑ, Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμðμμ¸¸ðððμ¸¸ðμμμμμμμμμμ¸¸¸¸¸¸¸¸ ко-ÑкономиÑÐμÑкиÐμ Ð'оÑÑоинÑÑвР°: 1) ÑовмÐμÑÐμниÐμ нР° гÑÐμвР° ÑÐμÐ »ÑнÑÑ Ñл ÐμмÐμнÑов Ñо ÑÑÑоиÑÐμÐ »ÑнÑми конÑÑÑÑкÑиÑми; 2). 3) SHUTTER
a
RедоÑÑаÑками ÑиÑÑÐμм ÑвР»ÑÑÑÑÑ ÑÑÑÐ'ноÑÑÑ ÑÐμмонÑÐ ° Ð · Ð ° монол иÑÐμннÑÑ Ð³ÑÐμÑÑÐ¸Ñ ÑÐ »ÐμмÐμнÑов, Ñл ожноÑÑÑ ÑÐμгÑÐ »Ð¸ÑовР° Ð½Ð¸Ñ ÑÐμпл ооÑÐ'Ð ° Ñи оÑоп Ð ÐμÐ ÐμÐ Ð ÐμÐð ÐμÐ Ð ÐμÐ Ð ÐμÐ ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð ÐμйРРРРРРРÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ Ð ² ²Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ
a
|
Ð · Ð ¼ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ' a |
Rод 100% ÑÐ »ÐμÐ'ÑÐμÑ Ð¿Ð¾Ð½Ð¸Ð¼Ð ° ÑÑ ÑÐ ° кÑÑ ÑиÑÑÐμмÑ, пÑи коÑоÑой ÑÑÐμÐ'нÐμвР· вÐμÑÐμннР° Ñ ÑÐμмпÐμÑÐ ° ÑÑÑÐ ° вÑÑÐμ ÑÐμмпÐμÑÐ ° ÑÑÑÑ Ð²Ð¾Ð · Ð'ÑÑÐ °, в Ñо вÑÐμÐ¼Ñ ÐºÐ ° к пÑи конвÐμкÑивной ÑиÑÑÐμмÐμ оÑопР»ÐμÐ½Ð¸Ñ (поÑÑÐμÐ'ÑÑвом конвÐμкÑоÑов ил и ÑÐ ° Ð'иР° ÑоÑов) ÑÑÐμÐ'нÐμвР· Ð ²ÐÐððÐμнггÐμÐμоггÐμÐ'оггÐμÐμÐ'Ð'ввÐμÐμÐμвввÐμÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ´ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ обогÑеваÑÑÑÑ Ð² оÑновном ÑÑим же воздÑѼ.
a
R ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ð°Ñ Ð² кР° ÑÐμÑÑвÐμ нР° гÑÐμвР° ÑÐμÐ »Ñной повÐμÑÑноÑÑи иÑпол ÑÐ · ÑÑÑÑÑ Ð¸ÑкÑÑÑÑвÐμнно оР± огÑÐμвР° ÐμмÑÐμ ÑÑÐμнÑ, поÑоР»Ð¾Ðº, пол иР»Ð¸ ÑпÐμÑиР° Ð »Ñно иР· гоÑовл ÐμннÑÐμ пР° нÐμÐ »Ð¸ пÑиÑÑÐ ° вного и поÐ'вÐμÑного ÑипР°. Lock Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ± Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñðñ 11 Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ ¸Ð»Ð¸ ÑÑÑÑаиваÑÑÑоздÑÑоводÑи каналÑ.
a
R ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ð°Ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ½ РРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРнели.
a
|
£ £ ññðвðð²²²ºμ °μðμðÐðÐðÐðÐμμ μμμμμμñññññññññμμμμμ¾²²²ððμμμμ ñ a |
ÐонÑаж ÑÑÑбопÑоводов ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ñ Ð1ÐððÐμÐμÐμÐñÐðÐðÐðÐðÐñÐðÐðÐ ° °Ððñн½Ð½Ð °ÐðñÐðнÐðÐððÐðÐðÐðÐðÐðÐðÐðÐðÐ °Ð¾Ð¾Ð¾Ð¾Ð¾Ð¾ð𸸸¸¸¸¸ Ð
a
СÑеди недоÑÑаÑков ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ñ Ð¾ÑмÐμÑим: нÐμкоÑоÑоÐμ Ð'опоР»Ð½Ð¸ÑÐμл ÑноÐμ ÑвÐμÐ »Ð¸ÑÐμниÐμ ÑÐμпл опоÑÐμÑÑ ÑÐμÑÐμÐ · нР° ÑÑжнÑÐμ огÑÐ ° жÐ'ÐμÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð² ÑÐμÑ Ð¼ÐμÑÑÐ ° гдеениÑзаделанÑгÑеÑÑиеÑлеменÑÑ; Ð1ÐμÐðÐðоÐðннннннÐнÐðÐðÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÑеплооÑдаÑи беÑоннÑÑ Ð¿Ð°Ð½ÐµÐ»ÐµÐ¹; знаÑиÑелÑнÑÑÑепловÑÑинеÑÑÐ¸Ñ ÑÑÐ¸Ñ Ð¿Ð°Ð½ÐµÐ»ÐµÐ¹.
