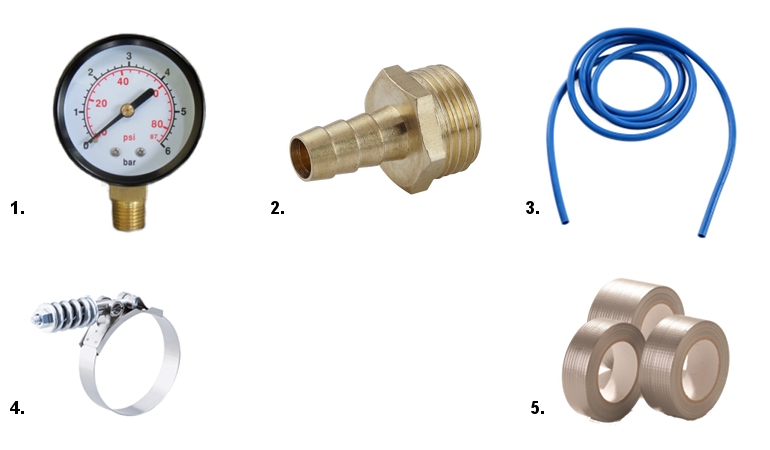
How to measure the water pressure in the system
The question disappears if you have already installed manometer
at the login. If not, then you need 5
minutes of time and the following useful things:
Manometer for water.
The union with a carving 1/2 inch.
Hose of suitable diameter.
Worm clamps.
Sanitary tape.
hose
We put one end on the pressure gauge, the other on the fitting. Fixing
clamps. We go to the bathroom. We unscrew the shower head and in its place we determine Union
. Repeatedly switch water
between shower-faucet modes to expel an airlock. If the joints are leaking, then we wrap the connection sanitary tape
. Ready. Take a look at the gauge
and find out the pressure in the water supply.
Pump head
Material from ThermalWiki - encyclopedia of heating
Pump head (H) - overpressure generated by the pump. Head is measured in (m).
The head that the pump must provide is the sum of the geodetic height difference and the head loss (= loss height) in the pipelines and fittings.
It should be borne in mind that when starting, and then during operation, the pump changes its mode of operation. The choice of pump motor power should be made from the conditions that it operates at maximum load in a certain period of time, for example, at H geo max. Consider how this value changes depending on the operating mode of the pump.
Consider an example: a pressure pipeline is laid over variable terrain and has several vertices. When starting, when the discharge pipeline is empty, the pump must raise water from the level NN (-1 m) to the height NN1 (10 m), and after filling the pipeline NN1 - NN2, it must raise the water to the height NN3 (11 m).
At the initial moment of time, to fill all sections of the pipeline, the pump must overcome the height Hgeo max, equal to:
Hgeo max = (NN1 - NN) + (NN3 - NN2) = + (11 m - 5 m) = 17 m
When the pipeline NN - NN 3 is filled with drains, the geodetic height decreases:
Comments on the calculation of geodetic heights: If the air is not removed from the pressure pipe, then geodetic height is defined as the sum of the heights of all ascending pipelines (plot 1 + plot 3), since additional energy is spent on compressing the air in the descending section (plot 2). Therefore, more energy is required to overcome high-altitude points.
When operating the pump without venting the pressure pipe: after the air is expelled from the pipeline, the pipeline is filled completely. Therefore, the head that the pump must provide is determined only by the geodetic height difference Hgeo between the outlet/transfer reserve NNA and the water level in the shaft NN, at which the pump is switched off.
If air is removed from the pipeline, then when the pump is turned on take into account the difference between the water level in the shaft (pump switch-on point) and the highest point Hgeo max.
When operating with venting: during operation, the pump operates in the same mode as “without venting”.
For the correct choice of pump and motor, it should be taken into account that they can operate at different modes. This must be done to prevent damage to the pump or motor and to ensure that they perform optimally.
Institutions responsible for water supply
Before contacting any authorities about poor water pressure, you must make sure that the cause of this is not clogging of the device with lime or other deposits, equipment malfunction, etc.
