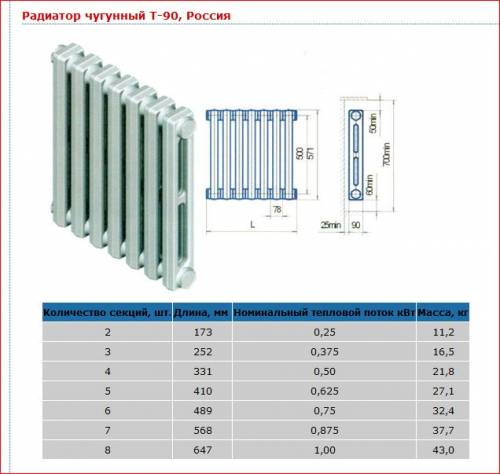
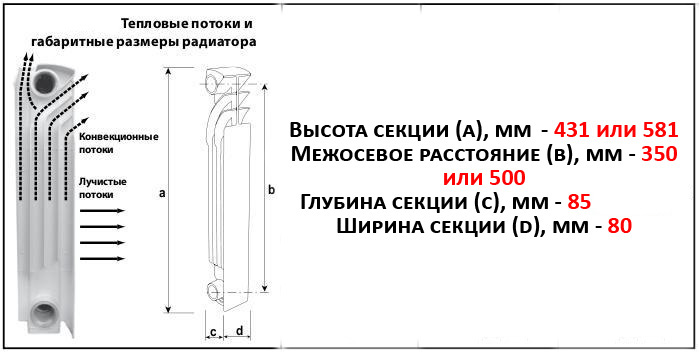
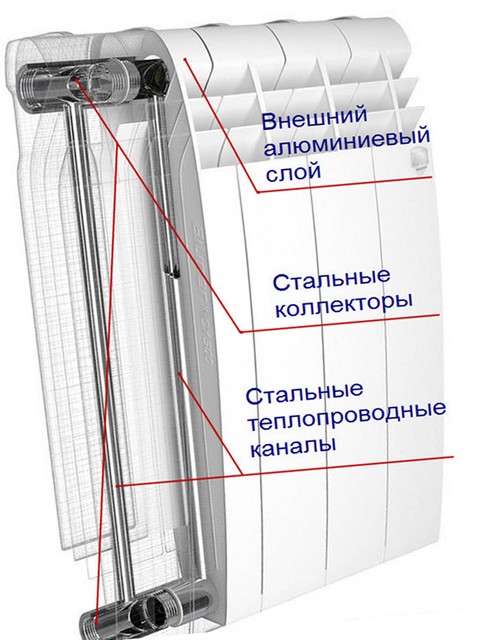
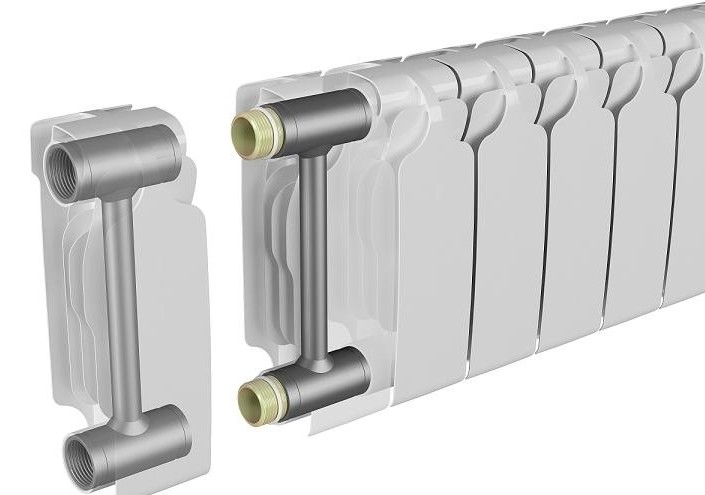
Real heat dissipation of the radiator section
As already mentioned, the power (heat transfer) of radiators must be indicated in their technical passport. But why, after a few weeks after the installation of the heating system (or even earlier), it suddenly turns out that the boiler seems to be heating as it should, and the batteries are installed in accordance with all the rules, but it is cold in the house? There can be several reasons for the decrease in the actual heat transfer of radiators.
