Calculation of the required thickness of insulation
The thickness of the insulation layer depends on the following factors:
- thickness, design, thermal conductivity of the wall material;
- climatic zone of the building;
- the presence of additional layers in the structure (for example, a layer of internal plaster).
For simplicity, we will calculate the thickness of the insulation for the wall of a house made of foam concrete blocks 30 cm thick with internal plaster 20 mm thick, built in the Moscow region.
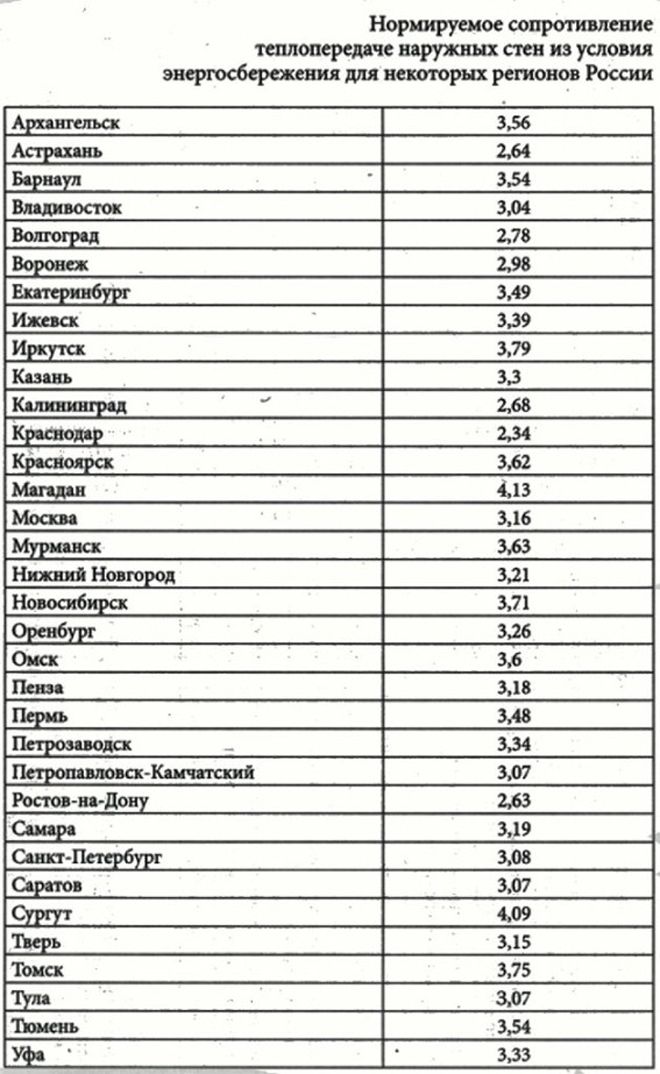
The normalized resistance to heat transfer of walls for different regions of the Russian Federation is determined by the table:
The heat transfer resistance of the wall should be 3.16 m2 °C/W.
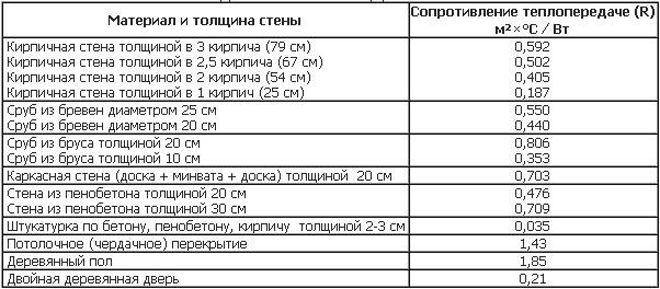
According to the table, we find data for the wall - 0.703 m2 °C / W and the plaster layer - 0.035 m2 °C / W.
We subtract individual data from the standard value:
3.16–0.703–0.035= 2.422 m2 °C/W
The thickness of the expanded polystyrene for wall insulation should provide such resistance to heat transfer.
The thickness is determined using the formula
- δ is the thickness of the insulation, m;
- λ is the thermal conductivity of the material, W/m2 °C.
