Combination of two-pipe and one-pipe options
In private two-story (or higher) houses, both two-pipe and one-pipe vertical risers can be used, along with horizontal one-pipe wiring in rooms with a variety of ways to connect heaters.
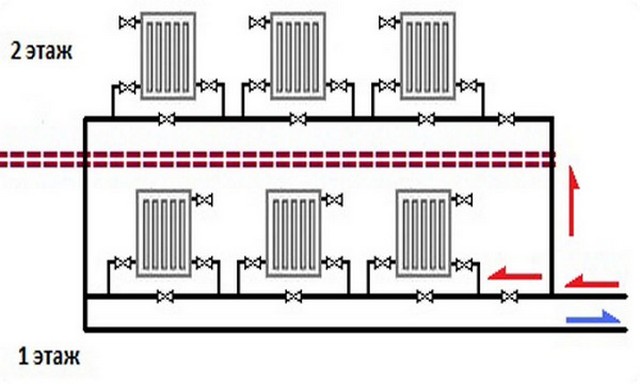
Scheme of a single-pipe heating system of a 2-storey building.
The temperature difference in room radiators in this case is calculated by the formula ∆T_p=∆T⁄P, where P is the number of heaters connected in series (in this case P=3). P times more liquid should flow through a horizontal single-pipe line than through horizontal pipes with two-pipe wiring. This will require an increase in pump power for its forced circulation and high energy costs, but the hydraulic stability of the circuit will be high.
Single-pipe heating with lower wiring do the system ourselves
The single-pipe arrangement of the heating system means that there is no separation of the pipeline for the coolant into the supply line and the return line: the liquid from the boiler moves along one ring, after which it returns back to the heating unit. When single-pipe heating systems with bottom wiring are created, the radiators are arranged in series, as shown in the photo. The liquid coolant enters them in turn: first - into the first battery, then into the second, then into the third, etc. As a result, the temperature of the heat carrier decreases gradually and in the very last device it is colder than at the initial stage.
In a two-pipe system, in contrast to a single-pipe design, there is both a supply and a return pipeline, which are interconnected by heating devices in the same way as jumpers. In this case, the coolant entering each battery has the same temperature.
One-pipe heating system with forced circulation old advantages and new opportunities
Today, there is a return of interest from the engineering community to such a heat supply tool as a one-pipe forced circulation heating system in multi-storey and individual construction. In the early 90s, it was rejected by domestic heating engineers after three decades of uncontested and widespread prevalence in buildings of any number of storeys and purposes. Traditional, fundamentally uncontrolled single-pipe heating did not fit into the concept of energy-efficient housing, and in the last two decades it has been widely replaced by two-pipe heating. But modern single-pipe designs combine their traditional advantages (hydraulic stability, efficiency) with the ability to control heating devices, as in two-pipe counterparts.
What is a single-pipe heating system and how is it different from a two-pipe
Single-pipe heating system of a private house, like two-pipe. includes:
- a boiler that generates thermal energy, which can use various fuels and can be of a wide variety of designs;
- radiators that directly heat the premises of the house;
- a pipeline through which a heat-transfer fluid circulates, ensuring the transfer of thermal energy from the boiler to the radiators;
- additional equipment that ensures circulation and efficient operation (expansion tank, shut-off and control valves, connecting elements, circulation pump (one or more), safety unit, etc.).
- Saving pipes and connecting elements;
- Less time and labor for installation work;
- With open piping, the main pipeline is less noticeable in the interior of the rooms.
But if you decide to use a single-pipe system, with self-installation of water heating in your house, then you must also take into account its disadvantages:
- Less uniform heating of radiators - as you move away from the boiler, a colder coolant will flow into the radiators;
- It can be difficult to control the temperature of individual radiators;
- It is more difficult to ensure good natural circulation of the coolant, especially with a long circuit length.
In order for the shortcomings of a single-pipe system not to affect the efficiency of its work, or at least to minimize them, it is necessary to choose the most suitable type of it.
Do-it-yourself installation procedure for single-pipe heating
To install a one-pipe heating system with your own hands, prepare the tools:
- knife for cutting pipes;
- soldering iron for polypropylene pipes and fittings;
- key for assembling heating batteries;
- fum tape.
Scheme of a vertical single-pipe heating system with a lower wiring.