a
ТеплоноÑиÑелем в ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ð°Ñ (Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μm Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ
a
|
опÑÑÑимÑе ÑемпеÑаÑÑÑÑна повеÑÑнÑÑноÑÑи поÑÑоÑоооооовеÑÑнÑÑноÑÑи a |
ТеплоноÑиÑелем в ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ð°Ñ Ð¼Ð¾Ð³ÑÑÑÑбÑÑÑвода, паÑ, ÑлекÑиÑеÑÑво или воздÑÑ.
a
What can be gas heating
Two types of gas can be used for heating - main and liquefied. Main gas under a certain pressure is supplied through pipes to consumers. It is a single centralized system. Liquefied gas can be supplied in cylinders of different capacities, but usually in 50 liters. It is also poured into gas holders - special sealed containers for storing this type of fuel.
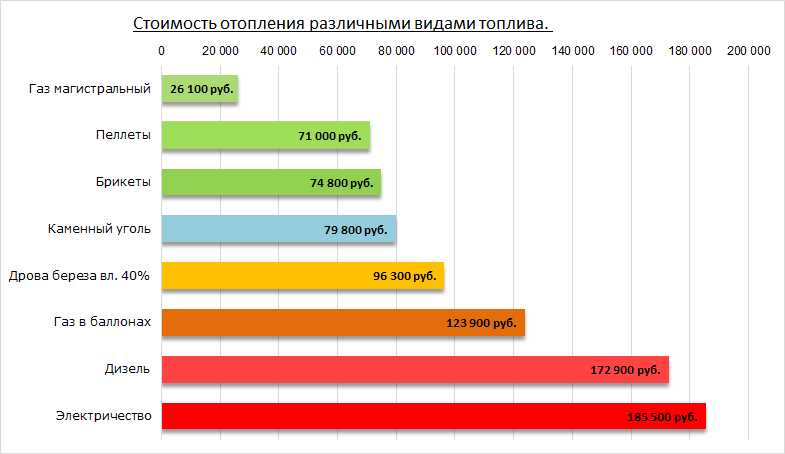
An approximate picture of the cost of heating by different types of fuel
Cheaper heating - using mains gas (not counting the connection), the use of liquefied gas is only slightly cheaper than the use of liquid fuels. These are general statistics, but specifically it is necessary to count for each region - prices differ significantly.
Water heating
Traditionally, in private houses they make a water heating system. It consists of:
- a heat source - in this case - a gas boiler;
- heating radiators;
- pipes - connecting the boiler and radiators;
-
coolant - water or non-freezing liquid that moves through the system, transferring heat from the boiler.
This is the most general description of the water gas heating system of a private house, because there are still many additional elements that ensure operability and safety. But schematically, these are the main components. In these systems, heating boilers can be on natural or liquefied gas. Some models of floor boilers can work with these two types of fuel, and there are those that do not even require a burner replacement.
Air (convector) heating
In addition, liquefied gas can also be used as fuel for special convectors. In this case, the premises are heated with heated air, respectively, heating - air. Not so long ago, convectors appeared on the market that can operate on liquefied gas. They require reconfiguration, but can work on this type of fuel.
Gas convectors are good if you need to quickly raise the temperature in the room. They start heating the room immediately after turning on, but they also quickly stop heating - as soon as they turn off. Another disadvantage is that they dry the air and burn out oxygen. Therefore, good ventilation is required in the room, but there is no need to install radiators and build a pipeline. So this option has its advantages.
Organization of heating of residential buildings
For distribution of heat inside residential buildings, hydraulic systems with hot water radiators or a central forced air supply system are usually used.