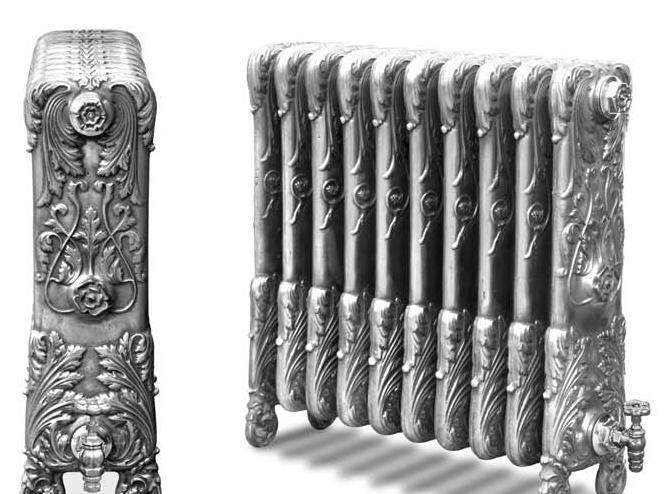
Pig-iron radiator Viadrus (Czech Republic)
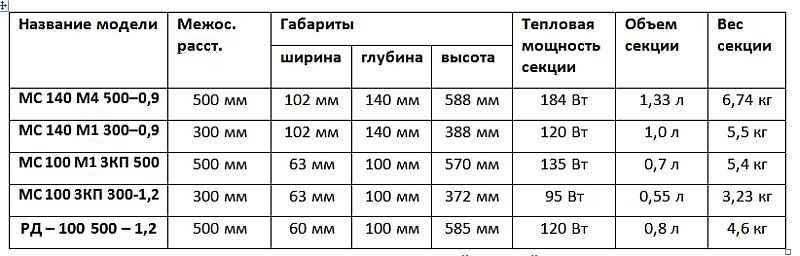
Here are the indicators of the heating surface and the declared heat transfer for the most common models of cast iron radiators. We will need these figures in the future for examples of calculating the real power of the radiator section.
As already mentioned, when using such radiators for medium-, low-temperature heating systems (for example, 55/45 or 70/55), the heat transfer of a cast-iron heating radiator will be less than stated in the passport. Therefore, in order not to be mistaken with the number of sections, its actual power must be recalculated according to the formula:
K is the heat transfer coefficient;
F is the heating surface area;
∆ t - temperature difference ° С (0.5 x ( t input +tout. ) - text .);
tin - the temperature of the water entering the radiator,
texit - water temperature at the outlet of the radiator;
text .- average air temperature in the room.
At the temperature of the incoming coolant 90 gr. outgoing 70 gr. and the temperature in the room is 20 gr.
∆ t \u003d 0.5 x (90 + 70) - 20 \u003d 60
The K coefficient for the most common cast iron radiators can be found here:
Even the real heat transfer of one section of an average cast-iron radiator with an area of 0.299 sq. m (M-140-AO) at an inlet water temperature of 90 gr. and outgoing - 70 gr will differ from the declared one. This is due to heat losses in the supply pipes, and for other reasons (for example, reduced pressure), which cannot be foreseen under laboratory conditions.
So, the heat transfer of a section with an area of 0.299 sq. m. at a temperature of 90/70 will be:
Considering that heat transfer is always indicated with some margin, we multiply this figure by 1.3 (this coefficient is used for most cast iron radiators) and we get: 125.58 x 1.3 = 163, 254 W - compared to the declared 175 W.
There will be even more difference in numbers if the water entering the radiator does not heat up above 70 degrees. (and the outgoing coolant, respectively, cools down to 60-50 degrees), so before buying new radiators, it is advisable to find out the real thermal parameters of your heating system.
How to save on heating?
The first rule of reasonable savings is to remember what you should never save on! Radiators should always be taken with a margin, because you can reduce the temperature in the room by reducing the temperature of the water in the system or by using stopcocks. But if the actual heat transfer is lower than declared by the manufacturer, the rooms will be cool at best. By the way, Conner cast-iron radiators, which are quite good in terms of most parameters, in real operation have a heat transfer of 20-25 percent lower than indicated in the passport
Radiator 1K60P-500 (Minsk)
As already mentioned, heat transfer may differ from the declared one due to the fact that the water temperature in the heating system is much lower than the “standard”, that is, the one at which the factory tests were carried out, since the declared radiation power is achievable only under laboratory conditions. Imagine that the section of the MS-140 radiator (power 160 W is indicated) at a water temperature of 60/50 degrees. (and more “the boiler does not pull”!) Will produce power of no more than 50 watts. And if you believed the technical data sheet and decided to install 5 heating sections, then instead of 800 W (160 x 5) you will get only 250.
However, it is quite possible to foresee this situation and even take advantage of it! Based on the calculations given above, the lower ∆ t (that is, the temperature of the heat carrier water), the larger the radiant surface of the radiator should be. So at ∆ t 60 for radiation of 1 kW, a radiator with a height of 0.5 m x 0.520 m is sufficient, and at ∆ t 30 - 0.5 m x 1.32 m.
"Traditional" cast iron radiator MS-140M2
However, it is precisely due to the low temperature of the carrier and an increase in the radiating area of \u200b\u200bthe radiator or the number of sections that it is possible to reduce heating costs.
Manufacturers, models, specifications
MS-140 is produced by the following factories:
- Nizhny Tagil Boiler and Radiator Plant (Russia);
- Minsk Plant of Heating Equipment (Belarus);
- Lugansk Foundry and Mechanical Plant (Ukraine);
- JSC "Santekhlit" Bryansk region (Russia);
- Descartes LLC Novosibirsk (Russia).
