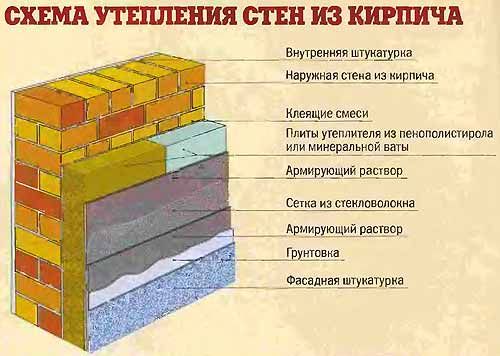
The thickness of the insulation is chosen in two stages
- They are chosen based on the need to provide the required resistance to heat transfer of the outer wall.
- Then check for the absence of steam condensation in the thickness of the wall. If the test shows otherwise, then it is necessary to increase the thickness of the insulation. The thicker the insulation, the lower the risk of steam condensation and moisture accumulation in the wall material. But, this leads to an increase in construction costs.
A particularly large difference in the thickness of the insulation, selected according to the above two conditions, occurs when insulating walls with high vapor permeability and low thermal conductivity. The thickness of the insulation to ensure energy saving is relatively small for such walls, and to avoid condensation - the thickness of the plates should be unreasonably large.
 |
| Rice. 6. Insulation of the walls of a private house with foam boards, expanded polystyrene - EPS, XPS. If the bearing part of the wall is made of aerated concrete, gas silicate blocks, then the inner surface of the wall should be protected with a layer of vapor barrier. |
When insulating aerated concrete walls (as well as from other materials with low resistance to vapor permeation and high resistance to heat transfer - for example, wood, large-porous expanded clay concrete) the thickness of the polymer thermal insulation according to the calculation of moisture accumulation turns out to be much larger than necessary according to the standards for energy saving.
To reduce the flow of steam, it is recommended to arrange vapor barrier layer on the inner surface of the wall (from the side of the warm room), Rice. 6. For the device of vapor barrier from the inside for finishing, materials with high resistance to vapor permeability are chosen - a deep penetration primer is applied to the wall in several layers, cement plaster, vinyl wallpaper.
A vapor barrier from the inside is mandatory for walls made of aerated concrete, gas silicate for any type of insulation and facade cladding. It should be borne in mind that the masonry of the walls of a new house always contains a large amount of building moisture. Therefore, it is better to let the walls of the house dry well outside. It is recommended to perform facade insulation works after the interior decoration is completed, and not earlier than one year after the completion of these works.
Thermal insulation protection
Some heaters require protection from getting wet, blowing or, for example, direct sunlight. Some of these tasks may be assigned to the finishing layer, but the main protection is provided by special membrane materials.
One of the most commonly used insulators in the Canadian frame - stone wool - has the property of sharply reducing the resistance to heat transfer when wet. The source of moisture can be precipitation or condensation of water vapor. In the first case, special synthetic burlap is used that allows air and water vapor to pass through, but retains water drops.

The penetration of steam from the inside cannot be completely limited, because the building must carry out natural gas exchange with the environment. However, it is possible to limit the amount of water vapor to such values that it will not be enough to raise the relative humidity in the cooled indoor air to 85-90%. Typically, such a calculation is carried out for the dividing point of the rows of a frame or a carrier system with external insulation. However, the same method can also be applied to layer-by-layer calculation of the dew point shift during the year inside homogeneous walls.
Insulation of the walls of the house with mineral wool boards
Mineral wool slabs are fixed on a load-bearing wall with an air ventilated gap between the surface of the slabs and brick lining, or without a gap, Fig.1.
Why a ventilated gap is needed and moisture accumulation in the wall is described in detail in the article “Dew point, vapor barrier and ventilated air gap”.
The calculations of the moisture regime of the walls show that in three-layer walls condensate in the insulation falls during the cold season in almost all climatic zones of Russia.
The amount of condensate falling out is different, but for most regions it fits into the norms established by SNiP 23-02-2003 "Thermal protection of buildings". There is no accumulation of condensate in the wall structure during the year-round cycle due to drying in the warm season, which is also a requirement of these SNiP.
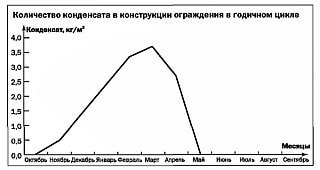
As an example, the figures show graphs of the amount of condensate in the insulation based on the results of calculations for various options for facing the three-layer walls of a residential building in St. Petersburg.