If the reason is not in the above, then if the pressure standards of the water supplied to the MKD are not observed, you can contact the following organizations:
- to the management company (MC), on the balance sheet of which this house is located. The UK, by definition, is an intermediary between the supplier of life support resources for an MKD and a citizen who is the owner or tenant of housing in this house.The following must be done:
- write an application to the Criminal Code with a description of the problem, with the requirements to eliminate the violation of water supply standards and recalculate the cost of paid services for housing maintenance,
- refer the complaint to the Criminal Code in 2 copies, one - to leave in the company, the other, with a note on the acceptance of the application - to pick up for yourself,
- expect the problem to be resolved, the Criminal Code is obliged to consider the complaint no later than 1 month after its acceptance.
to the city administration department, if the actions on the filed complaint were not considered in a timely manner by the Criminal Code. When contacting the administration, you should write a new application and attach to it a second copy of the complaint previously sent to the Criminal Code.
Water consumption
Let's deal with water consumption now. It is measured in liters per hour. In order to get liters per minute from this characteristic, you need to divide the number by 60. Example. 6,000 liters per hour is 100 liters per minute, or 60 times less. The water flow should be pressure dependent. The higher the pressure, the greater the speed of water in the pipes and the more water passes through the pipe section per unit time. That is, more pours out on the other side. However, everything is not so simple here. The speed depends on the cross section of the pipe, and the higher the speed and the smaller the cross section, the greater the resistance of the water moving in the pipes. The speed, therefore, cannot increase indefinitely. Suppose we have made a tiny hole in our pipe. We have the right to expect that water will flow out through this tiny hole with the first cosmic velocity, but this does not happen. The speed of the water, of course, grows, but not as much as we expected. Water resistance is shown. Thus, the characteristics of the pressure developed by the pump and the water flow are most closely related to the design of the pump, the power of the pump motor, the cross section of the inlet and outlet pipes, the material from which all parts of the pump and pipe are made, and so on. All this I say to the fact that the characteristics of the pump, written on its nameplate, are generally approximate. They are unlikely to be larger, but it is very easy to reduce them. The relationship between pressure and water flow is not proportional. There are many factors that affect these characteristics. In the case of our submersible pump, the deeper it is immersed in the well, the lower the water flow at the surface. A graph that relates these values is usually given in the instructions for the pump.
Specialist's Handbook
Pressure and performance units
It is quite easy for an uninitiated person to get confused in the abundance of pressure units that exist today, exacerbated by the use of relative and absolute scales. Therefore, we considered it necessary to give here, in addition to the correspondence table, several definitions and practical advice, which, in our opinion, should help an inexperienced customer to correctly determine the choice of the pump or compressor he needs.
First of all, let's deal with absolute and relative pressure.
Absolute pressure is pressure measured relative to absolute zero pressure, or, in other words, absolute vacuum.
Relative pressure (in compressor technology, excess pressure) is the pressure measured relative to the earth's atmosphere.
That is, if we use kgf / cm² (technical atmospheres) as the unit of measurement, then absolute vacuum will correspond to zero on the absolute scale and minus one on the relative scale, while atmospheric pressure will correspond to one on the absolute scale and zero on the relative scale. For compressors, everything is simpler - the excess pressure will always be 1 atmosphere less than the absolute one.
Since in the territory of the former USSR Bourdon tubes are often used as vacuum gauges, showing the relative pressure in technical atmospheres (at. or kgf / cm²), most often our customers are faced with the need to convert relative technical atmospheres into absolute millibars and vice versa. To do this, use the formula:
=(1+)*1000
for example: -0.95 at. rel.=(1-0.95)*1000=50 mbar abs.
To convert millibars to Torr (mm Hg) or Pascals, remember the ratio:
1 millibar=100Pa=0.75 mm. rt. Art.