Calculation example
Suppose, for thermal insulation, we purchased material of the brand PPS20 F RG. The density of the foam is 20 kg/m3, the thermal conductivity under the worst operating conditions is 0.033 W/m2 °C.
δ \u003d 2.422x0.033 \u003d 0.079, or rounded 80 mm
Since slabs up to 50 mm thick can most often be found on sale, it makes sense to use two 50 + 30 mm or 2x40 mm slabs for insulation.
How does the density of foam affect its cost?
There are several points of view related to the concept of density. The unit of this parameter is kilogram per meter cubed. This value is calculated from the ratio of weight to volume. It is impossible to determine with absolute accuracy the qualitative characteristics of polystyrene foam associated with its density. Even the weight of the insulation does not affect its ability to retain heat.
Thinking about the issue of buying insulation, buyers are always interested in its density. Based on these data, one can judge the strength of the material, its weight and thermal conductivity. Foam density values always refer to a certain range.
During the production of expanded polystyrene boards, the manufacturer determines the cost of production. Based on the formula for determining the density, the weight of the insulation will affect this value. The greater the weight of the material, the denser it is, so its cost is higher. This is due to the fact that polystyrene, as a raw material for heat insulator plates, plays an important role. It is about 80% of the total cost of finished products.
How does a change in the thermal conductivity of foam affect its density?
Styrofoam is made from expanded polystyrene balls containing air.
Any thermal insulation material contains air in the pores. The improved thermal conductivity depends on the amount of atmospheric air contained in the material. The larger it is, the lower the thermal conductivity coefficient. Styrofoam is produced from expanded polystyrene balls containing air.
From this we can conclude that the density of expanded polystyrene does not affect its thermal conductivity. If this value changes, then changes in thermal conductivity occur within percentages. One hundred percent air content in the insulation is associated with its high heat-saving ability, since air is characterized by the lowest coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation, a high degree of energy saving is ensured. If we compare polystyrene with bricks, then their energy-saving ability will differ significantly, since 12 cm of the thickness of the heat insulator corresponds to 210 cm of the thickness of a brick wall or a 45 cm wooden wall.
The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the foam, expressed in digital terms, belongs to the interval 0.037 W / mK - 0.043 W / mK. This value can be compared with the thermal conductivity of air equal to 0.027 W/mK.
Types of foam as it is classified Video
Styrofoam classification
According to the production method, this material is conditionally divided into two large classes, which have completely different characteristics. The first is made at high temperatures by sintering pellets. The second involves mixing the granules at elevated temperatures with the further addition of a special blowing agent and removal from the extruder.
The first class is called pressureless, it is easy to determine by eye. The material looks like balls linked together, somewhat similar to a bee hive. Suffice it to recall the foam in which any household appliances (microwave oven, refrigerator) were supplied. The second class is called press, because the granules are interconnected much stronger. It is much more difficult to break or crumble. In accordance with this, various brands are distinguished.
Styrofoam grades
The marking of foam plastic of domestic manufacturers is indicated by two letters - PS. If the material is non-pressed, then three letters are used - PSB. Other numbers and letters can be additionally added to them through a dash. For example, PSB-S means self-extinguishing foam. So, we will describe the main existing brands so that you can know which foam to choose.
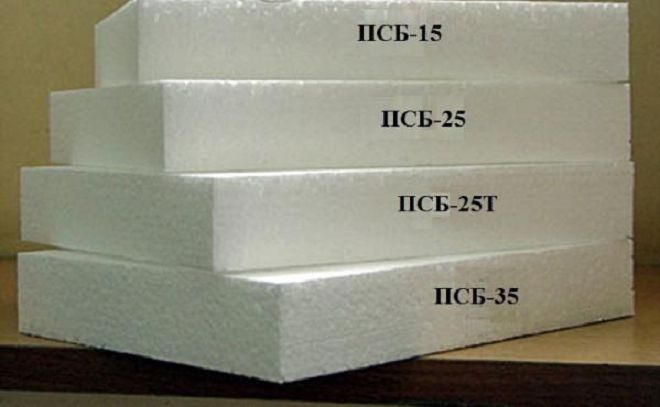
- PSB-S-15 - has a low density and is used to insulate those structures where special mechanical strength is not needed. This type of material is used to insulate attics, bare roofs, containers, wagons, and fill the distance between the rafters. It is environmentally friendly, not affected by any microorganisms, has high moisture resistance.