The products have some features and differences, there are models with a center distance of 300 mm and 500 mm, as well as a lower depth option MS-90.
Nizhny Tagil Boiler and Radiator Plant
The plant's products are certified according to the ISO 9001:2008 standard in the Russian Register certification, there is a certificate from the GOST R System and IQNet.
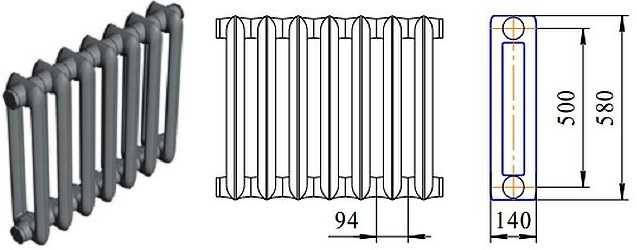
Overall dimensions of MS-140 manufactured by Nizhny Tagil
Heat carrier temperature up to +130 o C, working pressure up to 12 bar, other technical characteristics are given in the table.
Heat transfer surface of one section MS-140M - 0.208 m 2. BZ-140-300 - 0.171 m 2.
There are many interesting models in the assortment of this plant: there are with a bas-relief, with a flat frontal surface (a new sample, similar to aluminum), of different heights, widths and depths. There are plenty to choose from. In general, Belarusian cast-iron radiators are of high quality.
JSC "Santekhlit" Bryansk region
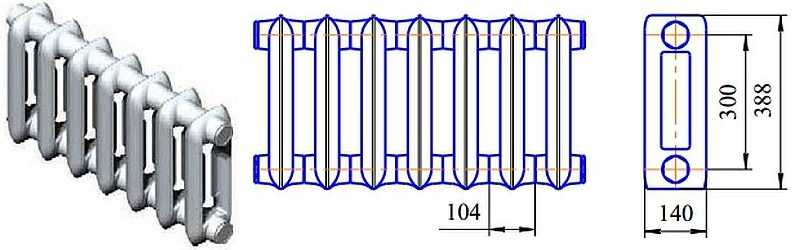
The operating pressure of heating devices from Bryansk is different for different models: for MS-140 - 9 Bar, for MS-100 and MS-85 - 12 Bar, the temperature of the working medium is +130 o C, the heating area of one section is MS-140M-500-0.9 - 0.244 m 2. material - gray cast iron SCH-10.
Heat output of the section
Dimensions MC-140-300
OOO Dekart Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk cast-iron radiators have an operating pressure of 9 bar, connection 1 ¼, temperature of the transported medium +130 o C.
Heat output of the section
So pour radiators
Lugansk Foundry and Mechanical Plant
The operating pressure of these heaters is 12 Bar, the standard temperature is +130 o C, the connection diameter is ¾”.
Technical characteristics of radiators of the Lugansk plant
The assortment of the Lugansk plant includes a radiator with a flat front panel RD - 100 500 - 1.2, its technical characteristics are given in the table.
Forced Initiative
In a panel house with central heating, you don’t have to worry about such issues as filling the system with coolant, this is the diocese of housing and communal services. But taking care of the estate or cottage is a huge responsibility that lies entirely on your shoulders. The opportunity to save time and money forces the owners to maintain thermal communications with their own hands, sometimes using non-standard methods.
In the photo - checking the battery
For example, the lack of a centralized water supply forces the use of natural sources - wells, wells, ponds.
Working with documentation
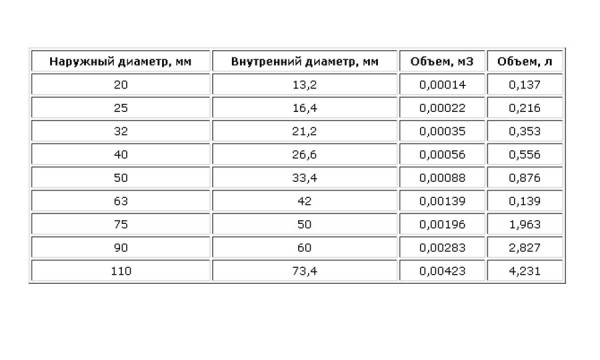
The answer to the question, how much water flows out of pipe "A", or rather, should go there, usually lies in the technical data sheet of the radiator and boiler. With pipes it is a little more difficult, but not deadly - knowing their inner diameter, on our website you can find a detailed table on the amount of water in liters / cubic meters per linear meter. The same can be said about the data on the volume of the fuel boiler or batteries.
Data on the internal volume of pipes
Knowing the filling capacity of each meter of the pipe, it is elementary to find out the total “pipe” volume of the coolant - multiply the tabular figure by the number of meters. To do this, it is not necessary to crawl around the house with a tape measure, but use a project plan and a ruler.