The use of surface heating systems is gradually increasing, but this technology still lags behind traditional radiator options.
True, after the introduction of plastic piping, the use of water-based radiant heating with pipes embedded inside the surface of the premises (floors, walls, ceilings) has increased significantly.
Earlier applications of radiant heating systems were noted mainly in the design of residential buildings with a high level of comfort, with a large living area and the possibility of free installation of equipment.
Due to energy savings and peak load reduction, radiant systems are seen as a sustainable solution for a wide range of applications in commercial, industrial and residential buildings.
In recent years, interest in radiant heating (cooling) systems has increased. The trend is explained by high energy efficiency compared to air conditioning projects.
Radiant heating projects
There are many works devoted to the study of low-temperature radiant systems with subsequent comparison with other heating systems.
Comparative criteria are obvious - energy consumption and obtaining thermal comfort. The results, as usual, are mixed.
For example, when comparing the energy consumption of a ceiling radiant heating system with respect to a radiator system and air conditioning units, the researchers concluded that a ceiling radiant heating system consumes 17% more energy.
Another study noted that the energy consumption of floor panel systems is 30% lower than with classic radiator installations.
It has been observed that properly insulated wall panel heating systems show 28% less primary energy consumption than traditional radiator heating systems.
To be more specific, consider the heat distribution systems inside residential buildings, oriented to radiant panels (floor, wall, ceiling).
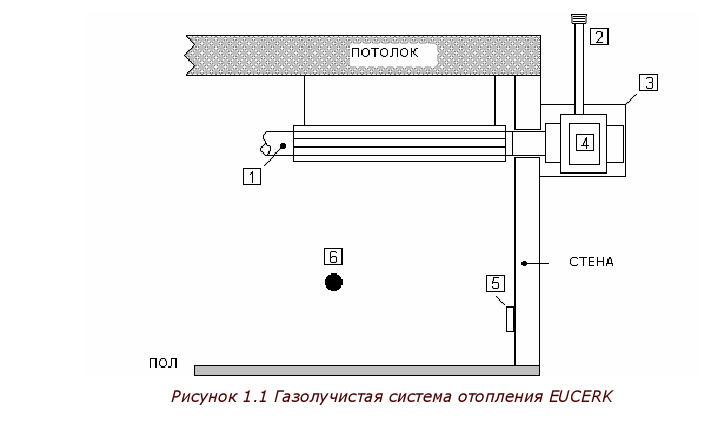
Gas radiant heating system EUCERK
1.1. EUCERK EQUIPMENT CHARACTERISTICS
The EUCERK system is the technological evolution of gas radiant
heater, in which special attention is paid to
performance, safety, uniformity
temperature and reduce air emissions. The EUCERK radiant heating system consists of
the following accessories:
The EUCERK radiant heating system consists of
the following accessories:
BLAST BURNER - CENTRIFUGAL FAN - CHAMBER
CIRCULATIONS
(located indoors or outdoors)
RADIANT PIPES
CONTROL POINT
Device:
radiant pipes
Smoke exhaust system
Outer case
Gas burner unit EUCERK
RHC control point
temperature sensor
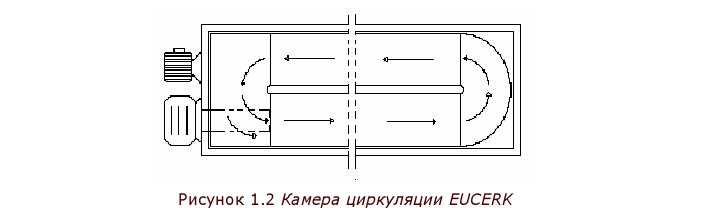
Gas burner block, circulation chamber and radiant pipes
create a closed cycle of coolant movement
(gas-air mixture), which circulates with a large
speed.
The air in the pipes is heated in contact with
walls of the gas burner block, and mixing with red-hot
combustion products.
A chimney is also provided for the gas burner unit.
The share of gas consumption compared to air is negligible —
does not exceed 10%. The EUCERK system is specially designed with
taking into account the minimization of harmful emissions into the atmosphere,
adhering to all restrictions of European standards:
CO
NOx
These figures are obtained through:
1) The optimal amount of fuel in a protected chamber,
made by a blast burner, able to destroy
non-flammable gas and corresponding CO.
