It is no coincidence that polypropylene pipelines are becoming increasingly popular with home craftsmen and professional installers. Polypropylene pipes have a number of advantages due to which they are gradually replacing products from traditional materials. The choice of plastic pipes today is simply huge and all products differ in their characteristics and purpose. To find out which of them are suitable for a heating system, cold or hot water supply, ventilation, decoding the marking of polypropylene pipes will help.
"Reading" information
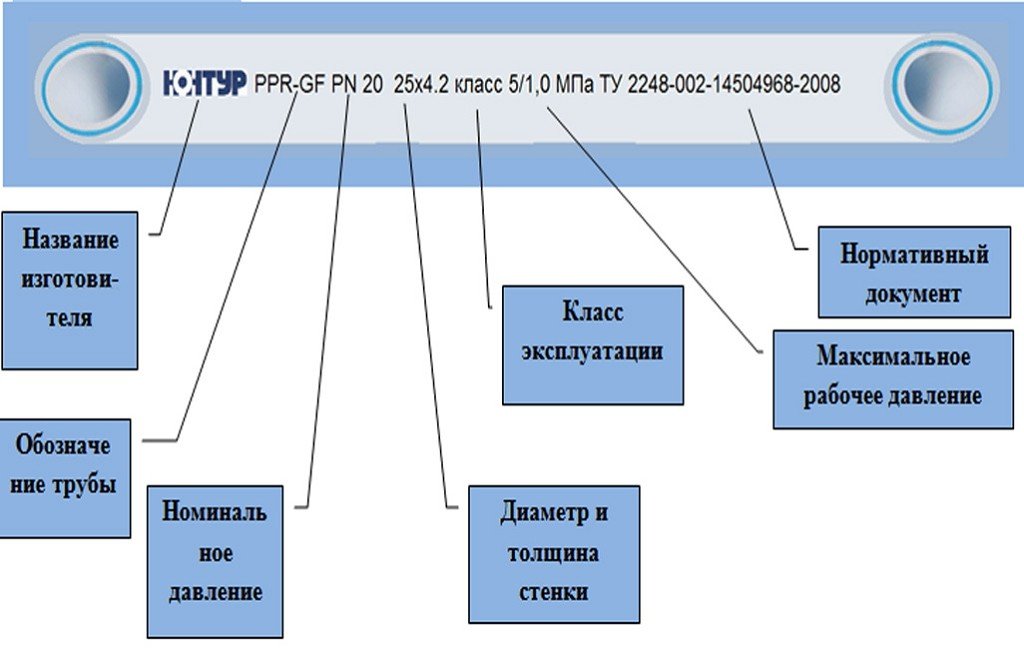
If you take it in hand polypropylene pipe, you can see on it a long row of symbols, abbreviations and numbers. Let's see what they mean. A detailed breakdown is in the image below.
- The name of the manufacturer usually comes first.
- Next comes the designation of the type of material from which the product is made: PPH, PPR, PPB.
- On pipe products, the working pressure must be indicated, which is indicated by two letters - PN, - and numbers - 10, 16, 20, 25.
- Several numbers indicate the diameter of the product and the wall thickness in millimeters.
- On domestic modifications, the class of operation in accordance with GOST may be indicated.
- Maximum allowable operating pressure.
Additionally indicated:
- Regulatory documents in accordance with which pipe products are manufactured, international regulations.
- Quality mark.
- Information about the technology by which the product is made, and the classification according to MRS (Minimum Long-Term Strength).
- 15 digits containing information about the date of production, batch number, etc. (the last 2 are the year of issue).
And now let us dwell in more detail on the most important characteristics of polypropylene pipes indicated in the marking.
Material and scope
Manufacturers from different countries use slightly different designations, but the PP marking will definitely be present, demonstrating that the pipe is made of polypropylene. Additional letters or numbers indicate a specific type of this material that has its own properties.
- PRN (PP-type 1, PP-1) - the pipe is made of a homopolymer. Due to the characteristics of this type of polypropylene, it is intended only for cold water, as well as for ventilation.