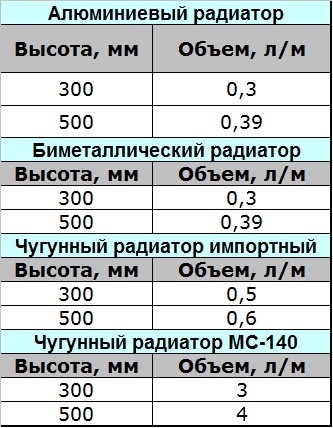
Note! On the Internet, a table of the volume of water in a heating radiator looks even more convenient. It can compare the capacity of radiators from different materials, which will give you the opportunity to choose the appropriate option.
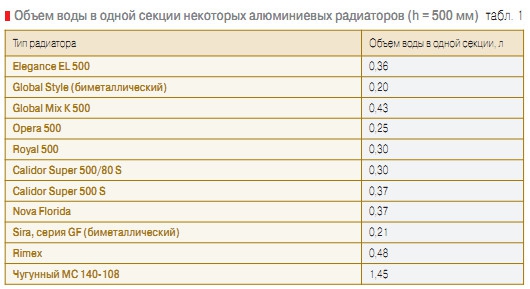
The volume of water does not depend on the type of radiator
From the presented table it can be seen that the volume of water in the section of the bimetallic radiator and the aluminum one is the same.So the material does not matter, the main dimensions of the heater.
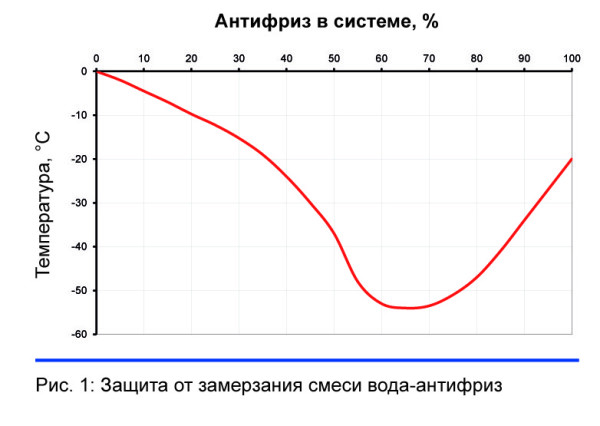
Non-permanent residence in the house obliges the owners to use antifreeze. Since this pleasure is not cheap (the price for 10 liters of domestic propylene glycol "Technology of Comfort" reaches a thousand rubles), you need to know exactly the amount of anti-freeze. Having determined the extreme minus threshold for the heating system, the substances are mixed in a certain proportion.
Note! Do not add antifreeze to a heating system made of galvanized pipes
Antifreeze lowers the freezing point of a liquid
Average cheat sheet
The average data that determines the volume of water in steel panel-type heating radiators are as follows:
- models Demrad, Thermogross 11 type for every 10 cm of length there is 0.25 l of coolant;
- in similar models of type 22, this figure increases to 0.5 liters for the same length.
Each section of the good old "cast iron" of different models has the following capacity:
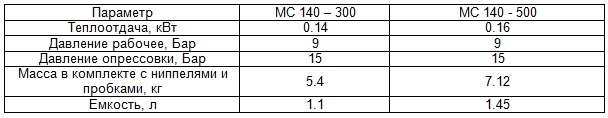
- MS 140 - 1.11-1.45 liters (from 5.7 to 7.1 kg);
- ChM 1 - 0.66–0.9 l s;
- World Cup 2 - 0.7–0.95 l;
- World Cup 3 - 0.155–0.246 l;
- Konner Modern - 0.12–0.15 l (3.5 kg).
Note! You can see how the traditional MC 140 differs from the Chinese Konner in weight, which you should pay attention to if you have floor models
But so much is included in the aluminum section
If your battery is a tricky author's thing, it is difficult to find out its volume, but it is possible. For example, the volume of water in a tubular steel radiator is calculated ingeniously simply - one hole is closed with a plug, and water is poured through the second to the top.
Note! Mark the amount of liquid poured immediately or later, when you pour the contents into a bucket / bath. This calculation method is applicable to a radiator of any complexity without documents
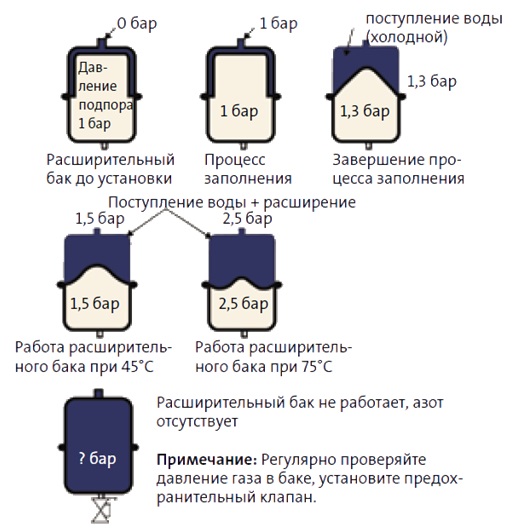
In the heat exchangers of a wall-mounted heating boiler, on average, from 3 to 6 liters are placed, and in the floor and parapet versions - from 10 to 30 liters of water. So, having learned the amount of coolant in all the corners that it reaches, you can carry out a responsible operation - calculate the volume of the expansion tank. It is on him that the optimal pressure in the system and the required volume of coolant depend.