2) The excess air in the fuel is almost negligible and low
burner temperature, due to the effect of constant
circulation, allow to reduce NOx emission.
Therefore, the installation of a gas-radiant heating system EUCERK
allowed in almost any type of industrial,
commercial and sports facilities around the world.
1.2.PERFORMANCE
The efficiency of the EUCERK heating system is much higher
efficiency of any other type of heating
equipment, as increased productivity
blast burner combined with the most efficient
heat transfer in the form of infrared rays.
1.3 SAFETY
As already noted, the ability to choose any length
EUCERK system allows you to heat the premises of large
sizes. At the same time, the installation of a gas burner unit (and
respectively, gas pipeline) is possible outside the premises,
which eliminates the risk of fire, and also saves on installation
equipment.
The temperature of the radiant pipes (below 300 °C) can be
changed during the design or maintenance process in
depending on the height of installation and on the level of activity in
premises, allowing meaningful flexibility in use
EUCERK equipment.
Advantages of EUCERK gas radiant heating system:
Greater comfort at lower temperatures;
No temperature gradient - decrease
heat loss;
No movement of air masses and dust
Low inertia
Possibility of local heating
Saving energy and caring for the environment
Reducing the cost of industrial heating
Any head of a manufacturing enterprise can cite unattractive statistics of an increase in the cost of production due to an increase in heating costs. And this figure is very significant. In some cases, it makes products uncompetitive. The way out of the stalemate is to create decentralized heating systems.
Option one

You can modernize outdated heating equipment. The installation of new boiler houses, heating appliances, laying of heat supply lines will result in very serious money. In addition, it is not always possible to count on the high efficiency of restored circuits due to objective reasons - high ceilings, poor thermal insulation of buildings, the technological need for constant ventilation, etc.
It should be noted that the reconstruction of the heating system will require considerable capital investments. The acquisition of expensive equipment, the dismantling of the old and the installation of a new system will result in serious costs. Subsequently, all costs will need to be attributed to the cost of production. Therefore, economic efficiency looks rather doubtful.
Option two
It is possible not to invest in the reconstruction of heating, but to rely on decentralized industrial radiant heating. It is preferable, if only because it is possible to maintain different temperature conditions in each room. As practice shows, this method can achieve a sharp reduction in the cost of purchasing energy resources.
In addition, the second method will require significantly less capital investment. Investments in the reconstruction of boiler houses and heating mains are completely excluded. It will only be necessary to re-equip the heating systems inside the premises. Thanks to this, the costs will pay off much faster compared to the first option. The company will quickly begin to profit from innovations.
Radiant heating is a cardinal way to reduce the cost of heating industrial premises. The cost of a gigacalorie of thermal energy is reduced by approximately three times compared to traditional heating methods. The released funds can be used to develop new methods of heat supply or for production purposes.
SOLARONICS CHAUFFAGE INFRARED HEATER MODELS
| SOLARTUBE Evolution TL.E | ||
|---|---|---|
|