To install a single-pipe heating system in a private house with your own hands, you first need to install a boiler, which must be located at a certain depth, but it is highly recommended not to place it in the basement. As a rule, a recess in the floor is prepared for the installation of a heating boiler. The preparation of such a recess involves pouring concrete and, at the request of the owners, ennobling with tiles.
After the boiler is installed, the chimney is installed. The connection of the boiler and the chimney is carried out using a corrugated metal pipe, when choosing which it is necessary to collect the required diameter. After that, the main pipe is connected to the boiler for the main. The diameter of this pipe is about 25 mm.
Only metal pipes can be connected to the boiler, as other materials are not able to withstand the high heating temperature. Adapters are not allowed. To stabilize the heating process, an expansion tank must be installed at a height of about 3 m. Thus, the expansion tank becomes the highest point of the heating system.
The next step is the installation of radiators and pipes. In parallel with this, Mayevsky's taps and valves are being installed. Batteries are installed under window openings
It is important that there is free space between the battery and the window sill, sufficient for the circulation of hot air flows. Pipes are installed straight and without bends
The presence of bends will impede the normal circulation of the coolant and reduce the efficiency of the heating system. This is especially important for single pipe systems.
The end of the pipes of the house heating system is attached to the reverse side of the heating boiler circuit. To prevent unnecessary and superfluous materials and impurities from entering the boiler, a special metal filter is installed on it.
When installing the heating system, it is necessary to perform work on the installation of a node that will perform the function of filling the heating system with water, if necessary, it will be possible to drain water through it.
Single pipe heating installation completed. After completion of all installation work, it is necessary to check the serviceability and correct operation of the boiler. To do this, the boiler is filled with water and turned on.
Features of a single-pipe heating system
The single-pipe heating system has gained wide popularity in private construction due to the following advantages:
- Hydraulic stability - replacement of the radiator, extension of sections, shutdown of individual circuits does not change the heat transfer of other elements of the system;
- Minimum number of pipes;
- A smaller amount of coolant in the system reduces its inertia and the heating time of the room;
- Aesthetic appearance, especially when installing a hidden highway;
- Easy installation;
- When using modern shut-off valves, it is possible to accurately control the operation of the entire system and individual elements;
- Serial connection of heating devices allows you to arrange a water-heated floor, mount heated towel rails, etc.
- Inexpensive installation and operation.
The thermostat on the radiator assembly allows you to adjust the heating temperature of the battery
The main disadvantage of single-pipe heat supply is the imbalance in the heating of devices along the length of the main. The farther the radiator is from the boiler, the less it heats up. Under the action of the pump, the heating of the radiators is carried out more evenly, however, the cooling of the coolant is still observed, especially with a sufficient length of the pipeline. The negative effect of this phenomenon is reduced in two ways:
- They increase the number of sections of the last radiators, due to which their power and the amount of heat given off to the room increase - uniform heating of the premises is achieved;
- They rationally design the passage of the highway through the rooms - they start with bedrooms, children's and "cold" rooms (corner, with windows to the north), then go to the living room, kitchen, bathroom, toilet and end with utility rooms.
Disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system
Along with the advantages, such a system has disadvantages:
1. Requirements for the diameters of the main pipeline.
2. In the first radiators, the temperature of the coolant is the highest, and in the subsequent ones, it is getting lower and lower due to the constant admixture to the main flow of the coolant from the passed radiators.
3. From the second point it follows that the last radiators need to be made larger than the first ones, otherwise they will be much colder.
4. And in general, with such a connection, you should not “plant” more than 10 radiators on one branch, because uniform heating will not work. Conclusion: “Leningradka” “lives” better in small houses.
I believe the one-pipe heating system is adequately lit. There are a couple of good radiator mounting schemes that relate to two-pipe systems. This is a radiant (collector) heating system and the Tichelman scheme. Read about them in the following articles.
single pipe heating system
2013-2017 Copyright Use of site materials is allowed with reference to vodotopim.ru
Features of connecting single-pipe heating in a two-story house
In two-story houses, natural air circulation, which is the rise of warm air to the 2nd floor and the flow of colder air to the 1st floor, is especially pronounced and can create significant discomfort. To maintain approximately equal temperatures on different floors of the house, you need to carefully consider the order of connecting radiators and the number of sections in them.