Table of relationships between the main units of pressure measurement:
| atm. | Bar | mbar | Pa | mm w.c. | mmHg. | psi | at. (kgf/cm2) | inch Hg | |
| atm. | 1 | 1.013 | 1013 | 101325 | 10332 | 760 | 14.696 | 1.0333 | 29.92 |
| Bar | 9.87*10-1 | 1 | 103 | 105 | 1.02*104 | 7.5*102 | 14.51 | 1.0198 | 29.53 |
| mbar | 9.87*10-4 | 10-3 | 1 | 102 | 10.2 | 7.5*10-1 | 1.45*10-2 | 1.02*10-3 | 2.95*10-2 |
| Pa | 9.87*10-6 | 10-5 | 10-2 | 1 | 0.102 | 7.5*10-3 | 1.45*10-4 | 1.02*10-5 | 2.95*10-4 |
| mm w.c. | 9.68*10-5 | 9.81*10-5 | 9.81*10-2 | 9.81 | 1 | 7.36*10-2 | 1.42*10-3 | 10-4 | 2.896*10-3 |
| mmHg. | 1.32*10-3 | 1.33-3 | 1.33 | 1.33*102 | 13.6 | 1 | 1.93*10-2 | 1.36*10-3 | 3.94*10-2 |
| psi | 6.8*10-2 | 6.9*10-2 | 68.95 | 6.9*103 | 7.03*102 | 51.7 | 1 | 7.03*10-2 | 2.04 |
| at. (kgf/cm2) | 9.68*10-1 | 9.8*10-1 | 9.8*102 | 9.8*104 | 104 | 7.36*102 | 14.22 | 1 | 28.96 |
| inch Hg | 3.3*10-2 | 3.39*10-2 | 33.86 | 3.386*103 | 3.45*102 | 25.4 | 0.49 | 3.45*10-2 | 1 |
Performance unit ratio table:
| m³/hour | m³/min | l/min | l/s | CFM | |
| m³/hour | 1 | 1.667*10-2 | 16.667 | 0.278 | 0.588 |
| m³/min | 60 | 1 | 103 | 16.6667 | 35.29 |
| l/min | 0.06 | 1*10-3 | 1 | 1.667*10-2 | 3.5*10-2 |
| l/s | 3.6 | 0.06 | 60 | 1 | 2.12 |
| CFM | 1.7 | 2.8*10-2 | 28.57 | 0.47 | 1 |
head drop
The output current will be less than the input current.
The fall is determined by several factors:
- Pipe diameter.
- Her length.
- The roughness of its walls.
- the flow rate in it.
The formula H = iL(1+K) is used for calculation.
In it:
- H is the pressure drop in meters. To convert it to atmospheres, it is enough to divide the resulting value by 10.
- i - hydraulic slope, determined by the diameter, material of the pipe and the flow rate in it.
- L is the length of the pipe in meters.
- K is a coefficient, for drinking water supply systems taken equal to 0.3.
Where can I get the hydraulic slope value? In the so-called Shevelev tables. Here is a fragment of one of them, relevant for a new steel pipe with a size of DN15.
The value of 1000i is the hydraulic slope for a pipe length of 1 km. To calculate the value of i for a linear meter, it is enough to divide it by 1000.
So, for a steel pipe DN15 25 meters long with a water flow through it of 0.2 l / s, the pressure drop will be (360.5/1000) * 25 * (1 + 0.3) \u003d 11.7 meters, which corresponds to the difference pressures of 1.17 kgf / cm2.
Pressure units
Unit
pressure measurements in the SI system - Pascal
(Pa).
Pascal
is a pressure with a force of 1 N on an area of 1
m2.
Off-system
units:
kgf/cm2;
mm water column; mmHg st; bar, atm.
Ratio
between units of measurement:
1
kgf/cm2
= 98066.5 Pa
1
mm water column = 9.80665 Pa
1
mmHg. = 133.322 Pa
1
bar = 105
Pa
1
atm \u003d 9.8 * 104
Pa
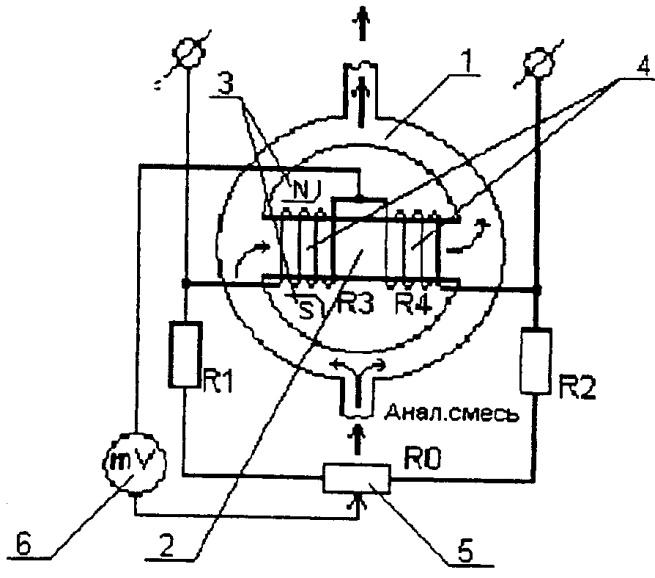
2.Thermomagnetic
oxygen gas analyzer
thermomagnetic
gas analyzer is used to determine
concentration
oxygen in the gas mixture.