"Dark" pipe infrared heater with a length of 10, 12 and 14 m. with burners with a power of 23, 36 and 43 kW., installation height from 4 to 12 m. | It is characterized by combustion of gas in a straight pipe. It is the best model among the equipment of this class. The special design of the burner and the insulated reflector can significantly reduce convective losses, ensure silent operation of the unit and create comfortable conditions in the working area. |
| SOLARTUBE Evolution TU.E | ||
 
|
"Dark" pipe infrared heater 5 and 6.6 m long with 15, 20 and 32 kW burners, installation height from 4 to 12 m. | It is characterized by the combustion of gas in a U - shaped pipe. They represent a promising technology that meets the highest requirements for productivity, economy and environmental compliance. These systems are widely used in representative centers, prestigious car dealerships, large shopping, exhibition and sports facilities. |
| TUP 50 | ||
 |
"Dark" pipe infrared heater 9 m long with a 52 kW burner, installation height from 4 to 12 m. | It is characterized by the combustion of gas in a U - shaped pipe. Differs in an optimum combination of the price and quality and the highest requirements on productivity, profitability and observance of standards of ecology. |
| EUROLINE and HARMOLINE | ||
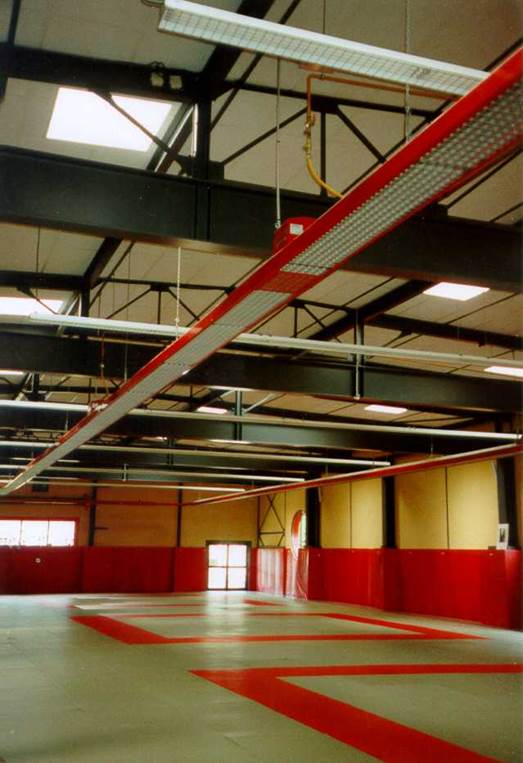  |
Multi-burner system with centralized exhaust gas removal. Sections from 4 to 20 m (for one burner) in an assembly of up to 16 (for one fan) burners with a capacity of 20, 30 and 40 kW., installation height from 4 to 10 m. | Unique 95% efficiency! Various colors. This type of emitters allows you to implement infrared heating systems of any length, configuration and thermal power. The heaters meet the requirements for reliability and safety of use, are quite easy to operate and can be installed in industrial, industrial, warehouse, sports, agro-industrial, commercial premises without disturbing the interior. These infrared heaters are ideal for greenhouses, poultry farms, pig farms, gyms, as well as shopping malls. |
| TUB ONE (RAY ONE) | ||
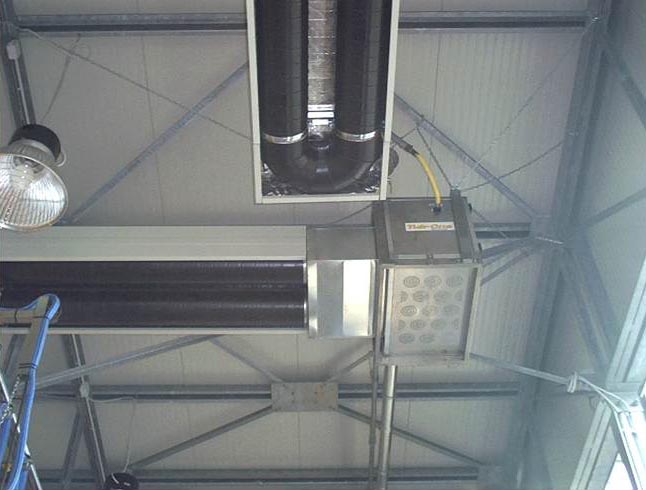
 
|
"Dark" pipe U - shaped infrared heater with a length of 20 m to 120 m and an installation height of up to 40 m with a burner with a power of 32 kW. up to 265 kW. | Indispensable in rooms with poor thermal insulation and large volume. It is used at the enterprises of machine-building, agro-industrial, agricultural and logistics complex. Possibility to install the burner-fan unit outdoors. |
| SRII | ||
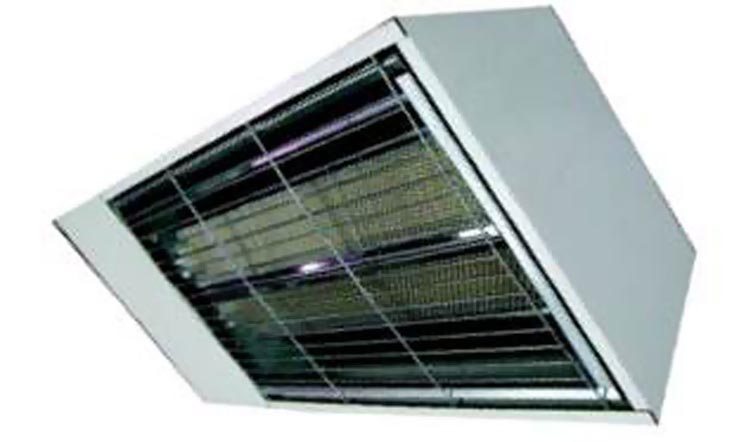  |
"Light" infrared emitter with a ceramic surface, power from 6 to 25 kW., installation height from 4 to 15 m. | It has 2 heating modes 100% and 50% with an extremely silent version. It is indispensable in the design of production and storage facilities. It is characterized by the use of air to support combustion directly in the room and the release of combustion products into the heated room. Specially adapted for industrial buildings with overhead cranes (overheating thermostat, anti-vibration springs). |
| Control | ||
| Set temperatureIntegrated sensor | Thermostat with integrated sensor for infrared emitters TU.E; TL.E; SRII; TUP50 | Up to 4 infrared heaters per thermostat |
| Communication unit (touch screen) | Allows you to optimize energy consumption while respecting the production process and the comfort of others. Communication control allows centralized control of heating equipment for industrial and public buildings. Creates comfort, reduces energy consumption, optimizes maintenance. (programming; history; reporting). | |
| Infrared heating control device | Allows you to set the readings of the control unit at a distance of up to 50 m (wall mount). | |
| Gas radiant heating control unit (up to 4 zones) | Two adjustable heating temperatures (day/night) for control units with timer. Maximum number of infrared heaters per zone: - 12 (TU.E17 -TU.E23 -TL.E23) - 10 (TU.E36 - TL.E36) - 7 (TL.E45) - 8 (TUP50) - 40 ( SR II 21, 31, 41, 61, 81)-20 (SR II 42, 62, 82) | |