You can, of course, solve this issue easier: block the door on the flight of stairs connecting the floors of the house. However, this can ruin the interior of the house, although such a do-it-yourself solution to the problem is quite common.
Scheme of one-pipe and two-pipe heating.
There is 2 option for uniform distribution of heat over a two-story house, called forced ventilation. However, it cannot be taken seriously, because at the first power failure, the discomfort will return, and such a system will cost quite a lot during installation and operation.
In order for the temperatures on the floors of the house to equalize or become at least closer, on the 2nd floor, instead of heating radiators, you can arrange a water-heated floor system made of metal-plastic pipes with a diameter of 20 mm.
It is almost impossible to solve the issue of equally comfortable heating of 2 floors, especially with your own hands, however, a thoughtful layout of the house and the installation of an autonomous heating system will reduce the difference in conditions. And it is best for heating a two-story building that a single-pipe heating system is suitable.
General provisions
Excessive reinforcing items affect the quality of the heating system and cause its elements to wear out faster. Loose pipes and connections (without collars and clamps) last much longer. This must be taken into account when connecting batteries to the system.
It should also be taken into account that the entire heating system must be made of the same material: polypropylene, metal (of the same brand).
Connecting a single-pipe heating system is suitable for small cottages, apartments.
This closed system (see diagram) will heat a room in which no more than 10 radiators can be placed. The rest of the heating devices will not make sense (even a large surface volume), since as they are removed, the cooled water will simply reach them through the pipes.
Single-pipe systems are simple both in terms of scheme and installation. They are more cost effective and low cost.
Connecting a heating radiator to a two-pipe system Connecting aluminum radiators Connecting an electric boiler to a heating system Scheme and steps for connecting a gas heating boiler to a heating system
Scheme of single-pipe heating what to consider
In one- and two-story houses, it is possible to use both vertical and horizontal one-pipe heating systems.
At the same time, an attic space is needed for the upper wiring, which is not always convenient. As a rule, the movement of the coolant in the heating system is natural. In order to increase the circulation rate of the coolant, it is planned to include a pump in the system.
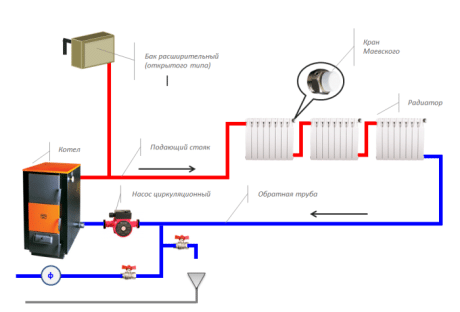
A simple one-pipe heating scheme: 1 - boiler; 2 - main riser; 3 - expansion pipe; 4 - reverse risers; 5 - top wiring; 6 - air collector; 7 - expansion tank; 8 - circulation pump; 9 - return line.
Control and shut-off valves are needed to close the emergency section when performing preventive and repair work, redistributing the coolant flow, replacing a broken element. It is practical, fast and very convenient. Mandatory conditions, without which it will not be possible to make the correct single-pipe heating system: the layout of the system elements for a particular room, the location of the pipe junction, connection to the heating boiler; places for an expansion tank, installation of radiators, valves and pumps; drain taps, etc.
In accordance with the area of the house, various options for the installation of the heating system are selected. For private houses up to 150 m², a heating system will suffice, in which antifreeze or water circulates naturally. Due to the difference in coolant density in different parts of the batteries, such a system, the scheme of which is shown in PICTURE 2, will work in a balanced way.
If the area of the house exceeds 150 m², then a forced circulation system must be used. For this, a water pump of suitable power is installed.
In any case, radiators must be additionally equipped with taps (valves), the installation of which will make it possible to shut off the water supply at a particular section of the main line at the right time. This is necessary to isolate a certain area during repair work and maintain heating of other rooms. At the same time, the rest of the premises in the building will be heated in the normal mode.
Limitations of the two-pipe heating scheme from the bottom wiring
Heating two-pipe systems with natural circulation of heat carriers and bottom wiring have serious limitations and therefore they are rarely implemented. The fact is that almost all batteries in such a scheme are finite and they require bleeders. And since the design solution also provides for an open-type expansion tank that communicates with the external environment, the residents will have to deal with air bleeding daily.