Principle
action is based on the property of oxygen
be attracted by magnetic
field. This property is called magnetic
susceptibility.
1)
annular chamber;
2)
glass tube;
3)
permanent magnet;
4)
platinum wire spiral;
5)
current standardization rheostat;
6)
millivoltmeter;
R1,
R2
– constant resistances from manganin;
R1,
R2,
R3,
R4
- the shoulders of the bridge.
Analyzer
consists of an annular chamber 1, in diameter
which is established
thin-walled glass tube 2 co
spiral 4, heated
current. The spiral consists of two sections,
which form two adjacent arms
unbalanced bridge (R3, R4).
The other two shoulders are two
Manganin resistance constants
(R1,
R2).
Left section of spiral R3
is in the field of constant
magnet 3.
Work
At
the presence of oxygen in the gas mixture
flow branches off into
glass tube, where
gas flow from left to right.
The resulting gas flow transfers heat
from the winding
R3
to R4,
so the temperature of the sections changes
(R3
cools down
R4
heats up), and their resistances change.
Bridge
gets out of balance. Measuring
the bridge is powered by a constant
current from the IPS. R0
- serves to set the power supply current
bridge. Millivoltmeter scale is calibrated
v
%
oxygen.
limits
measurements:
0-5; 0-10; 0-21; 20-35% oxygen.
3. Draw
pressure control scheme and select
appliances.

– The column top pressure is adjustable,
the valve is in the vapor outlet line
distillate from the column.
Pos.800
-1 intelligent overpressure sensor
pressure Metran -100 CI
Pos.800
-2 IS barrier input
Pos.800
-3 IS barrier output
Pos.800
-4–electropneumatic positioner
Pos.800
-5 - control valve.
4.Classification
electrical pressure sensors
V
data
appliances
measurable
pressure,
rendering
impact
on the
sensitive
element,
changes
his
own
electrical
pair-
meters:
resistance,
capacity
or
charge,
which
become
measure
this
pressure.
overwhelming
majority
contemporary
general industrial
IPD
implemented
on the
basis
three
major
principles:
1)
capacitive–
use
elastic
sensitive
element
v
form
capacitor
With
variables
clearance:
bias
or
deflection
under
action
attached
pressure
mobile
membrane electrode
relative to the fixed
changes
his
capacity;
2)
piezoelectric–
founded
on the
dependencies
polarized
charge
or
resonant
frequencies
piezocrystals:
quartz,
tourmaline
and
others
from
attached
To
him
pressure;
3)
tenzoRresistor–
use
addiction
active
resist-
tivleniya
conductor
or
semiconductor
from
degree
his
deformations.
V
recent
years
received
development
and
other
principles
work
IPD:
fiber optic,
induction,
galvanomagnetic,
volume-
foot
compression,
acoustic,
diffusion
and
etc.
On the
today's
day
most
popular
v
Russia
are
strain gauge
IPD.
Atmosphere pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the air pressure at a given location. It usually refers to the pressure of a column of air per unit surface area. A change in atmospheric pressure affects the weather and air temperature. People and animals suffer from strong pressure drops. Low blood pressure causes problems in people and animals of varying severity, from mental and physical discomfort to fatal diseases. For this reason, aircraft cabins are maintained at a pressure above atmospheric pressure at a given altitude because the atmospheric pressure at cruising altitude is too low.
The aneroid contains a sensor - a cylindrical corrugated box (bellows) associated with an arrow that rotates when the pressure rises or falls and, accordingly, the bellows is compressed or expanded
Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. People and animals living high in the mountains, such as the Himalayas, adapt to such conditions.