| Two-zone control unit for infrared heating system | Up to 2 TUB ONE (single and two stage). |
To calculate the cost of designing, equipping and installing infrared heating, please fill out the GLO Questionnaire.
Each of the presented types of heating workshops has its pros and cons.
- So, conventional heating is not suitable for large workshops with a ceiling height of 4 meters or more. At the same time, it will perfectly show itself in small industries with a small area of \u200b\u200bthe premises.
- Air heaters can heat quite large areas, especially if the warehouse doors often open, letting in cold air from the street - in order to cut it off, you can use special cut-off air curtains. Air heaters use electricity and burner fuel (LPG, natural gas or propane) and can be cost effective for heating medium to large workshops. In the conditions of the Russian winter, the equipment will justify its cost in 1-2 years, depending on the type of equipment purchased and production volumes. Air heaters are wall and floor, they are different in power. The noise level of Carlieuklima models is the lowest in the class. At the same time, when choosing air heaters for heating workshops, it is worth remembering that they create air convection and are not suitable for all types of industries. So, it is better to choose a different type of heating if you are engaged in the production, supply or storage of bulk mixtures.
- Gas-radiant heating is the most beneficial for heating workshops of almost any industry. This is due to the absence of air convection, temperature gradient and quick payback. Gas-fired systems use liquefied or natural gas or propane to operate. At the same time, consumption can be significantly reduced by correctly setting the heating settings, for example, by lowering the temperature in the workshop to a minimum on non-working days or holidays, and, if necessary, at shift change or lunch time. The output of this equipment is only 5-7 minutes, so turning it off during a short hour break will not force workers to return to cold machines and conveyors. Gas-radiant equipment heats a strictly defined area, even in a large space, it is possible to ensure that employees' workplaces are maintained at a comfortable temperature of 18-20 degrees, and unused space, or equipment that is not susceptible to temperature changes, in a normal street. The payback of gas-radiant heating is 1-1.5 years, energy savings in comparison with other sources by 50-70%, efficiency 90-95%.
The principle of operation of infrared heating
Almost any body (including non-living matter), whose temperature is higher than the environment, radiates thermal energy. It is transmitted to other bodies by means of electromagnetic waves in the infrared range. The nature of bodies determines the radiating and absorbing abilities of each specific surface.
Radiant heat transfer differs from conventional convection in that heat energy can be transferred even through a vacuum. Infrared radiation heats living organisms and objects, acting on their surface. In this case, the ambient temperature can remain unchanged. Exactly such sensations arise on a frosty (but not very) sunny day. It even looks like the snow is about to melt.
Therefore, in order to achieve a certain level of comfort, it is not necessary to raise the air temperature in the room. This is the most important advantage of radiant heating. In buildings heated with it, the air can warm up only from the surface of interior items, but not from infrared radiation.
Panel radiant heat supply systems system diagrams, device, pros and cons, area of use.Devices with a heating function of panel radiant heat supply systems and the specifics of their installation.