- РРВ (РР-type 2, РР-2) – the product is made of a block copolymer. It can be used for cold water supply and in low-temperature types of heating systems.
- PPR (PP-2, PPR, PP-random, PPRC) - the pipe is made from a random copolymer. Products with this marking are most common due to their versatility. Due to the increased heat resistance, they can be used in heating systems of any kind, as well as for supplying hot and cold water to apartments and houses.
Rated pressure
The letters PN are the designation of the permitted working pressure. The next figure indicates the level of internal pressure in bar that the product can withstand during a service life of 50 years at a water temperature of 20 degrees. This indicator directly depends on the wall thickness of the product.
- PN10. This designation has an inexpensive thin-walled pipe, the nominal pressure in which is 10 bar. The maximum temperature that it can withstand is 45 degrees. Such a product is used for pumping cold water and underfloor heating.
- PN16. Higher nominal pressure, higher limiting fluid temperature - 60 degrees Celsius. Such a pipe is significantly deformed under the influence of strong heat, therefore it is not suitable for use in heating systems and for supplying hot liquids. Its purpose is cold water supply.
- PN20. The polypropylene pipe of this brand can withstand a pressure of 20 bar and temperatures up to 75 degrees Celsius.It is quite versatile and is used to supply hot and cold water, but should not be used in a heating system, since it has a high coefficient of deformation under the influence of heat. At a temperature of 60 degrees, a segment of such a pipeline of 5 m is extended by almost 5 cm.
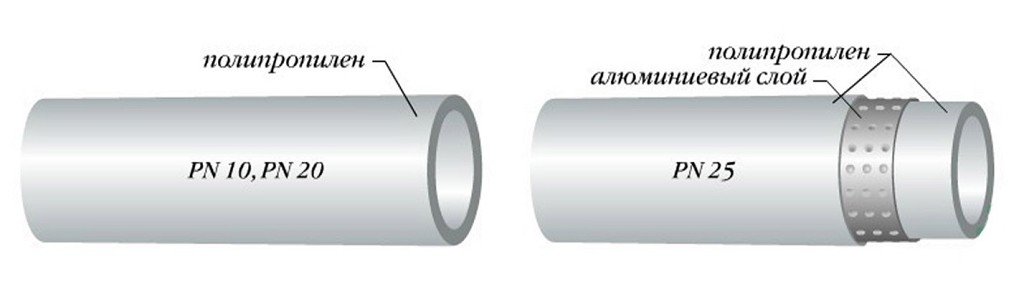
- PN25. This product has a fundamental difference from previous types, since reinforced with aluminum foil or fiberglass. In terms of properties, the reinforced pipe is similar to metal-plastic products, is less susceptible to temperature effects, and can withstand 95 degrees. It is intended for use in systems of heating, and also in GVS.
Operating class
When choosing polypropylene products of domestic production, the purpose of the pipe will tell you the class of operation according to GOST.
- Class 1 - the product is intended for hot water supply at a temperature of 60 °C.
- Class 2 - DHW at 70 °C.
- Class 3 - for underfloor heating using low temperatures up to 60 °C.
- Class 4 - for floor and radiator heating systems that use water up to 70 ° C.
- Class 5 - for radiator heating with high temperatures - up to 90 ° C.
- HV - cold water supply.
Dimensions
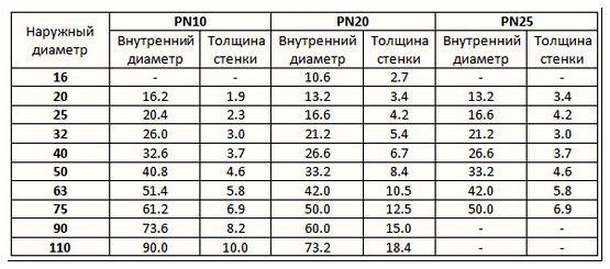
The dimensions of polypropylene pipes vary widely. Values for external and internal diameters, wall thicknesses can be found in the following table.