Rice. 4. The result of calculating the humidity regime of a wall insulated with mineral wool boards with a ventilated gap and a "siding" type coating (brick - 380 mm, insulation - 120 mm, siding). Facing - ventilated facade.
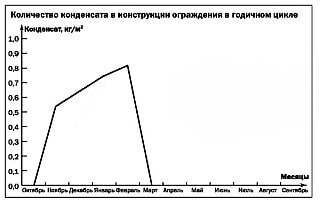
From the above graphs it is clearly seen how the lining barrier, which prevents ventilation of the outer surface of the mineral wool insulation, leads to an increase in the amount of condensate in the insulation. Although in the annual cycle of moisture accumulation in the insulation does not occur, but when facing with bricks without a ventilation gap, a significant amount of water condenses and freezes in the insulation every year in winter, Fig.2. Moisture also accumulates in the layer of brick cladding adjacent to the insulation.
Humidification of the insulation reduces its heat-shielding properties, which increases heating costs building.
In addition, water annually, when freezing, destroys the insulation and brickwork of the cladding. Moreover, the cycles of freezing and thawing during the season can occur repeatedly. The insulation gradually crumbles, and the brickwork of the cladding is destroyed. I note that the frost resistance of ceramic bricks is only 50 - 75 cycles, and the frost resistance of the insulation is not standardized.
Replacing a heater covered with brick cladding is an expensive pleasure. Hydrophobized high-density mineral wool boards are more durable under these conditions. But these plates have a higher cost.
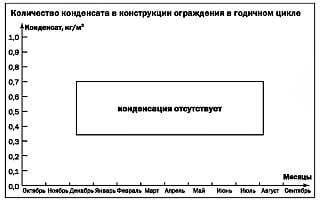
The amount of condensate is reduced or there is no condensation at all if better ventilation of the insulation surface is provided - fig.3 and 4.
Another way to eliminate condensation is to increase the resistance to vapor permeation of the load-bearing wall. To do this, the surface of the bearing wall is covered with a vapor barrier film or heat-insulating boards with a vapor barrier applied to their surface are used. When mounting on a wall, the surface of the boards covered with a vapor barrier must face the wall.
The arrangement of a ventilated gap, sealing the walls with vapor-tight coatings complicates and increases the cost of the wall structure. What does moistening the insulation in the walls in winter lead to is written above. Here, choose. For construction areas with severe winter conditions, the installation of a ventilated gap can be economically justified.
In walls with a ventilated gap, mineral wool boards with a density of at least 30-45 kg / m 3 are used, glued on one side with a windproof coating. When using plates without wind protection on the outer surface of the thermal insulation, wind protection coatings should be provided, for example, vapor-permeable membranes, fiberglass, etc.
In walls without a ventilated gap, it is recommended to use mineral wool boards with a density of 35-75 kg/m 3 . In a wall structure without a ventilated gap, heat-insulating boards are installed freely in a vertical position in the space between the main wall and the facing layer of bricks.The supporting elements for the insulation are fasteners provided for fastening the brick cladding to the load-bearing wall - reinforcing mesh, flexible connections.
In a wall with a ventilation gap, insulation and a windproof coating are attached to the wall using special dowels at the rate of 8-12 dowels per 1 m 2 of surface. Dowels should be deepened into the thickness of concrete walls by 35-50 mm, brick - by 50 mm, into masonry of hollow bricks and lightweight concrete blocks - by 90 mm.
Brickwork with insulation well masonry. Insulation from inside the room. Ventilated facades
Brick houses have been built for several hundred years, and many do it with their own hands. It is brick that is the most common building material at the present time. Both solid and hollow types of bricks are produced.
Photo - brickwork
Previously, almost all houses had a wall thickness of about 1 m, which was due to the lack of insulation in those days. It was with brickwork with insulation that the mass construction of warm buildings and structures began.
Insulation between walls
The difficulty of thermal insulation both from the inside and outside lies in the appearance of condensate. Water negatively affects not only thermal protection, but also the entire structure of the building.
The thickness of the applied insulation layer depends on a number of factors, such as:
- location of the building;
- wall material;
- wall thickness;
- type of insulation used.
Modern construction is regulated by the provisions of SNiP 23-02-2003, which precisely indicate the required amount of insulation.
Standard length, width and brick thickness
Since the brick has its own standard dimensions (6.5 x 12 x 25), the thickness of the brick wall will also have several standard dimensions, taking into account the thickness of the seam between adjacent bricks.