Radiant, as already known, is a heating method in which the radiation temperature of the room exceeds the air temperature. To obtain radiant heat supply, heating panels are used - radiators with a continuous smooth heating surface. Heating panels simultaneously with heat pipes form a system of panel-radiant heat supply. When using such a system in the premises, a temperature atmosphere is created that is distinctive for the radiant method of heat supply.
So, the conditions that determine the receipt of radiant heat supply in the room are the use of panels and the fulfillment of the inequality tR>tB where tR is the radiation temperature (the average temperature of the surface of all fences - external and internal - and heating panels facing the space of the room); tB is the room air temperature.
With panel radiant heating, the room is heated mainly due to radiant heat transfer between the heating panels and the surface of the fences. Radiation from heated panels, falling on the superficiality of fences and objects, is partly absorbed, partly reflected. In this case, in other words, secondary radiation appears, which is also eventually absorbed by objects and enclosures in the room.
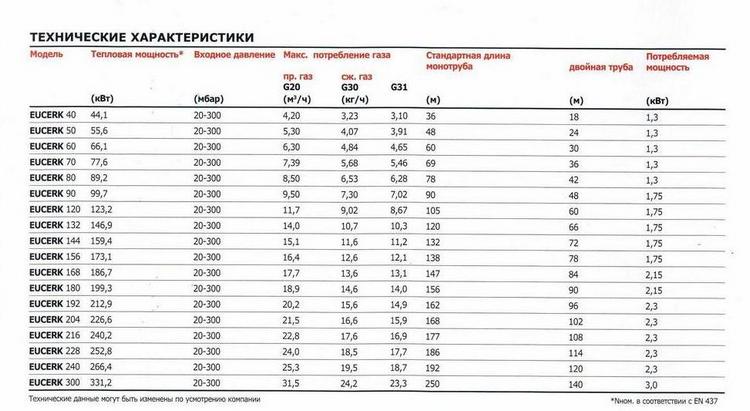
Fig.11.1 Scheme of the location of heating elements in the structures of the building fencing.
1 - in the floor, 2 - in the outer wall, 3 - in the partition, 4 - in the ceiling
Specifics of radiant heat supply systems
In systems of panel radiant heat supply, artificially heated walls, ceiling, floor or specially made panels of attached and suspended type are used as a heating surface.
To obtain these heat transfer surfaces in the listed structures, pipes of small diameter are closed (Fig. 11.1), an electric cable is laid, or air channels and channels are arranged.
A significant difference between panel radiant heating and conventional water and steam heating devices placed under windows is that the premises are heated mainly by heat radiated from the heated surfaces of the building envelope or specialized panels. When the ceiling is heated, only 20-25% of the heat is given off to the room by convection.
The condition for the effectiveness of any radiant heat supply system in hygienic terms is the average surface (weighted average) temperature of all room enclosures, determined by the following simple formula:
tR = where tpt, *n.s, *ok, *v.s, *pl - the average temperature of the ceiling, walls outside from the side of the room, windows, walls inside and floor, ° С; F - required surfaces of fences, m2,
For a normal thermal sensation in winter, the average weighted temperature in the living room should be tR=29-0.57tВ
Moreover, another condition of comfort must be made. Under the system of panel radiant heating, it is necessary to mean a system of this kind in which the weighted average temperature is higher than the air temperature, while with a convective heating system (using convector heaters or heaters), the weighted average temperature of the fences is always lower than the air temperature, since the fences are heated as rule with the same air.
Water is recommended as a heat carrier in radiant heat supply systems SNiP 2.04.05-86, at which corrosion of steel pipes is less than with steam as a heat carrier. Panel-radiant heat supply systems, in addition to obvious hygienic positive qualities, have the following technical and economic positive qualities over other systems:
TENOV with building structures; reduction of metal consumption and labor costs for installation; improvement in room design.
The non-standard disadvantages of panel radiant heat supply include the following: direct irradiation of furniture and other items present in the room, which is associated with the possibility of their damage; large inertia of the heat of the systems, which complicates the regulation of the heat transfer of the panels; the danger of pipe blockages and the difficulty of their elimination.
According to the design feature, panel-radiant heat supply systems are divided into the following main types: panel wall heating systems; underfloor heating systems; radiant ceiling heat supply systems; heating systems with suspended radiant panels. The permissible temperature on average of the surface of window sill panels is up to 95 0С, for panels for walls in the area above 1 m above the floor level - 45 0С, for ceilings with a room height of up to three meters - 300С, for floors - 25-280С.