- PSB-S-25 - is the most popular and versatile brand. It is used for warming walls, floors, facades of buildings, loggias. It is not affected by microorganisms, is environmentally friendly, has high resistance to aging and moisture.
- PSB-S-35 - used to a greater extent to isolate the foundation, underground utilities (including parking lots). It is also used to prevent swelling of soils in the arrangement of swimming pools, sports grounds, lawns. Plus, it is an ideal material for adverse climatic conditions. It is biologically safe, has high mechanical strength, is resistant to aging, moisture and the development of microorganisms.
- PSB-S-50 - has the highest density compared to all other brands. It is used in those conditions where mechanical strength is important. It is used in the construction of roads in wetlands, the arrangement of floors of interfloor ceilings. It is also well suited for insulating floors in barns, garages, industrial areas. The material is biologically safe, resistant to aging and moisture.
Types of foam
The first are made in a pressed and non-pressed way, the brands are described above. The second - polyurethane (PPU), in everyday life are common in the form of ordinary foam rubber. Still others - polyethylene (PPE), have the form of an elastic material in which the product is wrapped so that it does not break (a film with air pimples).
Fourth - polyvinyl chloride (PVC), very similar in appearance to extruded polyethylene foam. They are also very elastic, have the same properties. Plus, they do not contain highly toxic mixtures and are recognized as a self-extinguishing material.
In fact, there are more types. If you are interested in a particular material, then you should find out the information in the hardware store, where all varieties are listed in the catalogs.
Classes, thickness and grades of PPS, how to choose which one is better to use
At first glance, all the foam is the same, but this is only for those who first decided to insulate the house from the outside. Polyurethane foam is divided into classes and brands, and for this use the following features:
- production features;
- material density;
- edging method.
Styrofoam classes
Divide the material into 2 classes:
- Pressed - PS marking will be applied on the sheet. Insulation is made using press installations. The structure of the material is smooth and it is almost impossible to distinguish polystyrene granules.
- Pressless - in this case, the PSB marking is left on the foam. To create such products, high-temperature sintering of the substance is used. Although press installations are also used. The slabs consist of round or oval granules that are easy to distinguish from each other.
Letters or numbers are added to these markings, which will help determine the density of the material, where it is best to use it and the shape of the edge. Additional letters are:
- A - the correct shape of the plate.
- B - the edge cut is similar to the letter L.
- P - slabs were cut with a hot string.
- Ф - the product was created using a form, or a facade purpose.
- C - polystyrene foam decays on its own.
- H - suitable only for outdoor work.
PPS stamps
Now let's deal with the grades of the material. To determine the brand, manufacturers indicate a numerical value. For non-press and press representatives, these values \u200b\u200bare different. Let's take a closer look at each class separately.
Styrofoam grades
In the construction market, this class of insulation is represented by the following brands:
- 15 - low density foam. The cheapest. It is more often used for packing household appliances or fragile items. It is easy to damage;
- 25 - if the letter F is added to such numbers, then the material is suitable for facade decoration. The density is much higher, and hence the strength is improved. It is often chosen to create decorative elements in the interior or landscape - the density of the material allows;
- 35 - foam with this marking can be used for different purposes. It is a good insulation for the facade, as a component for multilayer panels (thermo, sandwich, reinforced concrete);
- 50 is the densest and most durable material, and also the most expensive. It is used for insulation of underground structures and communications.
Brands of press PPS
Using the press method, PVC foam is produced. Polyvinyl chloride resin is added to the composition. The material is very durable and reliable. It is used in all areas of construction and insulation. A number from 1 to 4 is added to the letters PS. The larger the numerical value, the higher the density, and hence the strength of the expanded polystyrene.
The material of the press production method is suitable for creating containers for aggressive substances. It is resistant to most known chemically active liquids.