Travelers, on the other hand, must take the necessary precautions so as not to get sick because the body is not used to such low pressure. Climbers, for example, can get altitude sickness associated with a lack of oxygen in the blood and oxygen starvation of the body.
This disease is especially dangerous if you stay in the mountains for a long time. Exacerbation of altitude sickness leads to serious complications, such as acute mountain sickness, high-altitude pulmonary edema, high-altitude cerebral edema, and the most acute form of mountain sickness. The danger of altitude and mountain sickness begins at an altitude of 2400 meters above sea level. To avoid altitude sickness, doctors advise avoiding depressants such as alcohol and sleeping pills, drinking plenty of fluids, and ascending altitude gradually, such as on foot rather than in transport. It's also good to eat plenty of carbohydrates and get plenty of rest, especially if the climb is fast. These measures will allow the body to get used to the lack of oxygen caused by low atmospheric pressure. If you follow these recommendations, then the body will be able to produce more red blood cells to transport oxygen to the brain and internal organs. To do this, the body will increase the pulse and respiratory rate.
First aid in such cases is provided immediately
It is important to move the patient to a lower altitude where atmospheric pressure is higher, preferably lower than 2400 meters above sea level. Drugs and portable hyperbaric chambers are also used.
These are lightweight, portable chambers that can be pressurized with a foot pump. A patient with mountain sickness is placed in a chamber in which pressure is maintained corresponding to a lower altitude above sea level.Such a chamber is used only for first aid, after which the patient must be lowered.
Some athletes use low blood pressure to improve circulation. Usually, for this, training takes place under normal conditions, and these athletes sleep in a low-pressure environment. Thus, their body gets used to high altitude conditions and begins to produce more red blood cells, which in turn increases the amount of oxygen in the blood, and allows them to achieve better results in sports. For this, special tents are produced, the pressure in which is regulated. Some athletes even change the pressure throughout the bedroom, but sealing the bedroom is an expensive process.
Legislation on the meter and millimeter of water edit edit code
In Russia, until 2015, the meter of water column and millimeter of water column were in the status of non-systemic units of measurement, which were subject to exclusion until 2016. According to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 15, 2015 No. 847 “On Amendments to Appendix No. 3 to the Regulation on Units of Values Allowed for Use in the Russian Federation”, the use of these units is allowed without time limits in all areas of application.
In accordance with the Regulations on units of quantities allowed for use in the Russian Federation, the meter and millimeter of water column:
- are not used with multiple and long prefixes SI;
- are used only in those cases when the quantitative values of quantities are impossible or impractical to express in SI units.
Quite often in everyday life, in order to connect or repair household appliances that run on water from the water supply network, you need to know what pressure is in the water supply in the apartment. Further in the article we will tell you how to find out the water pressure, what are the standards for this indicator and who to contact in case of violation of the established standards.
pressure in geology
Quartz crystal illuminated by a laser pointer
Pressure is an important concept in geology. Without pressure, it is impossible to form gemstones, both natural and artificial.
High pressure and high temperature are also necessary for the formation of oil from the remains of plants and animals. Unlike gems, which are mostly found in rocks, oil forms at the bottom of rivers, lakes, or seas. Over time, more and more sand accumulates over these remnants. The weight of water and sand presses on the remains of animal and plant organisms. Over time, this organic material sinks deeper and deeper into the earth, reaching several kilometers below the earth's surface. The temperature increases by 25°C for every kilometer below the earth's surface, so at a depth of several kilometers the temperature reaches 50-80°C. Depending on the temperature and temperature difference in the formation medium, natural gas may be formed instead of oil.
Diamond tools
natural gems
The formation of gemstones is not always the same, but pressure is one of the main components of this process. For example, diamonds are formed in the Earth's mantle, under conditions of high pressure and high temperature. During volcanic eruptions, diamonds move to the upper layers of the Earth's surface due to magma. Some diamonds come to Earth from meteorites, and scientists believe they were formed on Earth-like planets.
Synthetic gems
The production of synthetic gemstones began in the 1950s and has been gaining popularity in recent years. Some buyers prefer natural gemstones, but artificial gemstones are becoming more and more popular due to the low price and lack of problems associated with natural gemstone mining. Thus, many buyers choose synthetic gemstones because their extraction and sale is not associated with the violation of human rights, child labor and the financing of wars and armed conflicts.