The principle of operation of the expansion tank
The calculation instruction involves the use of a simple formula:
- Vc is the volume of coolant in the heating system (what was mentioned above - radiators + pipes + boiler heat exchangers);
- K is the expansion coefficient of the coolant (for water it is 4%, so 1.04 is used in the formula);
- D is the tank expansion efficiency;
- Vb is the capacity of the expansion tank.
You can find out the volume of coolant in radiators or pipes close to the real figure based on the power of the boiler using the formula:
x kW * 15=VS, where
- kW - boiler power;
- number 15 - the number of liters of water to obtain 1 kW of energy;
- VS is the total capacity of the system.
Thermal power
The photo shows an approximate heat transfer of cast iron.
In the room, heating devices are placed against the outer wall under the window opening. As a result, the heat emitted by the device is optimally distributed. The cold air coming from the windows is blocked by the heated flow going up from the radiator.
Cast iron batteries
Cast iron analogues have the following advantages:
- have a long service life;
- have a high level of strength;
- they are resistant to corrosion;
- excellent for use in utility systems operating on low-quality heat transfer fluid.
- Now manufacturers are making cast iron batteries (their price is higher than conventional analogues), which have an improved appearance, thanks to the use of new technologies for casting their cases.
Disadvantages of products: large mass and thermal inertia.
The table below announces how many kW are in the cast-iron radiator, based on its model.
Aluminum radiators
Products made of aluminum have a greater thermal power than analogues made of cast iron.When asked how many kW are in one section of an aluminum radiator, experts answer that it reaches 0.185-0.2 kW. As a result, 9-10 sections of aluminum sections will be enough for the standard level of heating of a fifteen-meter room.
The advantages of such devices:
- a light weight;
- aesthetic design;
- high level of heat transfer;
- temperature can be controlled by hand with the help of valves.
But aluminum products do not have the same strength as cast iron counterparts, such as a 2 kW oil cooler. Therefore, they are sensitive to surges in the operating pressure in the system, hydraulic shocks, excessively high temperature of the heat carrier.
Bimetallic products
Before finding out how many kW are in 1 section of a bimetallic radiator, it should be noted that such batteries have similar performance parameters with aluminum counterparts. However, they do not have the disadvantages inherent in them.
This circumstance determined the design of the devices.
- They consist of copper or steel pipes through which the coolant flows.
- The tubes are hidden in an aluminum plate case. As a result, the water circulating inside does not interact with the aluminum of the case.
- Based on this, the acidic and mechanical characteristics of the heat carrier do not affect the operation and condition of the device in any way.
Thanks to the steel pipes, the fixture has high strength. The increased heat dissipation is provided by external aluminum fins. When trying to find out how many kW are in a steel radiator, keep in mind that bimetal has the highest heat transfer - about 0.2 kW per fin.
Specifications for MC 140 batteries
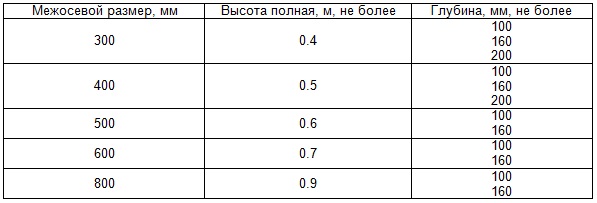
For the manufacture of this type of radiators, at one time, a whole GOST 8690-94 was developed, which regulates all the parameters of the product. In accordance with it, 5 standard sizes of batteries were produced with center distances of 300, 400, 500, 600 and 800 mm. The table below shows cast-iron heating radiators with technical dimensions in accordance with GOST 8690.
Previously, all standard sizes of these devices could be seen not only in apartments, but also in industrial or office buildings. It is advisable to review the characteristics of the two most "running" sizes of 300 and 500 mm, which are still in demand. Other modifications are now very rare, and they are made only to order.
The main technical characteristics of the MC 140 cast iron radiator with a center distance of 300 and 500 mm are shown in the following table.
Having studied all the characteristics, we can draw conclusions about the advantages and disadvantages of the considered heating devices. Their advantages are as follows:
- Durability. It is at least 30 years old.
- Heat dissipation. Despite the outdated design, the MC 140 cast iron radiator shows good thermal output.
- Unpretentiousness. Gray cast iron, from which the devices are made, is not subject to corrosion and calmly tolerates a bad coolant with a high oxygen content.
- Maintenance undemanding. It is not superfluous to flush the channels of the product once every 2 years, but if this is not done, then the MC 140 will continue to work safely. Only the heat transfer coefficient will begin to decrease.
- Inertia. It is both a plus of batteries and their minus. The advantage is that after turning off the heating, the device gives off heat to the room for a long time.