Air lines that loop the supply lines practically eliminate this problem, but in the end the system turns out to be even more complex and cumbersome in execution.
Two-pipe heating with a lower wiring, in terms of the number of pipes required for installation, is not inferior to a design with an upper wiring option. If preference is given to the second method, then the main advantage of the lower location of the pipes, which is the absence of the pipeline in sight, is lost.
Installation of overhead lines provides that the risers are located in the room, starting from the floor to the ceiling. And in this case, all meaning in the lower wiring is lost.
Positive aspects of a two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring
The scheme of heating a private house.
Thanks to this arrangement of the system, it becomes possible to control the temperature inside each individual room, without affecting any other elements that make up the heating system. Moreover, this configuration is also a great way to save on the purchase of a low-power pump, thanks to which the liquid circulation process starts in the pipes. This happens because the pressure losses in the pipes, with this kind of heating, are minimized, and sometimes, during warmer periods, completely disappear. The hydraulic resistance of a heating system with two pipes connected is also several times less than with a sequential single-pipe version. Therefore, inside the house with peace of mind it will be possible to install pipes of small diameters, which will significantly improve the appearance of the heated room, because large pipes and radiators located in the most prominent places in the room look very rude and unaesthetic.
The next important plus is the ability to turn off and replace one of the radiators, which for some reason is out of order. After all, even if one component of the system breaks down, it continues to function normally. Whereas sequential heating systems completely, in such situations, fail. Indeed, with a two-pipe heat distribution on the supply pipe, right next to the radiators, shut-off valves are installed, which, if there is an urgent need, can be closed.
Other undoubtedly positive features of a heating system with a lower wiring include:
- small heat losses, since the main is carried out through a basement or underground room;
- the ability to function in those premises where only the lower floors are equipped;
- the fact that not a single element of the shut-off valves on the supply and return risers remains in sight, since they are easy to install in the same basement.
The disadvantages of this kind of wiring include the fact that low liquid pressure is constantly maintained in the supply risers, as a result of which the level of flow of the coolant used also decreases.
Moreover, with such an organization of the heating system, there is a constant need to bleed air from the system manually. However, it is possible to organize an additional air pipe, but this will complicate an already complex system, making it also expensive.
Connection methods
You can connect radiators to pipes in different ways, depending on the installation location and the laying of pipes in the room and, of course, the heating scheme:
When the connection method is selected (see diagram), you must:
- Wipe all joints and pipes with sandpaper and degrease them.
- Attach the radiator. This can be temporary fixing or installation, depending on the complexity of the location of the pipes of the heating system according to your scheme.
- We screw in the adapters, which, by turning, can be adjusted to the direction of the pipes to which the elements are connected.If, for example, they are located on the floor, then the adapter is screwed down with a thread, if the pipes go deep into the room, then the direction of the adapter changes. So the main thing is to look carefully at the layout of a single-pipe heating system.
- Pipe adapters, preferably made of domestically produced polypropylene, as experts advise, are attached to the main pipe with a soldering iron.
- We install the valve from above and the plug from below, as shown in the diagram, or vice versa.
Options for a one-pipe system
The water heating main is without fail supplied with an expansion tank that equalizes the pressure. It accepts excess coolant during expansion and returns it to the pipeline when it cools, preventing pressure surges. There are two fundamentally different types of expansion tanks - open and closed. The type of heating system will depend on which of them will be built into the line.
Open heating system
An open-type heating system involves direct contact of the coolant with the atmosphere. It is used at the device of non-volatile or combined heating. An open expansion tank is a cylindrical or rectangular container, partially or completely open. At a certain level, a drain is performed to drain excess liquid into the street or into the sewer.
In the scheme of an open heating system with forced circulation, the expansion tank is included directly after the boiler, the outlet is arranged at the highest point of the main. The container itself should be located above all connected devices, so the tank is often taken to the attic. In this case, it must be insulated at low temperatures.