One of the technologies for growing diamonds in the laboratory is the method of growing crystals at high pressure and high temperature. In special devices, carbon is heated to 1000 ° C and subjected to a pressure of about 5 gigapascals. Typically, a small diamond is used as the seed crystal, and graphite is used for the carbon base. A new diamond grows from it. This is the most common method of growing diamonds, especially as gemstones, due to its low cost. The properties of diamonds grown in this way are the same or better than those of natural stones. The quality of synthetic diamonds depends on the method of their cultivation. Compared to natural diamonds, which are most often transparent, most artificial diamonds are colored.
Due to their hardness, diamonds are widely used in manufacturing. In addition, their high thermal conductivity, optical properties and resistance to alkalis and acids are highly valued. Cutting tools are often coated with diamond dust, which is also used in abrasives and materials. Most of the diamonds in production are man-made because of the low price and because the demand for such diamonds exceeds the ability to mine them in nature.
Some companies offer services to create memorial diamonds from the ashes of the deceased. To do this, after cremation, the ashes are cleaned until carbon is obtained, and then a diamond is grown on its basis. Manufacturers advertise these diamonds as a memory of the departed, and their services are popular, especially in countries with a high percentage of wealthy citizens, such as the United States and Japan.
Crystal growth method at high pressure and high temperature
The high pressure, high temperature crystal growth method is mainly used to synthesize diamonds, but more recently, this method has been used to improve natural diamonds or change their color. Different presses are used to artificially grow diamonds. The most expensive to maintain and the most difficult of them all is the cubic press. It is mainly used to enhance or change the color of natural diamonds. Diamonds grow in the press at a rate of approximately 0.5 carats per day.
Article author: Kateryna Yuri
Unit Converter articles were edited and illustrated by Anatoly Zolotkov
How is water pressure measured?
flow rate q (or Q) is the volume of the liquid Vpassing through the flow area per unit time t :
Flow units in SI m 3 /With, and in other systems: m 3 /h, m 3 /day, l/s.
Average flow velocity v (m/s) — is the quotient of the flow rate divided by the open area:
From here, the cost can be expressed as follows:
Water flow rates in water supply and sewerage networks of buildings are usually on the order of 1 m/s.
The next two terms refer to non-pressure flows.
wetted perimeter c (m) — this is the part of the flow area perimeter where the liquid comes into contact with the solid walls. For example, in fig. 7,in magnitude c is the length of the arc of a circle that forms the lower part of the flow area and is in contact with the pipe walls.
Hydraulic radius R (m) — is a relation of the form
which is used as a design parameter in the formulas for non-pressure flows.
Flow continuity equation
The flow continuity equation reflects the law of conservation of mass: the amount of incoming fluid is equal to the amount of outgoing fluid. For example, in fig. 8 the flow rates in the inlet and outlet sections of the pipe are equal to: q1=q2.

Considering that q=vw, we obtain the flow continuity equation:
And if we express the speed for the exit section
it can be seen that it increases in inverse proportion to the decrease in the free area of the flow. Such an inverse relationship between velocity and area is an important consequence of the continuity equation and is used in technology, for example, in extinguishing a fire to obtain a strong and long-range jet of water.
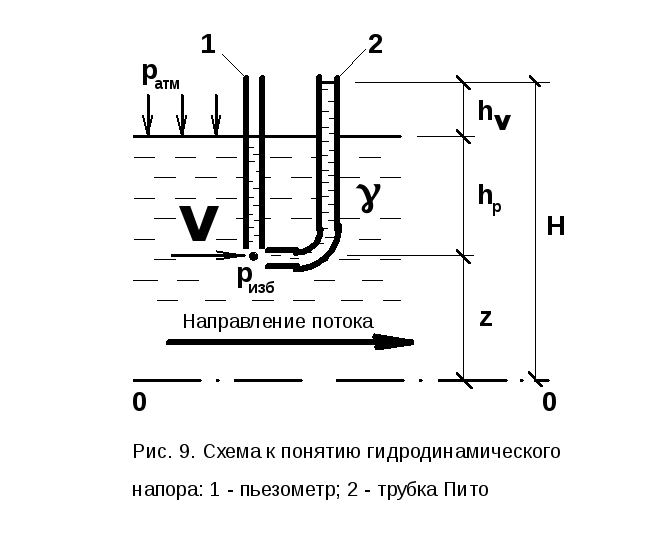
Hydrodynamic head
Hydrodynamic head H (m) — is the energy characteristic of a moving fluid.The concept of hydrodynamic head in hydraulics is of fundamental importance.