- Affordable cost.
Now about the shortcomings, of which there are also many. The same inertia of the devices causes their prolonged heating and excludes the possibility of regulation with the help of thermal heads. There are others:
- Large capacity of the coolant. This affects the rate of heating and cooling of the system, and also makes it necessary to spend a lot of thermal energy on heating a large volume of water.
- The considerable weight of the products affects the installation of radiators. They are very difficult to fix on walls made of porous lightweight materials, which are very popular in our time.
- Low working pressure threshold. This makes it impossible to install it in high-rise building systems.
- Fragility. The wall-mounted cast-iron radiator MC 140 500 is shock-resistant because it has thin walls. Cracks at the slightest freezing of water from frost.
- Unpresentable appearance compared to more modern analogues of cast iron batteries.
Safety
It is believed that a radiator heating element with a built-in thermostat is an absolutely safe heating device: turning off when the coolant reaches the set temperature will prevent dangerous overheating or boiling of water.
However, not all potential buyers of the device are aware that the safety and efficiency of work is ensured not only by the design of the device, but also by the correct installation.
- In the central heating system, when the heating element is turned on, the radiator shut-off valves must be closed. At the same time, a jumper must be mounted on the inlet in front of them, which will allow the coolant to circulate through the riser when it is started. In the absence of valves, your heater will heat the batteries throughout the riser; in the absence of a jumper, after an unsuccessful attempt to start the heating, a sad locksmith will come to you and utter many offensive words.
- Heating the coolant in a closed volume will turn your radiator into a full-fledged miniature boiler room and ... dramatically increase the pressure in it. Thermal expansion, you know. Hence the need to install on the supply line after the shut-off valve either a small expansion tank (its volume is taken equal to 10% of the radiator volume) or a safety valve. (See also the article Heating pipes: features.)
A small expansion tank will be able to accommodate the excess of the expanded coolant.
Note that the second scenario is undesirable, since the valve will periodically emit jets of hot water when heated.
- The cross section of the power cord must be at least 1 square millimeter per 8 amperes of current. With a heating element power of 2500 watts and a supply voltage of 220 volts, the current will be 2500/220 \u003d 11.36A; the minimum cross-section of the wire core, therefore, is 11.36 / 8 = 1.42 (rounded to the real value - 1.5 mm2).
- The maximum load per outlet should not exceed 3500 watts.
- Grounding is highly desirable.
The grounding pins in the socket must be connected to the body of the electrical panel.
The power of the heating element without a thermostat should not exceed the rated heat output of the radiator. For one aluminum section, it is taken equal to 200 watts, for cast iron - 160 watts. Heating element for heating radiators with a thermostat can be installed without power restrictions.
Preparatory actions
They provide for cleaning the surface of dirt and old paint. The preparation goes like this:
Wipe off dust with a damp cloth. You need to rub it very well. There should be no dirt left in the holes. To wipe hard-to-reach places, the rag is advanced between the ribs and pulled back and forth.
Get rid of the old layer of paint. This can be done either chemically or physically. The first involves the use of solutions Dufa, B52, SP-6, ACE. True, they are powerless against oil formulations made in the 50s of the twentieth century. The physical method is to use a drill with a metal brush attached to it. You can also use sandpaper and a file. If chemicals were used, then the cast iron will have to be cleaned with a metal brush mounted on a drill. Rusty places are treated with sandpaper.
Apply a layer of primer. Of course, it must withstand high temperatures and match the type of paint. It will be better if the brand of both is the same.
It can be carried out with any type of composition. but under one condition: the solution must be resistant to high temperatures. Otherwise, the updated look will not last long.
The surface of the heating battery is painted using a regular or curved brush.Of course, at the beginning, gloves are put on the hands and gauze, foam rubber or rags are placed nearby. They will be able to erase the paint that has flowed down the brush handle.
The coloring process is as follows:
- With a flexible brush, they update the look of hard-to-reach places (they are located between the pipes of the sections). In some parts, the brush will not touch the cast iron. The gauze folded into a tourniquet can save. It is placed between the sections, paint is applied to the middle and then the ends are pulled in turn. So, the paint will at least somehow fall on the alloy.
- Paint the top and easily accessible places.
- Always moving from top to bottom. It is better to apply the paint in several layers than one thick one.
Dimensions of cast iron radiators depending on their type Technical characteristics of cast iron radiators Calculation of the power of steel radiators Advantages and main nuances of long burning cast iron stoves
Modern cast iron radiators
For wall mounting, there are new products made of gray cast iron from various manufacturers, whose mass is much less than the traditional MC 140. For example, the Czech heating radiator Viadrus STYL 500, shown in the figure.
Its characteristics are as follows: the mass of 1 section is 3.8 kg, the water capacity is 0.8 l, for a total of 4.6 kg. With an available heat flux of 140 W, our room of 20 m2 will require 14 pieces, which will be 64.4 kg in weight along with water. This indicator is 40% less than that of the MC 140, and dividing it into 2 parts (32 kg each device), it becomes clear that it is possible to install cast-iron radiators on walls made of porous concrete without special additional tricks. An even lighter design is offered by a Russian manufacturer that sells its heaters under the EXEMET brand, namely the MODERN model.