The structure and composition of the foam
Styrofoam is a white material with a rigid foam structure, which contains 98% air and 2% polystyrene.
For its manufacture, a technology has been developed for foaming polystyrene granules, after which these microscopic particles are treated with hot steam. The procedure is repeated several times, as a result of which the density and weight of the material are significantly reduced.
The prepared mass is subjected to drying to remove residual moisture. The process is carried out outdoors in special drying containers. At this stage of production, the foam structure takes on its final shape. The sizes of the granules are in the range from 5 to 15 mm.
The dried foam granules are given the appropriate form in the form of plates. Pressing is carried out on special installations or machines that "pack" the foam and give it a compact shape.
After pressing the foam, it is once again treated with hot steam, as a result of which white blocks with the specified width parameters are formed. Blocks are cut with special tools according to the dimensions required by the customer. Styrofoam sheets can be standard or custom sizes. The thickness of the foam varies from 20 to 1000 mm, and the dimensions of the plates have the following dimensions:
- 1000x500mm;
- 1000x1000mm;
- 2000x1000mm.
This is interesting: Styrofoam sheathing at home
1 Styrofoam how much does a cubic meter weigh
Fashionable false opinion - the specific gravity of the foam should fit the brand. In other words, if we purchase brand 35 foamed plastic, then the specific gravity of one cubic meter of polystyrene foam should be 35 kg. In fact, in accordance with GOST, the figure in the brand indicates the maximum possible weight of a cubic meter, within the limits listed in the same GOST. So, the 15th density includes all foam polystyrene plates weighing up to 15 kg / m3 (actually 11–12 kg / m3), the demanded 25th the brand is attributed expanded polystyrene, whose specific gravity can range from 15.1 kg / m3 to 25 kg / m3 (very often, as practice has shown - 17–18 kg / m3), foamed plastic weighing from 25.1 to 35 kg / m3 is classified as grade 30 . In the latter option, very often manufacturers recommend expanded polystyrene with a real density of 26-27 kg / m3. Sell? Rather, savings - bearing in mind the high competition in the manufacturer's market, anyone is trying to offer the material more affordable than others. And this can only be done by reducing the number of raw materials and worsening the quality of products.
Determining the quality and brand of foam by density (weight to volume ratio, kg / m3) is a very big misunderstanding. Density is only one characteristic that plays a role in determining the grade of the material being produced. In accordance with GOST 15588-86, expanded polystyrene is distinguished by compressive strength, bending strength, thermal conductivity, moisture resistance, board burning time and structural stability. Of all these characteristics, density is far from being very key. For example, for the 25th density of foam plastic, GOST defines a compressive strength of at least 0.08 MPa. For the 15th grade, this characteristic is 0.04 MPa. There is one fundamental point in GOST - if the foamed plastic does not meet its own brand according to any characteristic, it must be assigned to a brand with a class lower. In other words, if, for example, you purchase foamed plastic, the specific gravity of which is from 15.1 to 25 kg / m3, but the compressive strength of the material is less than 0.08 MPa, it must be attributed to grade 15.
Where is polystyrene foam of different sizes used
This durable moisture-resistant insulation is used when performing outdoor work. To insulate a wall with polystyrene foam, you first need to determine what density, size, type of polystyrene foam will be required for work. The choice depends on the expected loads that this material will carry during operation. When insulating a vertical wall, the loads will be minimal; a sheet of any brand will do. Even PSB-S 15 will give the same result as PSB-S 25 when it comes to wall insulation in areas with mild winters. This is due to the fact that the principle of operation of the foam is based on gluing polystyrene balls, between which and inside there are multiple air chambers. It is known that the less mass and more air, the better the effect of thermal insulation. It is inconvenient to work with sheets of low density, which are more fragile and break. PSB-S 25 has a high density, it is easier to finish with it.
properties of expanded polystyrene.