Hydrodynamic head H (Fig. 9) is determined by the formula:
,
where z - geometric head (height), m,
v is the flow rate, m/s,
The hydrodynamic head, in contrast to the hydrostatic head (see p. 11), does not consist of two, but of three components, of which the additional third value hv reflects kinetic energy, that is, the presence of fluid movement. First two members z+hp, as well as for hydrostatic, represent potential energy. Thus, the hydrodynamic head reflects the total energy at a particular point in the fluid flow. The head is measured from the zero horizontal plane Oh-oh (see p. 12).
In the laboratory, the velocity head hv can be measured using a piezometer and a Pitot tube by the difference in liquid levels in them (see Fig. 9). The Pitó tube differs from the piezometer in that its lower part, immersed in the liquid, faces against the flow. Thus, it responds not only to the pressure of the liquid column (like a piezometer), but also to the velocity effect of the oncoming flow.
In practice, the value hv is determined by calculation by the value of the flow velocity v.
Glossary of physics
center>
A
B
V
G
D
E
F
W
AND
TO
L
M
H
O
P
R
WITH
T
At
F
X
C
H
W
E
YU
I AM
pressure in hydraulics
Head in hydraulics is a linear quantity expressing the specific (referred to a unit of weight) energy of a fluid flow in a given
point. Full stock beats. flow energy H (total H.) is defined by Bernoulli
equation
where z is the height of the considered point above the plane
countdown, ru
is the pressure of a fluid flowing at a speed u,
g - beats. the weight of the fluid, g is the free fall acceleration. The first two
terms of the trinomial determine the sum of beats. potential energies of position
(z) and pressure (pu/g),
i.e., the full supply of beats. potent. energy, called hydrostatic H., and the third term
- ud. kinetic energy (high-speed H.). Along the stream H. decreases. Difference
H. in two cross sections of a real fluid flow H1
- H2= hu
called lost H. When a viscous fluid moves through pipes, lost H.
calculated by the Darcy-Weisbach formula.
to the library
back to contents
Aether Physics FAQ
TOEE
CHP
TPOI
TI
Did you know, that it was only in the 1990s that Doppler measurements by radio telescopes showed marinov speed for CMB (cosmic microwave radiation), which he discovered in 1974. Naturally, no one wanted to remember Marinov. Read more in the Aether Physics FAQ.
| 11/19/2019 - 09:07: EDUCATION, EDUCATION, EDUCATION -> - Karim_Khaidarov.11/18/2019 - 19:10: WAR, POLITICS AND SCIENCE - War, Politics and Science -> - Karim_Khaidarov.16.11. 2019 - 16:57: CONSCIENCE - Conscience -> - Karim_Khaidarov.11/16/2019 - 16:53: EDUCATION, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> - Karim_Khaidarov.11/16/2019 - 12:16: EDUCATION, EDUCATION, EDUCATION – Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> – Karim_Khaidarov.11/16/2019 – 07:23: EDUCATION, EDUCATION – Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> – Karim_Khaidarov.11/15/2019 – 06:45: WAR, POLITICS AND SCIENCE – War, Politics and Science -> - Karim_Khaidarov.11.14.2019 - 12:35: EDUCATION, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> - Karim_Khaidarov.11.13.2019 - 19:20: ECONOMY AND FINANCE - Economy and Finances - > - Karim_Khaidarov.12.11.2019 - 11:53: EDUCATION, EDUCATION, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Edu cation -> - Karim_Khaidarov.12.11.2019 - 11:49: EDUCATION, EDUCATION - Upbringing, Inlightening, Education -> - Karim_Khaidarov.11.10.2019 - 23:14: EDUCATION, EDUCATION > - Karim_Khaidarov. |