There are other sizes, but they mainly differ in height, and the height of the brick does not affect the thickness of the wall.
| Number of bricks, pcs | Wall thickness, cm |
| 0,5 | 12 |
| 1 | 25 |
| 1,5 | 38 |
| 2 | 51 |
| 2,5 | 64 |
In addition to a thickness of 65 mm, there is a brick thickness of 88 mm - one and a half bricks and 138 mm - double. Those. dimensions 8.8x12x25 and 13.8x12x25. In general, the thickness (height) of the brick does not affect the thickness of the brickwork.
The main criterion for choosing the thickness of a brick wall is the purpose and location of the wall itself.
Proper dismantling of brick walls with your own hands
Often there are situations when it is necessary to dismantle brick walls in an apartment or house. It seems that there is nothing complicated in this, but in fact, there are some peculiarities and nuances here, the observance of which ensures both human safety and the absence of further destruction of what was not originally planned to be broken. Therefore, before proceeding with the dismantling of a brick wall, carefully read these rules and follow them strictly.
By following these simple tips, you can dismantle brick walls you don’t need without consequences.
More articles on this topic:
The sequence of performing the work of cutting the wall
To make an opening for a door in the wall at home, you will need a grinder as a tool. To perform larger-scale work, such as redevelopment of doors, windows, partitions and the entire dwelling, one cannot do without a stone-cutting machine.
In addition to the grinder, we prepare for work:
 An angle grinder device for cutting bricks.
An angle grinder device for cutting bricks.
- perforator equipped with a crown cutter of any size;
- crayon;
- ruler;
- cutting wheels;
- roulette.
We begin work by marking the future opening with chalk. It should look like the letter T, that is, the crossbar should protrude into its frame. A beam is inserted into it, which will support the upper masonry. For partitions, a strip of wood is used, semi-bearing walls are reinforced with a board 50 mm thick, and reinforced concrete or metal beams are used in the bearing brick wall.
If a window or door frame is inserted into the hole, then it must be larger in size than the inserted units. After fixing the latter, the gaps should be filled with mounting foam. It will be both a heater and a fixative.
Consider how a wall is cut along a brick wall with varying degrees of complexity. Let's start with a partition that is 1/2 or 1/4 brick deep. We equip the grinder with a disc with a diameter of at least 250 mm and coated with a diamond coating.
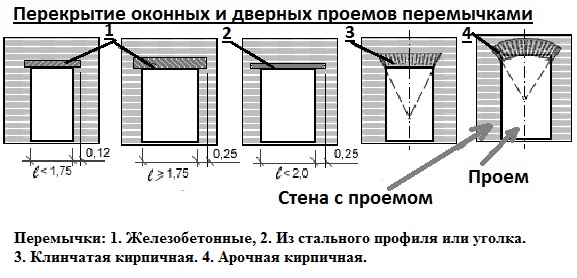
According to the markings, the grinder is incised. To make it easier to knock out bricks, several holes are cut with a perforator. As soon as the first elements of the brickwork pop up, things will go faster, taking a chisel, a hammer and a perforator to help. Only it will need to be re-equipped: instead of a crown, a chisel is inserted, switching the operating mode, eliminating rotation.
If you do not have a hole cutter, then a thick drill can replace it. They can drill masonry units by drilling them in several places and along their seams. With the same drill, we then help to pull out the filling of the opening.
In order to avoid door clamping or cracking in a thin wall, partition, you need to take a wooden beam with a thickness of at least 50 mm for the crossbar. Fix it in the opening and process it with cement mortar very tightly, eliminating the possibility of backlash.
The load-bearing wall will require more complex processing, but the peculiarity of obtaining a hole is the same as for thin partitions. For the crossbar, a channel is used - an I-beam. The opening should be reinforced with vertical posts, for them it is recommended to take profile corners 50 x 50 mm, instead of them a rectangular profile pipe 40 x 20 mm is suitable. For the screed, a metal strip is selected.
 Marking a hole in a brick wall.
Marking a hole in a brick wall.
The complexity of working with a load-bearing wall is explained by the fact that it has a difficult masonry - bricks and filler. But it is necessary to start work in the same way, with marking the future opening and basting it with a grinder. As soon as part of the inside was removed in the upper part, we wedge an I-beam there and substitute vertical supports from corners or pipes, rigidly fixing the beam. This is a very important moment. Any defect will cause subsidence of the overlap and the possibility of danger to the lives of workers employed in the patch.