In connection with the contact of the coolant and air in the tank, the hot water is saturated with oxygen and its natural evaporation. This implies the limitations and disadvantages of such a scheme:
- It is required to constantly monitor the level of coolant in the tank and replenish it on time;
- It is necessary to observe the slopes of the pipeline (5-7 degrees) so that the air released in the line is bled into the expansion tank and the atmosphere;
- Do not use antifreeze instead of water, as it releases toxic substances when evaporated;
- The presence of oxygen in the coolant reduces the life of heaters with steel parts.
Attention! The absence of slopes during the installation of the pipeline of an open heating system will lead to airing of the line. However, open heating has its advantages:
However, open heating has its advantages:
- It is not required to monitor the pressure in the line;
- The coolant can even be replenished with a bucket, simply adding it to the expansion tank capacity to the required level;
- Even if there are small leaks, the system will function properly - as long as there is enough water in the pipeline.
Scheme of an open-type heating system with forced circulation
Closed heating system
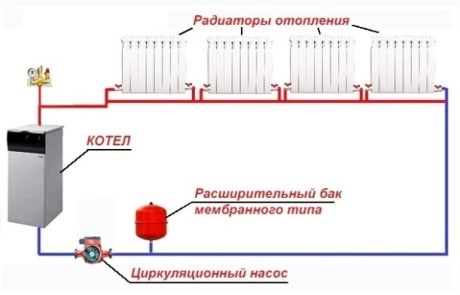
The scheme of a closed heating system with forced circulation is currently the most common. It is a closed hydraulic line, completely closed from air.
A closed water heating system involves the use of a membrane-type expansion tank. It is a sealed cylindrical metal case, the inner cavity of which is separated by a membrane. One part is filled with air, and water is squeezed out of the main line into the second, the volume of which increases when heated.
You can install a membrane expansion tank anywhere in the pipeline, but for ease of maintenance it is connected to the "return" - next to the boiler.
A feature of the closed circuit is the presence of a small excess pressure in the line. Therefore, a closed highway must contain a security group in its composition. This unit is installed on the pipeline leaving the boiler (supply) without shutoff valves. Contains pressure gauge, air vent and safety valve for emergency water release.
Important! A security group must be included in the scheme of a closed system
- The coolant under pressure warms up faster;
- The probability of airing the heating main is practically excluded;
- It is possible to fill with antifreeze, since the coolant does not evaporate and is not saturated with oxygen (relevant for buildings of periodic use);
- Ease of maintenance - all devices that ensure the operation, control and safety of the system are installed in one place;
- With the use of modern equipment, it is possible to make a closed heating system fully automated and integrate it with smart home programs.
The disadvantage is energy dependence. It is solved by purchasing an autonomous generator.
Scheme of a closed-type heating system with forced circulation
System start
When all the elements of Leningradka are mounted, the valve should be opened to fill the system with coolant. Next, air is removed from the system, and the central screw is unscrewed on the pump (located on the housing cover). The liquid that appears from under the screw will indicate the complete removal of air and the possibility of starting the equipment (the screw must be tightened before turning it on).
Photo of expansion tank and built-in pump
Video - Pump for the heating system
Water heating convectors: selection, principle of operation, installation Water heating convectors are increasingly being installed in modern houses and apartments. High heating efficiency.
Which boiler is better for a private house? A heating boiler will provide housing with heat without the need to connect to central communications, thanks to which.
Double-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler The specifics of the construction of country houses implies independent heating and hot water supply - laying.
Two-pipe heating system of a private house Already when designing a future building, the drawings indicate the places for laying communications - water supply, etc.
Good afternoon, tell me what brand you need to use a pump for forced circulation.
Good afternoon. Two years ago I installed a one-pipe system, with a bottom supply, and everything seemed to work, But .. only the top of the radiators is heated .. the next year I connected an electric pump, but ... as before, it heats the top of the radiators .. what's the matter .. there is one but ..mounted sections, twice as many as necessary ..that is, where 5 pieces are enough. I put 10 ... there is no air in the system. I check regularly..
Mounted an open-type single-pipe system with a pump. Main f32, taps to radiators f 20. I bleed air through Mayevsky's taps. but it always comes from somewhere. Then I noticed. that the penultimate radiator, when the top is cooled when the Mayevsky tap is opened, sucks in air. The main line is laid in the floor with anti-slopes. Radiators 6 pcs. I plan to convert the system to a closed one. Maybe I'll get rid of the air. Tell me how should I be? Thanks in advance.