Expanded polystyrene 25 is often used for external wall insulation of non-residential premises. They produce decoration of balconies, loggias, garages, shopping centers, various institutions. For northern regions with cold winters, it is believed that a sheet thickness of 5 cm is enough to keep warm inside the room on the frostiest nights. Styrofoam brand 100 is used for thermal insulation of industrial freezers, as well as for warming houses in the harsh climate of the far north. A sheet size of 10 cm will make the thermal protection indicator maximum. When choosing a brand of expanded polystyrene, you can choose a sheet that has different parameters.A non-standard sheet of 500x500 is sometimes much more convenient to work with than a standard long sheet with dimensions of 2000x1000 mm.
Sheets of 1000x1000 and 1000x500 mm are suitable for warming the walls of the house. It is convenient to work with them, it turns out fewer joints that will have to be hermetically sealed. To fill smaller areas, existing sheets are cut into suitable pieces. For all non-standard situations in finishing, it is better to use a large sheet to make it easier to cut configurations. In the process of laying, such sheets are adjusted to the desired parameters by cutting the polystyrene foam into pieces. This material cuts easily.
Expanded polystyrene, having dimensions of 2000x1000 mm, is more difficult to install. Working alone, it is easier to lay two sheets of 1000x1000 than one sheet measuring 2000x1000 mm.
Expanded polystyrene is a sought-after material in the construction market because its thermal insulation ability is much better than that of other building materials. It provides long life to buildings in any climatic conditions.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Ea94bC7aIp0
Comparing it in terms of thermal conductivity with other materials, we obtain the following results: 80 mm thick foam is equivalent to 100 mm of mineral wool, 274 mm of wood, 760 mm of brickwork and 1720 mm of concrete. This characteristic and low cost make this material especially popular in construction.
Types of expanded polystyrene
As we have already said, this material is divided according to the method of production. Figuratively speaking, the following options are distinguished: polystyrene, polyurethane, polyethylene, PVC expanded polystyrenes.
The first are made in a pressed and non-pressed way, the brands are described above. The second - polyurethane (PPU), in domestic conditions are popular as the usual foam rubber. Still others - polyethylene (PPE), have the form of an elastic material in which the product is wrapped so that it does not break (a film with air pimples).
Fourth - PVC (PVC), similar in appearance to extruded polyethylene foam. They are also very flexible, possess the same qualities. In addition, they do not have highly toxic mixtures in their composition and are recognized as a self-extinguishing material.
In fact, there are a decent number of species. If you're concerned about a particular material, it makes sense to check with a building supply store where the catalogs list all the different options.
Video about the production of various options for expanded polystyrene
Coefficient of thermal conductivity of foam boards
Home insulation can be carried out in various ways, for example, using polystyrene foam, which has high performance characteristics. These include: practicality, environmental friendliness, low weight, ease of installation, immunity to temperature changes, as well as an affordable price. But the main advantage is the low thermal conductivity of the foam, which makes it possible to achieve excellent energy savings.
What are the properties of the material?
The ability to conduct heat is influenced by many factors, in particular:
- Layer thickness. Sometimes, in order to achieve high-quality energy saving, it is necessary to apply a large amount of insulation. For example, the thermal conductivity of 5 cm foam boards will be lower than 1 cm at the same density.
- Structure. The porous structure leads to increased insulating properties, because the cells contain air, which perfectly retains heat.
- Humidity. Plates during storage must be protected from moisture. This is due to the fact that the liquid does not have a very favorable effect on the characteristics of heat-insulating foams: the more it accumulates, the worse.
- Average layer temperature. Its increase leads to a deterioration in the efficiency of the use of the insulator.
Types of foam and their performance
There are a huge number of insulation boards on the construction market.In general, polystyrene foam has a low thermal conductivity, but it varies depending on its type. Examples: sheets marked PSB-S 15 have a density of up to 15 kg / m3 and a thickness of 2 cm, while the described indicator is up to 0.037 W / (m * K) at an ambient temperature of 20-30 ° C. Its value for sheets of 2-50 cm with marking PSB-S 35, with a density of not more than 35 kg / m3 and 16-25 kg / m3 marking PSB-S 25 of the same size - 0.033 W / (m * K) and 0.035 W / (m*K), respectively.