Only after the channel is securely fixed, you can continue to knock out the hole. First, the sealant is removed, and then the bricks. If it is possible to access the back side of the wall, then the task will be facilitated. Pre-long drill make horizontal through holes. They are marked on the reverse side, cut through the contour and proceed to extract the material. At the same time, it is necessary to pull together with a metal strip two vertical supports forming the letter P.
Thus, using the rules, you can make a cut in the wall.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTHQ4YIjE6s
An I-beam and a flat corner are more expensive, but they will ensure the reliability of the hole.
Facing the exterior walls of the house with bricks
Facing the exterior walls of the house with brick is durable and, when using a special colored facing facing brick, and even better clinker brick. quite decorative. The disadvantages of cladding include the relatively large weight of the cladding, the high cost of special bricks, the need to broaden the foundation.
It should be especially noted the complexity and high cost of dismantling the cladding to replace the insulation. The service life of mineral wool and polymer insulation does not exceed 30 - 50 years. At the end of the service life, the heat-saving properties of the wall are reduced by more than a third.
With brick cladding use the most durable insulation, providing them with conditions in the wall structure for maximum long-term operation without replacement (minimum amount of condensate in the wall).It is recommended to choose mineral wool insulation of high density and polymer from extruded polystyrene foam, XPS.
In walls with brick cladding, it is most advantageous to use mineral heaters made from autoclaved aerated concrete or foam glass, the service life of which is much longer than mineral wool and polymer ones.
The laying of brick cladding is carried out in half a brick, 120 mm. on conventional masonry mortar.
A wall without a ventilated gap, insulated with high-density slabs (mineral wool - more than 50 kg / m 3, XPS), can be lined with brickwork on an edge - 60 mm. This will reduce the overall thickness of the outer wall and plinth.
Brick cladding is connected to the bearing wall masonry with corrosion-protected steel wire or reinforcing mesh, or with special flexible ties (fiberglass, etc.). Vertically, the grid or connections are placed in increments of 500-600 mm. (height of the insulation plate), horizontally - 500 mm., while the number of ties per 1 m 2 of a blank wall - at least 4 pcs. At the corners of the building along the perimeter of window and door openings 6-8 pcs. per 1 m 2.
The laying of brick cladding is longitudinally reinforced with masonry mesh with a vertical pitch of not more than 1000-1200 mm. The masonry mesh should go into the seams of the masonry of the load-bearing wall.
To ventilate the air gap in the bottom row of the facing masonry, special vents are arranged at the rate of 75 cm 2 for every 20 m 2 of the wall surface. For lower ventilation, you can use a slotted brick, placed on the edge so that the outside air through the holes in the brick has the opportunity to penetrate into the air gap in the wall. Upper vents are provided in the eaves of the wall.
Ventilation openings can also be made by partially filling the vertical joints between the bricks of the lower row of masonry with cement mortar.
Insulation materials
With the correct development of the frame, there comes a moment when the presence of cold bridges can be neglected, for safety net only by increasing the insulation layer by 5-10%. However, how to determine whether there will be enough thickness and thermal resistance to reduce heat loss to the required values?

A building is considered energy efficient if it loses no more than 100 kWh of thermal energy per square meter of total area in one year. Sometimes the total heat loss is determined by the maximum possible power of the heating equipment. Knowing the height of the enclosing walls and the length of the perimeter, it is enough to simply calculate the total area of the enclosing surfaces, divide them by type and calculate the proportion of walls in heat exchange with the outdoor environment. Considering that the heating period is at least 180 days, it is easy to determine what value the thermal conductivity of the walls should be limited to in order to maintain the initial heat balance.

To select the required thickness of the insulation, take into account its thermal conductivity and temperature difference, which depends on the internal climatic regime and the thermometer mark on the coldest five-day period. It should also be borne in mind that the thermal conductivity of the insulation may increase or change over time over the course of the year. If the calculation of heat losses was carried out not based on the maximum heating power, the temperature difference can be determined by the average temperature mark of January-February.
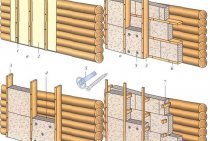
Masonry with insulation types, advantages and disadvantages
The technological process for the construction of a brick building with insulating material inside is classified according to the place where the insulation is attached. The lightweight well technique includes two independent structures, fastened inside with small horizontal brick bridges or polystyrene foam. Brick laying with insulation offers the following advantages:
- The thickness of the insulation does not exceed the thickness of the structure.
- The material inside is non-flammable.
- Outside, the masonry looks like a brick wall, which allows you to decorate the structure.
- Can be built at any time.