Here, one section of the radiator weighs only 3.2 kg with a heat output of 93 W; in a room of 20 m2, 22 sections with a total weight of 70.4 kg are needed. This indicator is also quite good, especially considering that the company manufactures these batteries with the possibility of floor installation.
It is impossible not to say a few words about such a product as a vintage cast iron battery, whose weight is even larger than the Soviet MS 140 and in some cases reaches 14 kg. These heaters, by their appearance, resemble the old ones, installed in residences and estates in the distant 19th century.
The EXEMET FIDELIA model shown in the figure has a weight of 12 kg with a heat output of 156 W, which makes the total weight of the cast-iron radiator for our example simply monstrous - 154 kg. But as you can see in the image, here the installation issue is solved differently: the first and last sections have legs for placing the heater on the floor.
How to calculate sections of heating batteries
Even the highest quality aluminum heating devices will not be able to heat a home if their heat output is insufficient to heat a certain area. Before determining the number of products, you need to calculate how many sectional elements each will have. According to the rules, it is considered that for heating 1 sq. m requires 100 W of heat - this is the required radiator power per square meter. It turns out that the calculation is carried out by area in several stages:
- First of all, you need to divide 100 by the power of one section of an aluminum radiator. If we take the last value equal to 180 W, then we get 100/180 = 0.556.
- For further calculations, the area of \u200b\u200bthe room is required, by which it is necessary to multiply the characteristic obtained in the previous paragraph, i.e. on the number of radiator sections per square meter. We take the area of \u200b\u200bthe room equal to 18 square meters. m and we get - 0.556 * 18 \u003d 10. If the number is not an integer, then it is rounded up so that there is a supply of thermal energy.
Such a thermal calculation of the room is simplified. For a more accurate calculation of the dimensions of the device, the orientation of walls and windows to the cardinal points, heat losses due to air infiltration through slots and ventilation, and a few more criteria are taken into account. There is also a calculation by volume:
- The condition is used that for heating 1 cubic meter. m requires 41 W in a panel house and 34 W in a brick house.
- The resulting area is multiplied by its height. It turns out - 16 * 2.7 \u003d 43.2 cubic meters. m, where 16 sq. m - the quadrature of the room, and 2.7 - the standard value of the height of the ceilings, taken as an example.
- Further, for a brick house, it will be required - 43.2 * 41/180 = 9.84, i.e. 10 pieces. and for the panel - 43.2 * 34/180 = 8.16, i.e. 9 pcs.
Weight of one section of cast iron battery
About cast iron batteries
The cast iron radiator belongs to the classics of the genre. It has been used for more than 100 years and not a single modern model is still capable of completely ousting it from the market. Cast iron radiators are in demand due to the characteristics of the material itself.
Important advantages of cast iron are:
- corrosion resistance,
- long service life,
- Undemanding to the quality of the coolant,
- Excellent heat transfer
- Undemanding in application.
Everything cannot be so smooth, and there are still two shortcomings.
One lies in the mass. How much does a cast iron battery section weigh? The weight of 1 section of a cast-iron radiator is approximately 7.5 kg. Thanks to simple reasoning, we can conclude that a standard battery of 7 sections will weigh 52.5 kg. To ensure a comfortable temperature in the room, one section of the heating element is usually not enough. Based on these circumstances, in order to ensure the reliability of the structure, it is necessary to think over ways of attaching the radiator elements to the wall. Let's do the calculation with an example. The Soviet model MS 140, which is still on the market, has a considerable mass - 7.12 kg. The volume of its one section is 1.5 liters of water, the total mass is 8.62 kg. The thermal power in this case is approximately 170 watts. How many sections are needed to heat a room of 20 m2? If it is necessary to heat a room of 20 m2, then 12 sections will be required, then the mass will be 85.4 kg, plus water - 103.4 kg.
The second negative point of cast iron is its brittleness.
Therefore, in order to carry out the transfer of a product with a large mass and its fastening, it is necessary to do all manipulations with it as carefully as possible, preventing the slightest impact in order to avoid microcracks invisible to the eye. Since in the process of working with an inevitable increase in pressure in the heating network, the resulting cracks will begin to increase, which will end in radiator leaks.
Heating area of cast iron radiator section
07 May 2013, 11:57
Igor_01 wrote: Calculate correctly, you can consult with your neighbors, see how they are and ask if it's good, are you warm girl, are you warm red?!
Consulting with neighbors is an entertaining business, but from the point of view of reliability it is doubtful. For some, +18 is normal, but for another, even at +24, it’s cold! The air temperature in residential premises is regulated by sanitary standards. The document is called SanPiN 2.1.2.2465-10 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises." Valid in the latest edition from 03/27/2011.