The dependence of the thermal conductivity of a foam insulation on its thickness is best seen when it is compared with various materials. So, a sheet of 50-60 mm replaces twice the volume of mineral wool, and 100 mm is equivalent to 123 mm of expanded polystyrene foam, which has approximately similar characteristics. Strongly loses and basalt wool. But the thermal conductivity of Penoplex is somewhat lower than that of polystyrene: in order to obtain normal temperature conditions in the room, it will take 20 and 25 mm, respectively.
How to determine which sheets to buy?
In order to most effectively apply one or another method of insulation, it is necessary to choose the correct dimensions of the material.
The technology of thermal insulation of walls from the outside with expanded polystyrene
There are several ways to install foam on the facade:
- For glue.
- Mechanical fastening with dowels.
- combination method. Use both glue and fasteners. He is more reliable.
Everyone can choose the appropriate option for themselves, but professionals recommend using the latter method. To keep the whole structure securely adhere to such a plan.
Preparatory work
It all starts with preparing the foundation. This stage is just as important as fixing the insulation or finishing it. Here they do the following:
- If the building was previously covered with trim, it is removed.
- Remove fasteners and hinged structures.
- The wall is cleaned of dirt, greasy stains, influx of solution, dust.
- Perform surface priming. For porous materials, such as foam or gas block, a deep penetration primer is chosen and applied in 2 layers. It is also desirable that the composition be antibacterial. Then the main structure will be protected from harmful microorganisms. The soil allows you to increase the adhesion of the material from which the load-bearing walls are made, and therefore securely fix the insulation on the base.
- Next, set the starting profile on the border of the basement and the beginning of the wall. It will act as a support for the foam. The profile is fixed immediately along the perimeter of the entire building. Be sure to check the horizontal with the help of the building level.
- Now proceed to the preparation of the adhesive solution. The adhesive should only be suitable for Styrofoam, other brands will not work. Cooking instructions are on the packaging. Be sure to adhere to the proportions, otherwise the material will not stick to the wall.
Board bonding
The finished solution must stand for some time so that all components react with each other. Next, proceed to gluing the insulation boards:
- A thin layer of the solution is applied around the perimeter of the foam plate. In these places, the mixture must be rubbed into the material - this increases adhesion.
- Make 2-3 small blots in the center.
- The plates are installed in the starting profile from the lower left corner of the house.
- The foam is pressed tightly against the wall so that the solution is evenly distributed under the sheet. If excess adhesive is visible, it is removed with a spatula. The evenness of the installation is checked with a building level.
- Glue is also applied to the next plate and pressed tightly against both the wall and the previous sheet.
- In the second row, the vertical joints should not match. To do this, the foam is shifted 15–20 cm to one side.
- After all the walls are completely covered with insulation and the adhesive solution has set, proceed to mechanical fixation.Holes are made with a puncher and dish-shaped dowels are installed.
Installation of the reinforcing layer
When the glue is completely dry, proceed to reinforce the surface of the foam. For this use:
- Adhesive solution, you can also the one that was used to fix the plates on the wall.
- Fiberglass mesh.
There is also a special technique for gluing the mesh:
- First of all, a thin layer of glue is applied with a spatula.
- Pieces of mesh 15–20 cm wide are glued to the corners. The grid element is laid in such a way that the two walls have the same segments. With a clean spatula, the fiber is pressed into the adhesive solution.
- If it doesn’t work, glue is added on top and smoothed.
- Next, proceed to the reinforcement of the wall.
- An overlap of 10 cm is laid on the corner element. It is also pressed into the solution with a spatula.
- When this layer dries, a finish is applied to completely hide the mesh under the glue.
Applying a decorative layer
After applying the last layer of glue, wait for it to dry completely. Further, it is customary to cover the foam insulation with plaster. This may be a decorative version with an original pattern or an ordinary even layer, painted in a suitable color.
After carrying out all the work, the house will be both warm and updated at the same time. And this is a solution to two problems at once. Of course, whether or not to choose polystyrene foam for home insulation is everyone's business. The nuances of choice and technical characteristics listed above are quite enough to make the right choice.