Despite all the advantages, double-layer walls have a number of disadvantages:
- require a large amount of work;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the insulation inside;
- thermal uniformity at a low level;
- bridges keep cold;
- difficult to repair.
Another option for using an insulating element in the masonry process is a three-layer construction. In this case, panels that retain heat are used. The insulation is attached through the use of anchors. Devices are pre-fixed in the wall. When using this technology, a vapor barrier is required to prevent condensation. It can be made from facing bricks or decorative stone is used.
It is dangerous to insulate walls in three layers, because such structures are subject to rapid deformation.
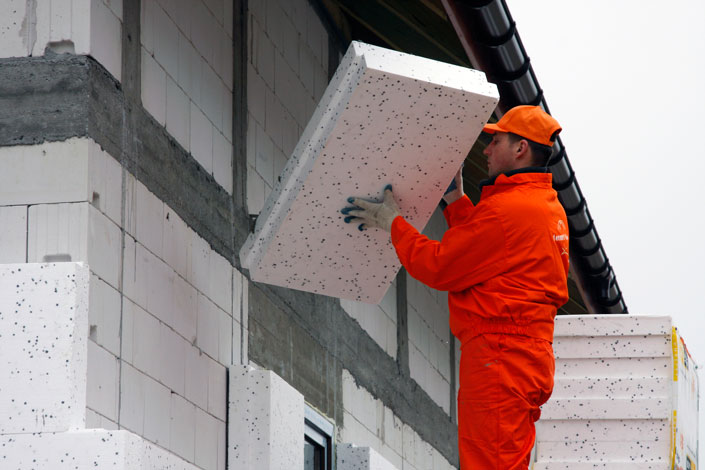
Wall insulation with polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam
Rigid slabs of foamed polymers are placed in the middle of a three-layer brick wall structure without a ventilated gap.
Polymer boards have a very high vapor permeability. For example, a wall insulation layer made of expanded polystyrene boards (EPS) has a resistance 15-20 times greater than that of a brick wall of the same thickness.
Insulation with hermetic laying is a vapor-tight barrier in a brick wall. Steam from the room simply does not get to the outer surface of the insulation.
With the correct thickness of the insulation, the temperature of the inner surface of the insulation must be above the dew point. When this condition is met, steam condensation on the inner surface of the insulation does not occur.
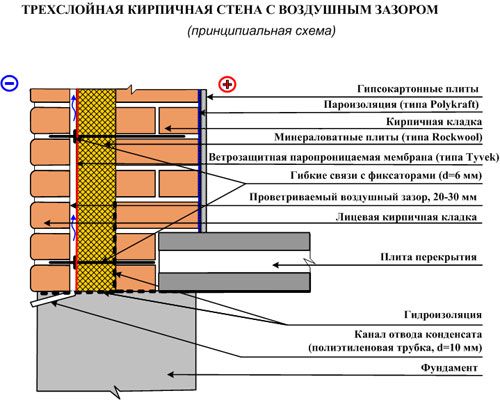
Three-layer masonry
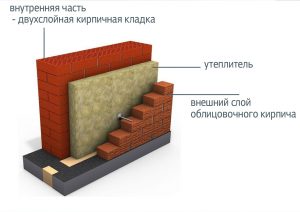
One type of insulated wall is a three-layer brickwork. Its structure looks like this:
- Inner wall made of bricks, cinder blocks, aerated concrete, etc. Carries out the bearing function for interfloor overlappings and a roof of the building.
- Insulation of brickwork. The insulation is placed in the internal cavities-wells between the outer and inner walls. Protects the inner wall from freezing during the cold season.
- Exterior wall with brick cladding. Performs decorative functions, giving the facade additional aesthetics.
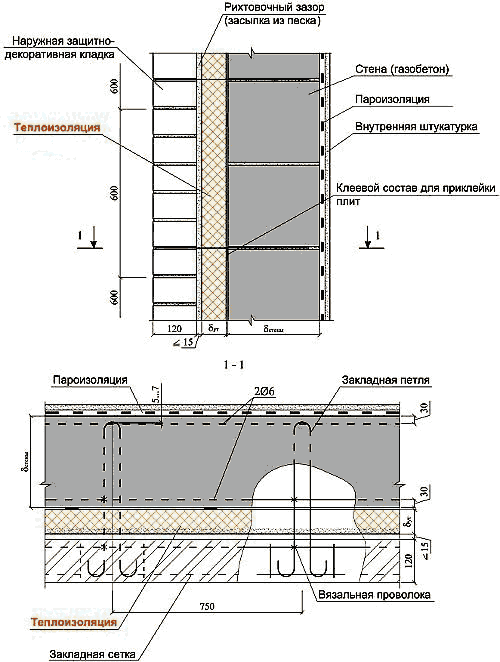
Three-layer wall in section
On the image:
No. 1 - interior decoration.
