In the construction of modern buildings, as a rule, they use polypropylene pipes. They are easy to install and mount, convenient to transport, they do not make a lot of noise. Structures made of polypropylene, more than metal ones, are modified in length with a change in temperature indicators, that is, they lengthen with increasing temperature and decrease with cooling. For this reason, the thermal expansion of a polypropylene pipeline is necessarily calculated when creating projects for a pipeline system with a large length. Taking into account that temperature transformations in the cold water supply system are not expressed, the expansion of polypropylene pipes is not taken into account. They attach importance to the parameter of linear expansion only in heating systems and with hot water supply.
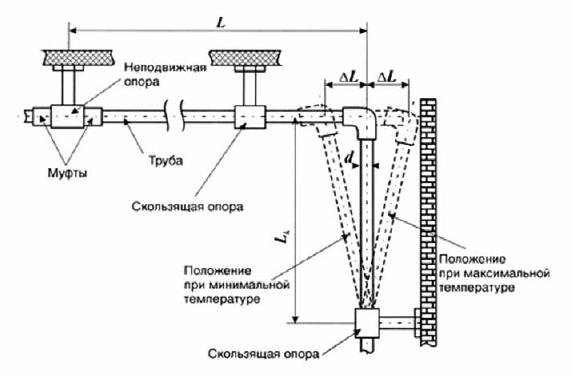
At system installation, structures are installed in such a way that they can easily move within the limits of the design expansion parameters. A similar alignment can occur as a result of the compensating ability of the pipes, the installation of temperature compensators and the competent adjustment of the fasteners.
What happens if thermal expansion is neglected?
- An increase in temperature indicators in polypropylene pipes can contribute to pulling out clips and other connections. A similar effect occurs on long sections (over 10 meters) of the pipeline for heating.
- Air chambers appear in the uppermost sections of the pipeline system. In this case, the pipe section narrows, the throughput decreases, and therefore, it acquires a wave-like shape.
- Warming up the batteries in the heating system becomes smaller, the pressure of hot water decreases. There are cases when the linear expansion of polypropylene pipes causes a breakdown in the heating system.
Recommendations for taking into account the coefficient of linear expansion
When creating pipeline projects, the coefficient of thermal elongation is taken into account.
When calculating changes during heating, a standard coefficient of expansion and an indicator of the difference in temperature values intended in the pipeline when the system is turned on and during installation are applied.
In non-reinforced structures, the coefficient of thermal expansion corresponds to 0.15 mm / mK, in reinforced pipes, this indicator ranges from 0.03 ─ 0.05 mm / mK. The pipeline reinforced with fiberglass or aluminum has a low coefficient, unlike polypropylene pipes. When mounting systems, this fact is decisive.
It is necessary to take into account the length of the pipes, calculating the value by which the structure elongates when heated. For example, with a length of a pipeline section equal to 5 m, the expansion value reaches 17.5 mm.
Ways to eliminate the effect of thermal expansion of pipes
- When installing a heating system, gaps of a certain size are assumed between the pipeline and the wall. Consequently, the pipes have the opportunity to expand when heated by several centimeters. In order to avoid complete breakdown, the heating system is not laid strictly along the walls;
- It is most carefully necessary to monitor the soldering of polypropylene pipes in the areas of the corners of the room. It is necessary to maintain gaps of a certain size to prevent pipes from resting against the wall;
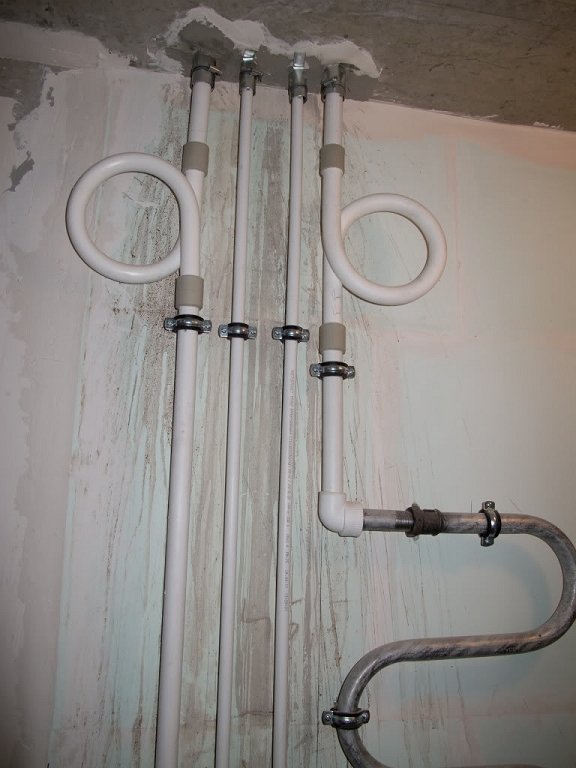
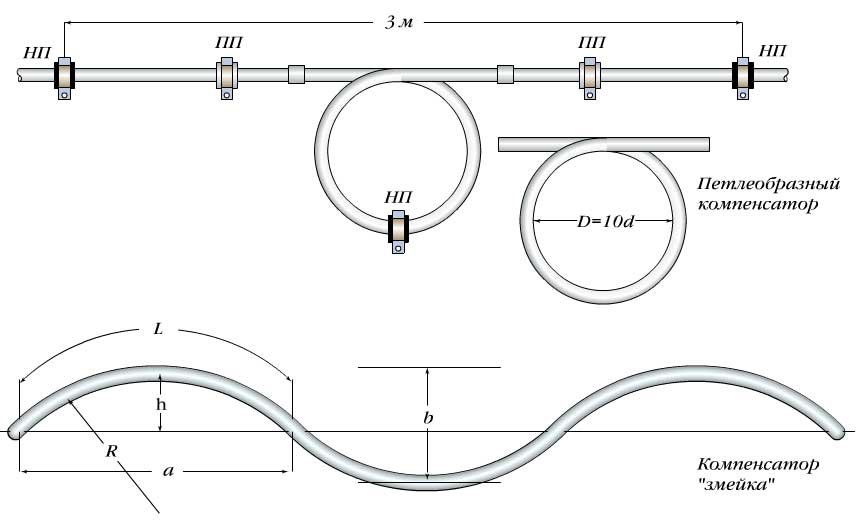
- On sections of a long pipeline, special compensators must be installed. In U-shaped zones, thermal expansion contributes to the mobility of polypropylene pipes. So that air chambers do not form in the upper sections of such expansion joints, they are installed with an inclination. In such a case, during the filling of the system with a hot coolant, air plugs will leave them;
- With proper use of supports and the selection of a certain form of pipeline, the problem of linear expansion is eliminated.
- The main mounting recommendations: the device of a flexible system, with a minimum number of rigid joints with a low ability to deform.
Polypropylene pipes, subject to the manufacturer's recommendations and installation rules, differ from other types in their low cost, ease of installation, long service life and safety.