Powered by phpBB phpBB Group.
phpBB Mobile / SEO by Artodia.
How is the heat transfer of a cast-iron heating radiator calculated?
One of the main parameters of the device for space heating is its heat transfer. But no less important when installing a heating system are indicators such as heat capacity and thermal inertness of the material from which the radiators are made. Cast iron radiators, which are mainly used in centralized heating systems of multi-storey buildings, have a high thermal output, but at the same time they are quite compact, withstand high coolant pressure and are not afraid of rust. The massiveness of cast iron and a large volume of coolant in each section (section MS 140 weighing 7.5 kg contains 4.2 liters of water) provides cast iron radiators with a greater heat capacity than heating batteries made of other materials, so the temperature in the room rises and falls gradually. So, the heat transfer of the MC 140 cast-iron radiator is much lower than that of a modern aluminum or bimetallic radiator, but it retains heat much longer.
Bohemia decorative cast iron radiator in retro style
Pros and cons of using cast iron radiators
Stylized cast iron radiator
Any heating system that exists today has both pluses and minuses, consider them.
The nominal value of the thermal power of each section is 160W. Approximately 65% of the released heat flow heats the air that accumulates in the upper part of the room, and the remaining 35% warms the lower part of the room.
- Long period of use, ranging from 15-50 years.
- High level of resistance to corrosion processes.
- Possibility of use in heating systems with gravitational circulation of the coolant.
- Low efficiency of heat transfer index correction;
- High level of labor intensity during installation;
Important! In order not to run into a problem during installation, be sure to consider the above pros and cons of cast iron radiators. Their installation is not cheap, and repeated installation work will require a lot of financial resources.
Calculation of sections (cavities) of radiators
And so, how many kW are in 1 section of a cast-iron radiator? To calculate the number of sections and their power, it is necessary to determine the V of the room, which will later appear in the calculations. Next, select the value of thermal energy. Its meanings are as follows:
- heating 1 m 3 of a house from panels - 0.041 kW.
- heating 1 m 3 of a brick house with double-glazed windows and insulated walls - 0.034 kW.
- heating of 1 m 3 of premises built according to modern building codes - 0.034 kW.
The heat flux of one cavity MS 140-500 is 0.160 kW.
Next, the following mathematical operations are carried out: the volume of the room is multiplied by the heat flux. The resulting value is divided by the amount of heat released by one cavity. The result is rounded up and we get the desired number of sections.
How many kilowatts are in a cast iron section? Each type of radiator has a different value, which the manufacturer calculates during their manufacture and indicates it in the accompanying documentation.
Let's make an approximate calculation according to the available data.
The room has the following data: type of room - panel house, length - height - width - 5x6x2.7 m, respectively.
- We calculate the volume of the room V:
- Based on this, the number of radiator sections is as follows:
where 0.16 is the thermal power of one section. Specified by the manufacturer.
- We round the value up, based on which the number of required sections is 21 pieces.
Important! Always round up the resulting value. It will be hot - you can ventilate, it will be cold - you will not heat
Working and crimping pressure
Among the technical characteristics, in addition to the fact that the power of cast-iron heating radiators is important, mention should be made of pressure indicators. Typically, the working pressure of the liquid heat carrier is 6-9 atmospheres. Any type of battery with such a pressure parameter can cope without problems. The standard pressure for cast iron products is exactly 9 atmospheres.
In addition to the working one, the concept of “pressure pressure” is used, which reflects its maximum allowable value that occurs during the initial start-up of the heating system. For the cast iron model MS-140, it is 15 atmospheres.
According to the regulations, in the process of starting the heating system, it is necessary to check the possibility of smoothly starting centrifugal pumps, which should operate in automatic mode, but in reality everything is far from being the way it should be.
Unfortunately, in most homes, automation is either missing or out of order. But the instruction for this type of work provides that the initial start-up should be carried out with the valve closed. It may only be smoothly opened after the pressure has equalized in the heating medium supply line. But utility workers don't always follow instructions. As a result, in case of violation of the regulations, a water hammer occurs.With it, a significant pressure jump leads to an excess of the permissible pressure value and one of the batteries located along the path of the coolant is unable to withstand such a load. As a result, the service life of the device is significantly reduced.
Why is TEN needed?
TEN for radiators ensures uninterrupted operation of the heating system, even if it is not possible to use the usual method of heating. In fact, a heating element is a metal tube with a spiral sealed inside it. These elements are isolated from each other using a special filler. The heating element is connected to the pipeline system as an additional equipment. In addition, a heating element inserted into an old cast-iron battery will be able to heat a small garage, greenhouse or other outbuilding. And there are a lot of such examples, if you believe the statements of our skilled men on various thematic forums.
Installing heating elements for batteries allows you to take advantage of all the advantages of electric heating - ease of operation, reliability and high efficiency. But unlike electric heaters, these devices are installed directly into the system, so they are completely invisible and do not take up additional space. Thanks to the temperature control function, the heating element is able to maintain the set temperature.