No. 2 - the bearing wall of the building.
No. 3 - insulation between brickwork.
No. 4 - ventilation gap between the internal insulation and the facing wall.
No. 5 - external wall with brick lining.
No. 6 - internal reinforcement connecting the inner and outer wall.
Brickwork with insulation inside, like other building technologies, has its pros and cons. Its positive qualities include:
- Less masonry volume, which allows to reduce the estimated cost due to savings on the amount of building material.
- Less weight of the building, which makes it possible to use lighter and more inexpensive foundations.
- High thermal insulation performance, allowing you to keep warm in the winter.
- Improved sound insulation. The thermal insulation layer can significantly reduce the noise level, which is especially important if the building is located on a central street with heavy traffic.
- External walls lined with decorative bricks do not need additional decorative finishing.
Among the disadvantages of multilayer walls, you can specify:
- Greater labor intensity associated with insulation, compared with brickwork in 3 - 3.5 bricks.
- Three-layer walls do not allow periodic replacement of insulation, while its service life is always shorter than the service life of brick walls.
Wall insulation in three-layer masonry
As a heater, rigid mineral wool boards or sheets of foamed polymers are usually used: expanded polystyrene - extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) or expanded polystyrene board (PPS), PSB foam.
Heat-insulating slabs made of cellular concrete and foam glass are less commonly used, although these materials have a number of advantages compared to the above-mentioned heaters.
The thickness of the insulation is chosen depending on the climatic conditions of the construction area.
How to determine the required heat transfer resistance of the wall and calculate the thickness of the insulation, read the article "Heating costs and heat transfer resistance."
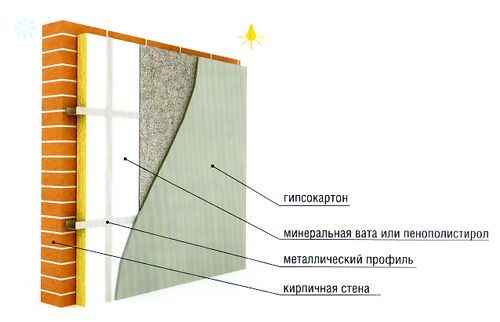
Warming inside and outside
In modern houses, the wall is a multilayer structure made of various materials. The main rule for combining them is: the vapor permeability of the layers increases from the inside out. Insulation from the inside is considered the worst option, since it is very difficult to fulfill the requirement.
Warming scheme
The second major drawback of this solution: if you insulate the wall from the inside, then the dew point - the conditions for the formation of condensate, will be inside the room, and not outside. The third drawback is that thermal insulation takes at least 15 cm of internal space.
You have to take such a step in those cases when you need to insulate a finished, lined house. Moreover, if the sheathing is done with siding, it is recommended to donate it and insulate the building from the outside.
If we are talking about a project, or about a house that is at the stage of foundation construction, then the issue of thermal insulation must be resolved in favor of another method.
Preparation for finishing
After installation and protection of the insulation, it is the turn to equip the supporting subsystem for ventilated cladding or a plane for finishing with a wet facade. In the latter case, the wind and hydroprotection of the insulation can be provided with a layer of plaster finish and / or paint.
Installation in both cases takes place according to different schemes. To ensure the necessary strength of the crate for the installation of panel materials, the installation step of the frame racks is pre-selected quite often. After temporarily fixing the waterproof membrane with brackets to the ribs of the frame, it is knocked out with spacer rails about 25–30 mm thick. In this case, space is provided for the runoff of water that has got inside and ventilation. If desired, the junction of the rails can be sealed with fresh oil paint or mastic.
 Frame house wall pie: 1 - OSB inner lining; 2 - vapor barrier; 3 - insulation; 4 - wooden frame; 5 - superdiffusion membrane; 6 - counter-lattice; 7 - facade decoration (siding, wall paneling, block house)
Frame house wall pie: 1 - OSB inner lining; 2 - vapor barrier; 3 - insulation; 4 - wooden frame; 5 - superdiffusion membrane; 6 - counter-lattice; 7 - facade decoration (siding, wall paneling, block house)
When constructing a continuous crate for plastering, sheet materials are used that serve as an excellent vapor barrier. A high concentration of moisture can provoke the condensation of drops, for the removal of which air is provided between the hydroprotection and the sheets. The sheets, in turn, exclude the blowing of the insulation.
 Plastering of the walls of a frame house: 1 - OSB inner lining; 2 - vapor barrier; 3 - wooden frame; 4 - insulation; 5 - superdiffusion membrane; 6 - counter-lattice; 7 - OSB outer skin; 8 - basic plaster; 9 - plaster mesh; 10 - decorative plaster
Plastering of the walls of a frame house: 1 - OSB inner lining; 2 - vapor barrier; 3 - wooden frame; 4 - insulation; 5 - superdiffusion membrane; 6 - counter-lattice; 7 - OSB outer skin; 8 - basic plaster; 9 - plaster mesh; 10 - decorative plaster
In some cases, the remote cladding system is mounted on top of sheet materials. This decision may be made due to the high dew point offset range. The possible formation of condensate in the ventilated layer does not pose any particular problems when using moisture-resistant sheets. However, in this case, the connection to the plinth and cornice has a more complex device.
One of the strongest and most durable building materials today is brick. And this is despite the fact that the construction market is replenished every year with the latest technologies, which they could not even dream of before.Brick walls, most likely, will never go out of fashion, thanks, precisely, to their strength and durability, proven over many decades. And what should be the optimal thickness of the brick wall of the house? We will talk about this further.
Modern waterproofing of a brick wall is essential
Brick is a rather porous material and perfectly absorbs moisture.
And if the wall of your house is made of brick, then you should not even hope that the brick will be wet only at the very bottom at the basement level - precisely because of the porous structure of the brick, moisture can rise through it to the highest floors, which means that It is very important to pay close attention to the waterproofing of a brick wall. Waterproofing of a brick wall should be carried out outside the building, since there is simply no point in doing it from the inside of a brick wall - of course, in this way you can protect yourself from moisture inside the house, but the brick itself cannot be protected from it, and excessive moisture will lead to the destruction of the brick
Today, there are many materials that can be used as waterproofing - these can be various mixtures with water-repellent properties based on concrete, asphalt plaster, rolled waterproofing or its liquid form.
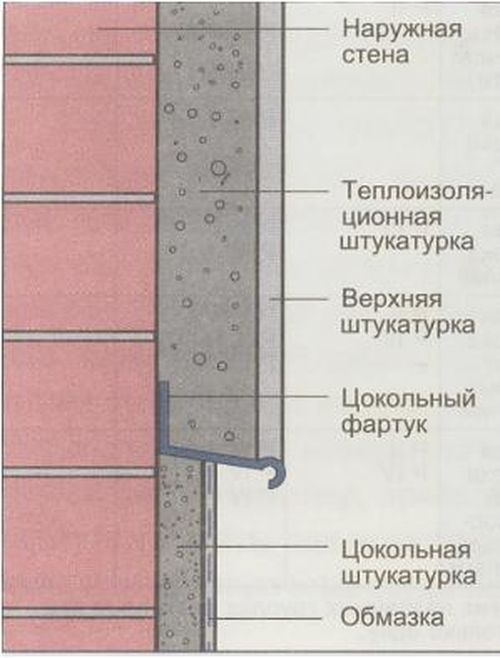
Thermal insulation of a brick house from the outside
wall insulation outside
The outer part of the house must first of all be insulated in places of contact with the ground (ground floor, outer walls of the foundation) and only then, if necessary, and, in fact, the walls themselves. Before proceeding with the installation of the insulation layer, it is necessary to clean the surface of dust and debris in order to improve the contact between the heat-insulating material and the wall. At the same time, do not forget that the layers of insulation must be vapor-tight.
In most cases, foam or extruded polystyrene foam is used to work outside, before installation of which a number of preparatory measures should be carried out, namely:
- clean the surface from dust and dirt;
- plaster the walls, leveling the existing irregularities;
- remove construction waste;
- treat the plane with a soil solution.
thermal insulation material
Then, using dowels or glue, fasten the heat-insulating material to the wall. We carry out the whole procedure in the direction from bottom to top, placing the sheets in a checkerboard pattern. Such a nuance will further strengthen the structure. After the sheet is glued to the wall, it must be additionally attached with a dowel, and the locations of the caps should be covered with a reinforced mesh, plastered with a finishing mixture.
An equally popular way to insulate external walls is the construction of a ventilated facade. The warming process is carried out according to the following scheme:
- vapor barrier layer;
- fasteners using frame anchors made of metal or wood;
- a heat insulator (mineral or basalt wool) is placed in the slats of the frame;
- waterproofing layer.
warm plaster installation diagram
After installing all of the above layers of the "pie", you can proceed with the installation of the outer skin, which can be used as siding, porcelain stoneware, etc.
The most budget option for insulation, which is available to all segments of the population, is the use of "warm" plasters. The work is not at all difficult, which even a person who does not have any skills in this field can do. First of all, of course, the surface should be cleaned of all kinds of contaminants, and then thoroughly soaked with a soil mixture. With the help of simple tools, a plaster mesh and beacons are attached to the wall, on top of which plaster will subsequently be applied. After the layer of “warm” plaster has completely dried, you can proceed to finish the facade with other decorative materials, or simply paint over the surface.
Wall insulation characteristics
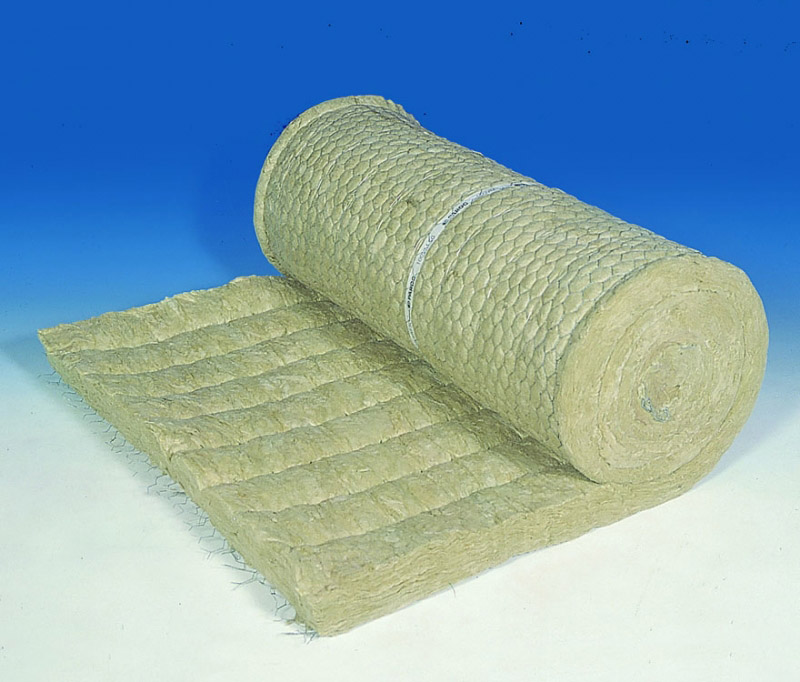
The advantages of mineral wool are: resistance to biological negativity, resistance to fire and low thermal conductivity.
It is necessary to select a heater taking into account, firstly, its thermal conductivity: the higher the thermal conductivity, the better the insulation. Secondly, vapor permeability. With a temperature difference, steam penetrates through the load-bearing wall, insulation and facing wall into the street.
Each subsequent stage must have a higher vapor permeability than the previous one, otherwise the steam will linger in the insulation and condensate will form inside the structure, which will reduce the thermal insulation properties of the insulation by an order of magnitude, which cannot be repaired. Glass wool, rock wool or basalt wool insulation has a higher vapor permeability than brick, and they are ideal for their functions. Styrofoam insulation is much higher and cannot be used to insulate brick walls.
Thirdly, the insulation must be moisture resistant, because it is impossible to completely eliminate the ingress of moisture. Therefore, when laying walls, it is necessary to provide outlet pipes.
Built into the walls in such a way as not to create cold bridges, they will quite cope with the removal of steam from the system.
And lastly, the insulation must be non-combustible. Insulation made of glass wool and all mineral wool fully meets this requirement - they not only do not burn, but are also able to protect adjacent elements of the entire structure from fire.
These are various brands of heat-insulating slabs made of stone wool of basalt rocks. These plates are produced specifically for the insulation of brick walls and have certain specified parameters and dimensions. Heaters of the Beton Element Butts brand - rigid heat-insulating plates, Cavity Butts - light heat-insulating plates have proven themselves.
In addition to ready-made plate and rolled heat-insulating materials, bulk materials can be used as heaters. It can be lightweight concrete based on sawdust, slag, expanded clay, mineral wool granules. Backfilling of heaters is carried out in stages into each well and carefully compacted. And in order to completely eliminate the shrinkage of the material in the wells, horizontal diaphragms are arranged. They are made from reinforced cement-sand mortars or they simply release bricks inside the walls, in every 2-3 rows.